| Developer(s) | Emily Chen, Nagappan A., et al.[1] |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 28, 2005[2] |
| Stable release | 3.5.0
/ May 1, 2013[3] |
| Repository | github |
| Written in | Python, C#[4] |
| Operating system | Linux, macOS, Windows[5] |
| Type | Automated testing |
| License | GNU LGPL[6] |
| Website | ldtp |
The Linux Desktop Testing Project (LDTP) is a testing tool that uses computer assistive technology[7] to automate graphical user interface (GUI) testing.[8] The GUI functionality of an application can be tested in Linux, macOS, Windows, Solaris, FreeBSD, and embedded system environments.[9] The macOS version is named PyATOM,[10] and the Windows version is Cobra.[11] The LDTP is released as free and open-source software under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
LDTP can test any accessibility-enabled GNOME application, Mozilla, OpenOffice.org, any Swing-based Java, Qt 4-based and KDE 4.x applications.[12]
LDTP is/was used by the following companies and organizations:[13]
History
LDTP version 0.1.0 was released in January 2005 and then showcased and discussed at GNOME Users And Developers European Conference (GUADEC) 2005. It was then used at the Google Summer of Code in 2006[16][17] for Tinderbox integration, Evolution automation, and LDTP regression suite under GNOME organization. Then again in 2007,[18][19] it was used by the Mozilla Foundation for Firefox automation and Tinderbox integration.
Example
This is an example of how LDTP would test writing in gedit:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# The standard import stuff.
from ldtp import *
from ooldtp import context as locate
from time import sleep
# Here we open the app.
launchapp("gedit")
# Now we find it and make sure it is open.
gedit_win = locate("*gedit")
gedit_win.waittillguiexist()
# Now we type into gedit.
text_field = gedit_win.getchild("txt1")
text_field.enterstring("G'Day mate!")
# Save a picture to prove we did it.
imagecapture("*gedit", "/tmp/foo.png")
# Quit gedit.
quit = gedit_win.getchild("mnuQuit")
quit.selectmenuitem()
# Close without saving.
dont_save = locate("Question")
dont_save.waittillguiexist()
button = dont_save.getchild("btnClosewithoutSaving")
button.click()
# Wait until gedit is gone.
gedit_win.waittillguinotexist()
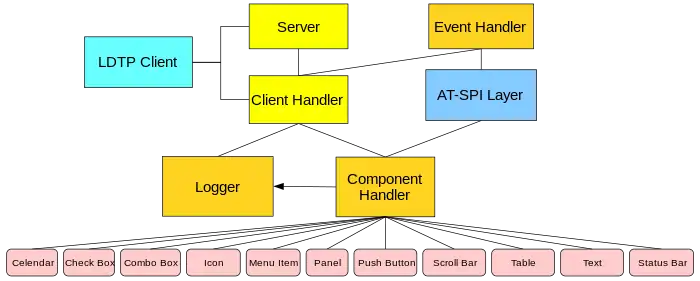
Diagram of how LDTP works
See also
References
- ↑ "Team Members". ldtp.freedesktop.org. Retrieved 25 December 2017.
- ↑ "FAQ".
- ↑ LDTP2 Releases - GitHub
- ↑ "Linux Desktop Testing Project". dtp/ldtp2. Retrieved 25 December 2017 – via GitHub.
- ↑ "ldtp 3.5.0: Python Pakage Index".
- ↑ "Download".
- ↑ "ldtp".
- ↑ "LDTP 3.0 automates GUI testing on Linux - The H Open: News and Features".
- ↑ "ldtp".
- ↑ "pyatom/pyatom - GitHub".
- ↑ "ldtp/cobra - GitHub".
- ↑ "ldtp".
- ↑ "FAQ".
- ↑ "Executing scripts remotely".
- ↑ "How to control GNOME apps remotely using LDTP - YouTube". Archived from the original on 2021-12-13.
- ↑ "SoC".
- ↑ "SoC06".
- ↑ "SoC".
- ↑ "SoC07".
- ↑ "ldtp-tutorial" (PDF).
External links
- Official website
- Mago Ubuntu wrapper using LDTP