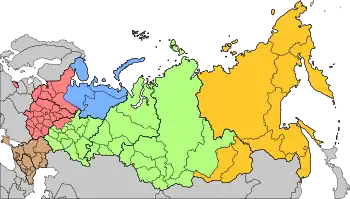
The military districts in Russia serve as administrative divisions for the Russian Armed Forces. Each has a headquarters administering the military formations within the Russian federal subjects that it includes.
There are currently four military districts in Russia: Western, Central, Eastern, Southern plus the Northern Fleet operating as a joint strategic command, effectively a fifth military district.
List of military districts
26 December 1991

After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia maintained a diminishing number of former Soviet Armed Forces military districts.
27 July 1998
Military districts of Russia according to Decree of the President of Russia No. 900 on 27 July 1998.[1]
1 September 2001
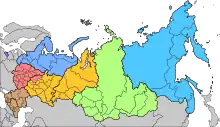
Volga Military District and Urals Military District was merged into the Volga-Urals Military District according to Decree of the President of Russia № 337с on 24 March 2001.[2] The new district was to be with the boundaries of the Republic of Bashkortostan, Mari El, Republic of Mordovia, the Republic of Tatarstan, the Udmurtian Republic, the Chuvash Republic, the Kirov, Kurgan, Orenburg, Penza, Perm, Samara, Sverdlovsk, Tyumen, Ulyanovsk, and Chelyabinsk regions, the Komi-Permyak, Khanty-Mansi, and Yamal-Nemets autonomous areas.
Decree of the President of Russia No. 1764 (12 December 2008)[3] changed names of regions after federal subjects mergers.
1 September 2010

Leningrad Military District, Moscow Military District and Kaliningrad Special Region were merged to form the Western Military District.
1 December 2010

Since 1 December 2010, all military districts except the Western Military District had been replaced by three larger districts, based on recommendations of the 2008 Russian military reforms. The Central Military District was formed from a merger of the Volga-Urals Military District and most of the Siberian Military District, with the remainder (Buryatia and Zabaykalsky Krai) transferred to the Far East Military District to form the Eastern Military District. The North Caucasus Military District was replaced with the Southern Military District. The reform was according to Decree of the President of Russia No. 1144 on 20 September 2010.[4][5]
- Western Military District with headquarters in Saint Petersburg
- Southern Military District with headquarters in Rostov-on-Don
- Central Military District with headquarters in Ekaterinburg
- Eastern Military District with headquarters in Khabarovsk
2 April 2014

The Southern Military District was enlarged to include disputed territories of the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol following the 2014 Russian annexation of Crimea.
15 December 2014

On 15 December 2014, the Northern Fleet of the Russian Navy was removed from the Western Military District and the boundaries of its jurisdiction expanded to form the Northern Fleet Joint Strategic Command. The new military command included Murmansk Oblast, Arkhangelsk Oblast, and numerous Russian islands in the Arctic Ocean.[6]
1 January 2021
The Northern Fleet Joint Strategic Command was the only military command to be transformed into a fully fledged military district, according to President Vladimir Putin's Decree of 5 June 2020.[7] Since 1 January 2021, the Northern Fleet has held the status of a military district, and its joint strategic command has become the Northern Military District.[8]
2 February 2023
Southern military district was expanded to include the occupied parts of Donetsk Republic, Luhansk Republic, Zaporizhzhia Oblast and Kherson Oblast.[9]
2 June 2023
Russian authorities announced that the Moscow and Leningrad Military Districts would be reactivated in the course of 2023.[10][11] It was also announced that a subordinate branch of the Black Sea Fleet in the Sea of Azov would be established.[12]
It appears that the creation of the new commands will take place in 2023. The creation of Moscow and Leningrad Military Districts will take place on 1 March 2024. The Northern Fleet will also lose its district status.
See also
References
- ↑ "УКАЗ Президента РФ от 27.07.1998 N 900 'О ВОЕННО - АДМИНИСТРАТИВНОМ ДЕЛЕНИИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ'". Archived from the original on 2015-05-24. Retrieved 2013-05-09.
- ↑ "УКАЗ Президента РФ от 24.03.2001 N 337с (Выписка) 'ОБ ОБЕСПЕЧЕНИИ СТРОИТЕЛЬСТВА И РАЗВИТИЯ ВООРУЖЕННЫХ СИЛ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ, СОВЕРШЕНСТВОВАНИИ ИХ СТРУКТУРЫ'". graph.document.kremlin.ru. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ↑ "УКАЗ Президента РФ от 12.12.2008 N 1764 'О ВНЕСЕНИИ ИЗМЕНЕНИЙ В УКАЗ ПРЕЗИДЕНТА РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ ОТ 27 ИЮЛЯ 1998 Г. N 900 "О ВОЕННО - АДМИНИСТРАТИВНОМ ДЕЛЕНИИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ'". graph.document.kremlin.ru. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ↑ "Dmitry Medvedev signed Executive Order on reform of military administrative division of the Russian Federation and establishment of new military districts". President of Russia. Retrieved July 23, 2019.
- ↑ "УКАЗ Президента РФ от 20.09.2010 N 1144 'О ВОЕННО - АДМИНИСТРАТИВНОМ ДЕЛЕНИИ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ'". graph.document.kremlin.ru. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ↑ "История : Министерство обороны Российской Федерации".
- ↑ "Северный флот станет пятым военным округом России с 2021 года". armstrade.org. 2 September 2020.
- ↑ "Северный флот России получил статус военного округа". Interfax (in Russian). 1 January 2021.
- ↑ "New Russian regions included in Southern Military District". dan-news.ru. 2023-02-02. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
- ↑ "Russia-Ukraine war live: UK foreign secretary would like Ukraine to get Leopard tanks as Putin ally warns of 'global catastrophe'". the Guardian. 2023-01-22. Retrieved 2023-01-22.
- ↑ "Moscow Reorganizing Russian Military for Offensive War and to Protect Putin Regime". Jamestown. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
- ↑ "UK intel explains why Russia creates Azov Naval District in occupied Mariupol". www.ukrinform.net. 2023-07-08. Retrieved 2023-09-18.
External links
![]() Media related to Military Districts of Russia at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Military Districts of Russia at Wikimedia Commons