Mills County | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Iowa | |
 Iowa's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 41°01′59″N 95°37′08″W / 41.033055555556°N 95.618888888889°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1851 |
| Seat | Glenwood |
| Largest city | Glenwood |
| Area | |
| • Total | 441 sq mi (1,140 km2) |
| • Land | 437 sq mi (1,130 km2) |
| • Water | 3.2 sq mi (8 km2) 0.7% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 14,484 |
| • Density | 33/sq mi (13/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 3rd |
| Website | www |
Mills County is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,484.[1] The county seat is Glenwood.[2] The county was formed in 1851 and named for Major Frederick Mills of Burlington, Iowa who was killed at the Battle of Churubusco during the Mexican–American War.[3]
Mills County is included in the Omaha–Council Bluffs, NE–IA Metropolitan Statistical Area.[4]
History
The future county's first permanent settlement was Rushville, founded in 1846 by persecuted members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints as they were being driven out of Nauvoo, Illinois. This is not to be confused with the state's present-day Rushville in Jasper County. A nearby settlement, also founded by the Mormon settlers, was called Coonsville after Dr. Liberius Coons, one of the first arrivals. That settlement continued after the Mormons moved on; its name was changed to Glenwood in 1853.
In Glenwood, the first courthouse was a small frame building which served until 1857. It was replaced by a two-story building, which was enlarged in the 1900s and received a clock tower in 1910. In 1959 this building was replaced with the present building, dedicated on August 29, 1959.[5]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 441 square miles (1,140 km2), of which 437 square miles (1,130 km2) is land and 3.2 square miles (8.3 km2) (0.7%) is water.[6]
Major highways
Adjacent counties
- Pottawattamie County (north)
- Montgomery County (east)
- Fremont County (south)
- Cass County, Nebraska (southwest)
- Sarpy County, Nebraska (west)
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 4,481 | — | |
| 1870 | 8,718 | 94.6% | |
| 1880 | 14,137 | 62.2% | |
| 1890 | 14,548 | 2.9% | |
| 1900 | 16,764 | 15.2% | |
| 1910 | 15,811 | −5.7% | |
| 1920 | 15,422 | −2.5% | |
| 1930 | 15,866 | 2.9% | |
| 1940 | 15,064 | −5.1% | |
| 1950 | 14,064 | −6.6% | |
| 1960 | 13,050 | −7.2% | |
| 1970 | 11,832 | −9.3% | |
| 1980 | 13,406 | 13.3% | |
| 1990 | 13,202 | −1.5% | |
| 2000 | 14,547 | 10.2% | |
| 2010 | 15,059 | 3.5% | |
| 2020 | 14,484 | −3.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[7] 1790-1960[8] 1900-1990[9] 1990-2000[10] 2010-2018[11] | |||

2020 census
The 2020 census recorded a population of 14,484 in the county, with a population density of 32.9065/sq mi (12.7053/km2). 95.16% of the population reported being of one race. 90.05% were non-Hispanic White, 0.53% were Black, 3.18% were Hispanic, 0.21% were Native American, 0.33% were Asian, 0.07% were Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander and 5.63% were some other race or more than one race. There were 6,110 housing units, of which 5,512 were occupied.[1]
2010 census
The 2010 census recorded a population of 15,059 in the county, with a population density of 34.4971/sq mi (13.3194/km2). There were 6,109 housing units, of which 5,605 were occupied.[12]
2000 census
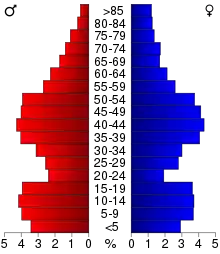
As of the census[13] of 2000, there were 14,547 people, 5,324 households, and 3,939 families residing in the county. The population density was 33 people per square mile (13 people/km2). There were 5,671 housing units at an average density of 13 units per square mile (5.0 units/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 97.97% White, 0.28% Black or African American, 0.27% Native American, 0.29% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.36% from other races, and 0.82% from two or more races. 1.23% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 5,324 households, out of which 34.80% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.70% were married couples living together, 8.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.00% were non-families. 22.30% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.10% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.60 and the average family size was 3.04.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 26.80% under the age of 18, 7.00% from 18 to 24, 28.10% from 25 to 44, 25.50% from 45 to 64, and 12.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 100.60 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $42,428, and the median income for a family was $49,592. Males had a median income of $31,721 versus $24,938 for females. The per capita income for the county was $18,736. About 5.80% of families and 8.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.30% of those under age 18 and 7.60% of those age 65 or over.
Communities

Cities
Unincorporated communities
- Rushville
Census-designated place
Townships
Population ranking
The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2020 census of Mills County.[1]
† county seat
| Rank | City/Town/etc. | Municipal type | Population (2020 Census) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | † Glenwood | City | 5,073 |
| 2 | Malvern | City | 1,046 |
| 3 | Emerson | City | 403 |
| 4 | Silver City | City | 245 |
| 5 | Mineola | CDP | 154 |
| 6 | Hastings | City | 152 |
| 7 | Henderson | City | 144 |
| 8 | Pacific Junction | City | 96 |
| 9 | Tabor (mostly in Fremont County) | City | 86 (1,014 total) |
Law enforcement
The current Sheriff of Mills County is Eugene Goos. He and his 11 full-time deputies patrol approximately 447 square miles in the county. The Mills County Sheriff's Office provides police services under contract for all of the towns and cities and Mills County except for the City of Glenwood which has its own police department.
The first Mills County Sheriff was W.W. Noyes[14] who was appointed by the Iowa General Assembly on August 1, 1851. He was succeeded by James Hardy who served as the first elected sheriff of the county and assumed the office on August 31, 1851.
Politics
Mills County is one of the most consistently Republican counties in Iowa. It has backed the Republican in all but five elections in its history, its inaugural election in 1852 prior to the founding of the Republican Party, in 1912 when former Republican turned Progressive Theodore Roosevelt caused a split in the vote, allowing Democrat Woodrow Wilson to take the county with a sub-40% plurality, in the two landslide victories for Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1932 and 1936, and for Lyndon B. Johnson in his 1964 landslide, who even then barely took Mills County by only 39 votes and less than 1%.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 5,585 | 67.55% | 2,508 | 30.33% | 175 | 2.12% |
| 2016 | 5,067 | 65.82% | 2,090 | 27.15% | 541 | 7.03% |
| 2012 | 4,216 | 58.46% | 2,848 | 39.49% | 148 | 2.05% |
| 2008 | 4,183 | 57.44% | 2,976 | 40.86% | 124 | 1.70% |
| 2004 | 4,556 | 65.65% | 2,308 | 33.26% | 76 | 1.10% |
| 2000 | 3,684 | 62.28% | 2,039 | 34.47% | 192 | 3.25% |
| 1996 | 2,958 | 51.25% | 2,068 | 35.83% | 746 | 12.92% |
| 1992 | 2,699 | 43.77% | 1,798 | 29.16% | 1,669 | 27.07% |
| 1988 | 3,212 | 59.82% | 2,092 | 38.96% | 65 | 1.21% |
| 1984 | 3,994 | 72.80% | 1,434 | 26.14% | 58 | 1.06% |
| 1980 | 3,581 | 69.09% | 1,244 | 24.00% | 358 | 6.91% |
| 1976 | 2,722 | 57.79% | 1,908 | 40.51% | 80 | 1.70% |
| 1972 | 3,531 | 74.94% | 1,060 | 22.50% | 121 | 2.57% |
| 1968 | 2,916 | 62.41% | 1,216 | 26.03% | 540 | 11.56% |
| 1964 | 2,424 | 49.58% | 2,463 | 50.38% | 2 | 0.04% |
| 1960 | 3,436 | 65.37% | 1,820 | 34.63% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1956 | 3,539 | 64.89% | 1,897 | 34.78% | 18 | 0.33% |
| 1952 | 4,028 | 69.04% | 1,792 | 30.72% | 14 | 0.24% |
| 1948 | 2,921 | 57.20% | 2,155 | 42.20% | 31 | 0.61% |
| 1944 | 3,288 | 60.65% | 2,106 | 38.85% | 27 | 0.50% |
| 1940 | 3,873 | 57.39% | 2,862 | 42.41% | 14 | 0.21% |
| 1936 | 3,424 | 48.40% | 3,610 | 51.02% | 41 | 0.58% |
| 1932 | 2,420 | 38.07% | 3,861 | 60.75% | 75 | 1.18% |
| 1928 | 3,429 | 60.86% | 2,179 | 38.68% | 26 | 0.46% |
| 1924 | 3,348 | 57.38% | 1,750 | 29.99% | 737 | 12.63% |
| 1920 | 3,683 | 69.00% | 1,592 | 29.82% | 63 | 1.18% |
| 1916 | 1,707 | 50.58% | 1,600 | 47.41% | 68 | 2.01% |
| 1912 | 850 | 25.41% | 1,312 | 39.22% | 1,183 | 35.37% |
| 1908 | 1,959 | 55.01% | 1,522 | 42.74% | 80 | 2.25% |
| 1904 | 2,252 | 61.06% | 1,274 | 34.54% | 162 | 4.39% |
| 1900 | 2,212 | 55.00% | 1,733 | 43.09% | 77 | 1.91% |
| 1896 | 2,153 | 51.93% | 1,958 | 47.23% | 35 | 0.84% |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "2020 Census State Redistricting Data". census.gov. United states Census Bureau. Retrieved August 12, 2021.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ↑ Mills County
- ↑ United States Office of Management and Budget. "Update of Statistical Area Definitions and Guidance on Their Uses" (PDF). pp. 5, 36. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2006. Retrieved July 21, 2006.
- ↑ ""History" - Mills County". Archived from the original on August 11, 2018. Retrieved August 11, 2018.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved July 20, 2014.
- ↑ "Population & Housing Occupancy Status 2010" (PDF). United States Census Bureau – American FactFinder. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 16, 2020. Retrieved August 15, 2022.
- ↑ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ↑ History of Mills County Sheriff's Office Archived 2011-10-15 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 27, 2018.