 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-bromomesitylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.552 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11Br | |
| Molar mass | 199.091 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.3220 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −1 °C (30 °F; 272 K) |
| Boiling point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
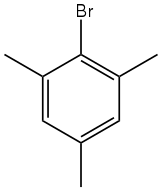
Mesityl bromide is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3C6H2Br. It is a derivative of mesitylene (1,3,5-trimethylbenzene) with one ring H replaced by Br. The compound is a colorless oil. It is a standard electron-rich aryl halide substrate for cross coupling reactions.[2] With magnesium it reacts to give the Grignard reagent,[3] which is used in the preparation of tetramesityldiiron.
It is prepared by the direct reaction of bromine with mesitylene:[4]
- (CH3)3C6H3 + Br2 → (CH3)3C6H2Br + HBr
References
- ↑ "2-Bromomesitylene". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ Farina, Vittorio; Krishnamurthy, Venkat; Scott, William J. (1997). "The Stille Reaction". Organic Reactions. pp. 1–652. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or050.01. ISBN 0471264180.
- ↑ Lee Irvin Smith (1931). "Isoodurene". Org. Synth. 11: 66. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0066.
- ↑ Lee Irvin Smith (1931). "Bromomesitylene". Org. Synth. 11: 24. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0024.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.