| Montes Jura | |
|---|---|
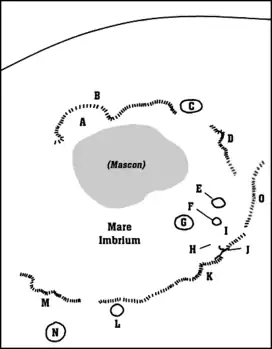 Detail map of Mare Imbrium's features. Montes Jura is the feature marked "B" | |
| Highest point | |
| Listing | Lunar mountains |
| Coordinates | 47°06′N 34°00′W / 47.1°N 34.0°W |
| Geography | |
| Location | the Moon |
Montes Jura is a mountain range in the northwest part of the near side of the Moon. The selenographic coordinates of this range are 47.1° N 34.0° W. It has a diameter of 422 km, with mountains rising to approximately 3800m[1] above the level of Sinus Iridum. They were named after the Jura Mountains in eastern France / western Switzerland.[2]
This range of mountains form a visually pleasing semi-circular ring around the Sinus Iridum, a bay along the northwestern edge of Mare Imbrium. The blunt, east-facing cape at the southwestern end of the range is named Promontorium Heraclides, while the east-facing wedge at the northeast end is called Promontorium Laplace. As the terminator advances near this range two to three nights after the first quarter moon,[3] the peaks of this range catch the sunlight at their tops. This produces a string of bright points that have been described as the 'jewelled scimitar' effect.[4]
Ten to eleven days after new moon the crater rim is already illuminated by the sun when the moon is waxing, while the Sinus Iridum is still in shadow. This creates the illusion of a handle, so that the illuminated crater rim is also called Golden Handle.
The only crater of note in this range is Bianchini, which lies across the north-northwestern portion of the curve. A little farther to the west is Sharp, and to the northeast is the ruined crater Maupertuis.
Peter Grego describes a figurine of "The Moon Maiden", seeing her facial profile in Promontorium Heraclides, her hair in the hills to the west, and her body in Montes Jura. She appears upside down when viewed in binoculars from the Northern Hemisphere.[5]
History
In the distant past this range once formed the outer wall of a crater about 260 km in diameter. The southeast face of this crater was then removed and the interior flooded with basaltic lava. As a result, the side of the range facing the mare ends in the nearly level plains, which the opposite side merges with a region of rough and irregular terrain.
References
- ↑ "KADIAS".
- ↑ "Montes Jura". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- ↑ Westfall, John Edward (2000). Atlas of the Lunar Terminator. Cambridge University Press. pp. 116, 120. ISBN 0-521-59002-7.
- ↑ Siew Meng Chong; Albert Chee Hoon Lim; Poon Seng Ang (2002). Photographic Atlas of the Moon. Cambridge University Press. p. 44. ISBN 0-521-81392-1.
- ↑ Grego, Peter (2006). The Moon and How to Observe It. Springer. p. 109. ISBN 978-1-84628-243-0.