 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl phenylacetate | |
| Other names
Methyl 2-phenylacetate Methyl benzene acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 878795 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.674 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C024906 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.1745 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.055±0.060 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| Boiling point | 218 °C (424 °F; 491 K) |
| 2070 mg/L | |
| Vapor pressure | 17.3 Pa |
| −92.73×10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.505±0.020 at 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 90.6 °C (195.1 °F; 363.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
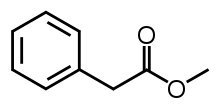
Methyl phenylacetate is an organic compound that is the methyl ester of phenylacetic acid, with the structural formula C6H5CH2COOCH3. It is a colorless liquid that is only slightly soluble in water, but soluble in most organic solvents.
Methyl phenylacetate has a strong odor similar to honey. This compound also occurs in brandy, capsicum, coffee, honey, pepper, and some wine. It is used in the flavor industry and in perfumes to impart honey scents.
Methyl phenyldiazoacetate, precursor to cyclopropanation agents, is prepared by treating methyl phenylacetate with p-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl azide in the presence of base.[1]
References
- ↑ Huw M. L. Davies, Wen‐hao Hu, Dong Xing (2015). "Methyl Phenyldiazoacetate". EEROS: 1–10. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00444.pub2. ISBN 9780470842898.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Methyl Phenyl Acetate."(February 22, 2007). Chemical Information The Good Scents Company. Retrieved on January 22, 2008.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
