
Satellite image of Hurricane Igor on September 21, 2010, as it made landfall on Newfoundland
There have been 25 recorded Newfoundland hurricanes, or Atlantic Ocean hurricanes that have made a direct landfall as a tropical or subtropical cyclone on the island of Newfoundland since official records began in 1851. Significant hurricanes such as the 1775 Newfoundland hurricane are also included on this list, even though they occurred prior to the start of official record-keeping.
Note: Hurricanes that made landfall in Newfoundland as a post-tropical cyclone (such as Hurricane Michael in 2000) are excluded from this list.
| Storm | Classification at time of Newfoundland landfall | Date of Newfoundland landfall | Approximate landfall location | Region(s) affected | Impact on Newfoundland | Other areas affected | Track |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1775 Newfoundland hurricane | Unknown | September 9, 1775 | Unknown | Eastern coast | 4,000-4,163+ fatalities at sea, making this the eighth-deadliest Atlantic hurricane on record.[1] | North Carolina, Virginia | Unavailable |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | August 27, 1851 | St. Jacques-Coomb's Cove | Southern Coast | Unknown | The Caribbean, Southeastern United States |  |
| Unnamed | Category 1 hurricane | September 23, 1866 | Cape La Hune | Southern Coast | Some damage to telegraphs reported. | None |  |
| 1873 Nova Scotia Hurricane | Category 1 hurricane | August 26, 1873 | Point Lance | Avalon Peninsula | Severe damage, estimated at $3.5 million (1873 USD). 100 deaths in Newfoundland, many of which were due to shipwrecks, and 900 homes were destroyed.[2] | Nova Scotia[nb 1] |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | August 7, 1874 | Hermitage-Sandyville | Southern Coast | Unknown | None |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | August 20, 1879 | Channel-Port aux Basques | Southern Coast | Unknown | The Bahamas, East Coast of the United States[nb 2] | 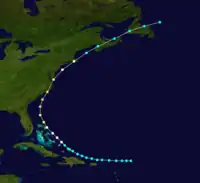 |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | September 10, 1880 | St. Lawrence | Southern Coast | Unknown | None |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | September 2, 1884 | Merasheen Island | Avalon Peninsula | Unknown | None |  |
| Unnamed | Category 1 hurricane | August 24, 1886 | Point May[3] | Burin, Avalon Peninsula | Unknown | Nova Scotia |  |
| Unnamed | Category 1 hurricane | September 8, 1891 | Channel–Port aux Basques | Western Coast | A number of small vessels were destroyed.[4] | Nova Scotia, especially Cape Breton |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | October 20, 1891 | Coppett | Southern Coast | Unknown | Saint Croix, Virgin Islands |  |
| Unnamed | Category 1 hurricane | August 18, 1893 | Southern Harbour | Burin, Avalon Peninsula | Made landfall with maximum sustained winds of 145 km/h (90 mph). | None |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | October 7, 1893 | Fortune, Newfoundland and Labrador | Southern Coast | Unknown | Yucatán Peninsula, Florida, The Bahamas[nb 3] |  |
| 1898 Georgia hurricane | Tropical depression | October 6, 1898 | Connaigre Peninsula | Burin, Avalon Peninsula | Unknown | Southeastern United States[nb 4] |  |
| Unnamed | Category 1 hurricane | September 15, 1899 | Cape Race | Avalon Peninsula, entire island | Severe damage at fishing premises,[5] sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) at landfall. The schooners Angler, Daisy, and Lily May either capsized or were driven ashore, resulting in 16 deaths.[6] | Lesser Antilles, Bermuda |  |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | September 18, 1908 | South East Bight | Burin, Avalon Peninsula | Unknown | The Bahamas | 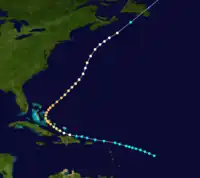 |
| Unnamed | Tropical storm | September 9, 1943 | McCallum | Southern Coast | Unknown | None |  |
| Hurricane Alice | Tropical storm | July 6, 1973 | Channel-Port aux Basques | Western Coast | Unknown | Bermuda |  |
| Hurricane Evelyn | Category 1 hurricane | October 15, 1977 | Channel-Port aux Basques | Western Coast | Light rain and tropical storm-force winds in areas. | Bermuda, Sable Island, Nova Scotia |  |
| Subtropical Storm One | Subtropical storm | October 25, 1979 | Rose Blanche-Harbour le Cou | Western Coast | Unknown | None |  |
| Hurricane Dean | Tropical storm | August 8, 1989 | Point May | Burin Peninsula, entire island | Winds of 80 km/h (50 mph), and moderate rainfall peaking at 2.7 in (68.58 mm). | Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico, Bermuda | 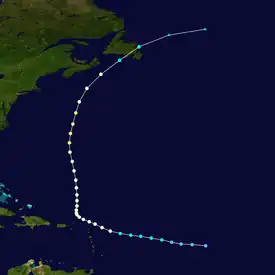 |
| Hurricane Gustav | Category 1 hurricane | September 12, 2002 | Burnt Islands | Southern Coast | Strong winds, gusts over 100 km/h (62 mph) were recorded. | North Carolina, Nova Scotia (especially Cape Breton Island) |  |
| Hurricane Bill | Tropical storm | August 24, 2009 | Point Enragée | Avalon Peninsula, entire island | A wind gust of 130 km/h (81 mph) was recorded in Cape Race. In St. John's, trees were blown down by the strong winds. Rainfall peaked at 2.75 in (70 mm) in Gander.[7] | Bermuda, Nova Scotia[nb 5] |  |
| Hurricane Igor | Category 1 hurricane | September 21, 2010 | Cape Race | Avalon Peninsula, entire island | Extreme damage, the most destructive hurricane ever to strike Newfoundland, as well as the worst storm of tropical origin to hit Newfoundland since 1935.[9] Third wettest hurricane on record, and maximum sustained winds at landfall of approximately 140 km/h (87 mph). Also caused $200 million in damage, and 1 fatality.[10] | Cape Verde; Bermuda (minimal) |  |
| Hurricane Maria | Tropical storm | September 16, 2011 | Cape St. Mary's | Avalon Peninsula | Minor wind damage, wind gusts up to 102 km/h (63 mph). | Lesser Antilles | 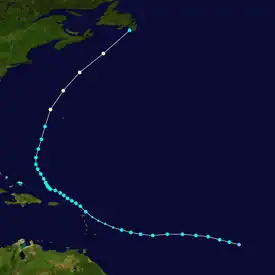 |
| Hurricane Larry | Category 1 hurricane | September 11, 2021 | South East Bight | Avalon Peninsula | Maximum sustained winds at landfall of approximately 150 km/h (92 mph). | Bermuda (minimal) |  |
See also
Notes
- ↑ This hurricane caused an additional 500 deaths off the coast of Nova Scotia due to shipwrecks.
- ↑ This hurricane caused major damage and 46 deaths in the United States.
- ↑ This storm was responsible for an estimated 56 deaths.
- ↑ This hurricane was responsible for $1.5 million (1898 USD) in damage, and 179 deaths.
- ↑ This hurricane caused an estimated $10 million (2009 USD) in damage throughout Atlantic Canada.[8]
References
- ↑ "Seven Seas". Storms: The Great Newfoundland Hurricane of 1 775. The Art Gallery of Nova Scotia. Archived from the original on 29 March 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2011.
- ↑ Martins, Daniel. "Eight devastating Canadian Hurricanes". The Weather Network. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
- ↑ "Unisys Weather". 1886 Hurricane/Tropical Data for Atlantic. Retrieved 16 September 2011.
- ↑ Fernández-Partagás, José; Diaz, Henry F. (1997). A Reconstruction of Historical Tropical Cyclone Frequency in the Atlantic from Documentary and other Historical Sources Part IV: 1891-1890. Boulder, Colorado: Climate Diagnostics Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ Jose F. Partagas (1996). Year 1899 (PDF). Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (Report). Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. pp. 71–83. Retrieved May 22, 2013.
- ↑ "Newfoundland Hurricane" (PDF). The New York Times. St. John's, Newfoundland. September 19, 1899. Retrieved August 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Tropical storm Bill soaks Newfoundland". CBC News. August 25, 2009. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- ↑ Glenn McGillivary (January 2010). "Annus Horriblis, The Sequel" (PDF). Institute for Catastrophe Loss Reduction. Retrieved February 17, 2010.
- ↑ Government of Canada. "Notable Canadian Tropical Cyclones". Environment and Climate Change Canada. Retrieved January 16, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Igor attacks Newfoundland". CBC. 22 September 2010. Retrieved 16 September 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.