The following is a list of interoceanic canals, that is, canals or canal proposals, which form waterways for traffic to connect one ocean to another.
List
| Canal | Place | Location | Map | Status | Oceans | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canal of the Pharaohs | Egypt | 30°20′N 32°23′E / 30.333°N 32.383°E |  |
|
|
This ancient canal once connected the Suez Rift Valley to the Nile River. | |
| Suez Canal | Isthmus of Suez | 30°42′18″N 32°20′39″E / 30.70500°N 32.34417°E |  |
|
|
The level (lock-less) canal follows the Suez Rift Valley, from the Gulf of Suez to the Mediterranean | |
| Palestine Canal | Israel | 31°30′N 35°30′E / 31.500°N 35.500°E | Proposed |
|
From the Gulf of Aqaba to the Dead Sea to the Mediterranean, the modern version would expand two proposed water conveyance canals (Red Sea to Dead Sea, and, Mediterranean Sea to Dead Sea) into ship canals. Various proposals have existed since the construction of the Suez Canal. | ||
| Panama Canal | Isthmus of Panama | 9°04′48″N 79°40′48″W / 9.08000°N 79.68000°W |  |
|
|
This lock-encumbered canal takes advantage of the Chagres River, used to create Gatun Lake, over the western side of the continental divide | |
| Nicaragua Canal | Central America | 11°30′N 85°00′W / 11.5°N 85.0°W | 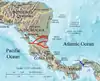 |
Proposed |
|
Proposals use Lake Nicaragua to shorten the built canal distance | |
| Honduras Canal | Central America | Proposed |
|
||||
| Guatemala Canal | Central America | Proposed |
|
||||
| Mexico Canal | Isthmus of Tehuantepec | 17°12′47″N 94°44′24″W / 17.213°N 94.740°W | Proposed |
|
One of the proposed paths connects the Goatzacoalcos River to Tehuantepec | ||
| Thai Canal (Kra Canal) | Malay Peninsula | 10°11′N 98°53′E / 10.183°N 98.883°E | 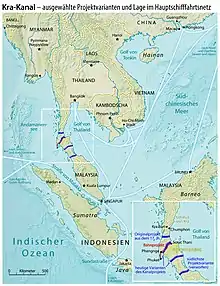 |
Proposed |
|
A level crossing across the Kra Isthmus would need to dig out the Tenasserim Hills | |
| White Sea–Baltic Canal | Russia | 62°48′N 34°48′E / 62.800°N 34.800°E |  |
|
|
See also
References
- ↑ Jean-Jacques Aubert (2015). Federico Romanis; Marco Maiuro (eds.). "Trajan's Canal: River Navigation from the Nile to the Red Sea?". Across the Ocean: Nine Essays on Indo-Mediterranean Trade. Columbia Studies in the Classical Tradition. Brill. 41: 33–42. doi:10.1163/9789004289536_004. ISBN 9789004289536. ISSN 0166-1302. S2CID 127255583.
- 1 2 3 4 Henri Stuckle (1870). Interoceanic Canals, an Essay on the Question of Location for a Ship Canal Across the American Continent. A. Carr and Co.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fred Pearce (11 April 2017). "Mega-canals could slice through continents for giant ships". New Scientist.
- ↑ "The Palestine Canal". New York Times. 27 September 1885.
- ↑ "Billion-dollar Palestine Canal Urged As Substitute for Suez". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 29 November 1937.
- 1 2 Alfred Williams (1880). The inter-oceanic canal and the Monroe doctrine. G.P. Putnam's and Sons.
- ↑ Jonathan Watts (24 November 2016). "Nicaragua canal: in a sleepy Pacific port, something stirs". The Guardian.
- ↑ ANDRÉS OPPENHEIMER (5 July 2017). "Four years later, Nicaragua's $40 billion interoceanic canal remains a pipe dream". Miami Herald.
- ↑ William Herbert Hobbs (1952). A Proposed Open-ditch and Tunnel Sea-level Ship Canal Across Honduras. XVII-th International Geographical Congress. Edwards Brothers. International Geographical Union.
- ↑ Danilo Valladares (10 June 2011). "Guatemala: Future Interoceanic Corridor Will Rival Panama Canal". Inter Press Service (IPS).
- ↑ Robert Bolton (1862). Bolton: England and America. John A. Gray.
- ↑ J.J. Williams (1870). Tehuantepec Railway And Ship Canal. Government of Mexico.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.