
Memento is a United States National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (NDIIPP)–funded project aimed at making Web-archived content more readily discoverable and accessible to the public.
Technical description
Memento is defined in RFC 7089[1] as an implementation of the time dimension of content negotiation.[2] HTTP accomplishes negotiation of content via a variety of headers that allow clients and servers to find content that the user desires.
| Request Header | Response Header | Dimension | Examples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accept | Content-Type | content-type of the representation | text/html
text/plain image/png |
RFC 7231[3] |
| Accept-Language | Content-Language | language of the representation | en
en-US cz |
RFC 7231 |
| Accept-Encoding | Content-Encoding | medium, typically compression, that the content has been encoded with | compress
gzip deflate |
RFC 7231 |
| Accept-Charset | Content -Type | the character set used by the web page | iso-8859-5
unicode-1-1 |
RFC.
7231 |
| Accept-Datetime | Memento-Datetime | time of the representation | Fri, 15 Aug 2014 13:43:03
GMT |
RFC 7089 |
To understand Memento fully, one must realize that the Last-Modified header provided by HTTP[4] does not necessarily reflect when a particular version of a web page came into existence. Also, the Last-Modified header may not exist in some cases. To provide more information, the Memento-Datetime header has been introduced to indicate when a specific representation of a web page was observed on the web.[5]
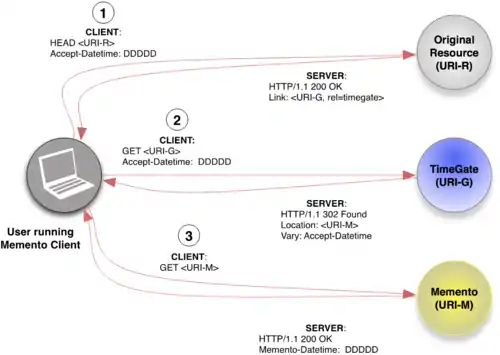
Usage
One can find copies of page by simply navigating, in a web browser, to a link formatted, replacing urltoarchive with the full URL of the page desired:[6]
JSON description of a Memento:
http://timetravel.mementoweb.org/api/json/YYYY/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/api/json/YYYYMM/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/api/json/YYYYMMDD/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/api/json/YYYYMMDDHH/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/api/json/YYYYMMDDHHMM/urltoarchive- or
redirect to a Memento with a datetime that is close to a desired datetime:
http://timetravel.mementoweb.org/memento/YYYY/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/memento/YYYYMM/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/memento/YYYYMMDD/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/memento/YYYYMMDDHH/urltoarchivehttp://timetravel.mementoweb.org/memento/YYYYMMDDHHMM/urltoarchive
References
- ↑ RFC 7089: HTTP Framework for Time-Based Access to Resource States -- Memento
- ↑ Berners Lee, Tim. "Web Architecture: Generic Resources". World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). 1996. http://www.w3.org/DesignIssues/Generic Archived 2015-06-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ RFC 7231: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content
- ↑ RFC 7232: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Conditional Requests
- ↑ Nelson, Michael L. "2010-11-05: Memento-Datetime is not Last-Modified". Web Science and Digital Libraries Research Group. November 5, 2010. http://ws-dl.blogspot.com/2010/11/2010-11-05-memento-datetime-is-not-last.html Archived 2015-05-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Time Travel APIs". timetravel.mementoweb.org. Archived from the original on 2018-05-21. Retrieved 2018-05-15.
External links
- Memento Project
- The When of the Web - Extensive information about the proposal and experiment is available in the November 2009 paper
- Memento: Time Travel for the Web
- http://lanlsource.lanl.gov/hello
- http://www.cdlib.org/cdlinfo/2010/02/04/web-archive-discovery-memento-implementation-meeting/