 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Maduramycin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
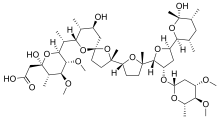
| Formula | C47H80O17 |
| Molar mass | 917.140 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Maduramicin (maduramycin) is an antiprotozoal agent used in veterinary medicine to prevent coccidiosis.[1][2] It is a natural chemical compound first isolated from the actinomycete Actinomadura rubra.[3]
References
- ↑ Maduramicin Ammonium, Canadian Food Inspection Agency
- ↑ McDougald LR, Fuller AL, Mathis GF, Wang GT (1990). "Efficacy of maduramicin ammonium against coccidiosis in turkeys under laboratory and floor-pen conditions". Avian Diseases. 34 (3): 634–638. doi:10.2307/1591256. JSTOR 1591256. PMID 2241692.
- ↑ Fleck WF, Strauss DG, Meyer J, Porstendorfer G (1978). "Fermentation, isolation, and biological activity of maduramycin: a new antibiotic from Actinomadura rubra". Zeitschrift Fur Allgemeine Mikrobiologie. 18 (6): 389–398. doi:10.1002/jobm.3630180602. PMID 362738.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.