
An aurora is a natural phenomenon.
A natural phenomenon is an observable event which is not man-made. Examples include: sunrise, weather, fog, thunder, tornadoes; biological processes, decomposition, germination; physical processes, wave propagation, erosion; tidal flow, and natural disasters such as electromagnetic pulses, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes and earthquakes.[1][2]
History
Over many intervals of time, natural phenomena have been observed by a series of countless events as a feature created by nature.
Physical phenomena
The act of:
Gallery
 Crystal in VCGS furnace
Crystal in VCGS furnace Liquid hydrogen bubble chamber photograph of an anti-proton colliding with a proton
Liquid hydrogen bubble chamber photograph of an anti-proton colliding with a proton.jpg.webp) Children notice an effect of static electricity
Children notice an effect of static electricity
Chemical phenomena
Biological phenomena
- Metabolism
- Catabolism
- Anabolism
- Decomposition – by which organic substances are broken down into a much simpler form of matter
- Fermentation – converts sugar to acids, gases and/or alcohol.
- Growth
- Birth
- Death
- Population decrease
Gallery
 Decomposition:a decaying peach over a period of six days. Each frame is approximately 12 hours apart, as the fruit shrivels and becomes covered with mold.
Decomposition:a decaying peach over a period of six days. Each frame is approximately 12 hours apart, as the fruit shrivels and becomes covered with mold.
Astronomical phenomena
 Supernova
Supernova
Geological phenomena
- Mineralogic phenomena
- Lithologic phenomena
- Rock types
- Igneous rock
- Igneous formation processes
- Sedimentary rock
- Sedimentary formation processes (sedimentation)
- Quicksand
- Metamorphic rock
- Igneous rock
- Rock types
- Endogenic phenomena
- Plate tectonics
- Phenomena associated with igneous activity
- Earth's magnetic field
- Exogenic phenomena
- Slope phenomena
- Weathering phenomena
- Glacial and peri-glacial phenomena
- Atmospheric phenomena
- Impact phenomena
- Coupled endogenic-exogenic phenomena
Gallery
 Geology: parabola-shaped lava flow illustrates Galileo's law of falling bodies, as well as blackbody radiation. The temperature can be discerned from the color of the blackbody.
Geology: parabola-shaped lava flow illustrates Galileo's law of falling bodies, as well as blackbody radiation. The temperature can be discerned from the color of the blackbody.
Meteorological phenomena
Violent meteorological phenomena are called storms. Regular, cyclical phenomena include seasons and atmospheric circulation. climate change is often semi-regular.

 A tornado on May 3, 1999 in central Oklahoma
A tornado on May 3, 1999 in central Oklahoma
Atmospheric optical phenomena

The Belt of Venus over Paranal Observatory atop Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert, northern Chile[3]

Crepuscular rays at sunrise in Malibu, California
Atmospheric optical phenomena include:
- Afterglow
- Airglow
- Alexander's band, the dark region between the two bows of a double rainbow.
- Alpenglow
- Anthelion
- Anticrepuscular rays
- Aurora
- Auroral light (northern and southern lights, aurora borealis and aurora australis)
- Belt of Venus
- Brocken Spectre
- Circumhorizontal arc
- Circumzenithal arc
- Cloud iridescence
- Crepuscular rays
- Earth's shadow
- Earthquake lights
- Glories
- Green flash
- Halos, of Sun or Moon, including sun dogs
- Haze
- Heiligenschein or halo effect, partly caused by the opposition effect
- Ice blink
- Light pillar
- Lightning
- Mirages (including Fata Morgana)
- Monochrome Rainbow
- Moon dog
- Moonbow
- Nacreous cloud/Polar stratospheric cloud
- Rainbow
- Subsun
- Sun dog
- Tangent arc
- Tyndall effect
- Upper-atmospheric lightning, including red sprites, Blue jets, and ELVES
- Water sky

A double rainbow at Minsi Lake, Pennsylvania

Atmospheric optical phenomenon
Oceanographic
- Oceanographic phenomena include tsunamis, ocean currents and breaking waves.
gallery
 Tsunami by Hokusai 19th century
Tsunami by Hokusai 19th century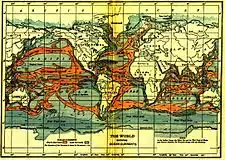 Source: "Physiography for High Schools" by Albert L. Arey, Frank L. Bryant, William W. Clendenin, and William T. Morrey. 1911, USA.
Source: "Physiography for High Schools" by Albert L. Arey, Frank L. Bryant, William W. Clendenin, and William T. Morrey. 1911, USA. Shoreline wave-breaking (surf); Human riding surfboard.
Shoreline wave-breaking (surf); Human riding surfboard.
See also
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Natural phenomena.
- ↑ Missy Allen; Michel Peissel (1993). Dangerous Natural Phenomena. Chelsea House. ISBN 079101794X.
- ↑ William R. Corliss (1977). Handbook of unusual natural phenomena. Sourcebook Project. ISBN 0915554011.
- ↑ "Belt of Venus over Cerro Paranal". Picture of the Week. ESO. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
