Logging as a service (LaaS) is an IT architectural model for centrally ingesting and collecting any type of log files coming from any given source or location such as servers, applications, devices etc. The files are "normalized" or filtered for reformatting and forwarding to other dependent systems to be processed as “native” data, which can then be managed, displayed and ultimately disposed of according to a predesignated retention schedule based on any number of criteria.
In an enterprise situation, the IT datacenter becomes the hub for all log files and normalization. In a managed service provider (MSP) environment, the log sources would be coming from applications outside the enterprise but still hosted and managed by the MSP as needed.
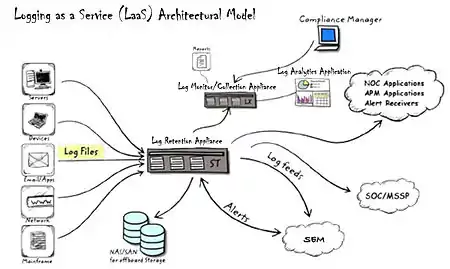
Under this model, the IT datacenter acts as the "private cloud" under the concept of cloud computing to provision the logs to various stakeholders within the organization for future forensics[1] or analysis to identify risks, patterns of activity or predict behaviors based on the data collected within the logs. Just as IT becomes the "hub" of the service, the stakeholders become the beneficiaries of the centralized data in the form of alerts, reports or any periphery applications for predictive analysis or insight from big data through graphical display.