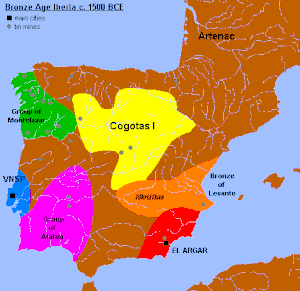
The motillas were the early settlements of La Mancha (Spain) belonging to the Middle Bronze Age, and connected to the Bronze of Levante culture. These were human-made hills atop of which are placed fortified settlements. Their height is usually between four and five meters and the motillas are separated from each other by a distance of four to five kilometers. Their construction started c. 2200 BCE and they were used for about 1000 years.
History of research
The motillas were first believed to be antique burial mounds. However, this hypothesis was ruled out when an excavation at the Motilla del Azuer that took place in the seventies proved their defensive and management faculties. This way, a wide area could be controlled easily.
Some similar sites in the foothills of Sierra Morena mountains are fortified towns of larger size.
Construction and use
.jpg.webp)
The motillas were constructed in the period of c. 2200 BCE–1200 BCE.[1] Their use started at the time of the 4.2 kiloyear event. They were needed as a consequence of severe aridification that affected this wide geographical area. They were also used as a control center of agricultural resources. They were no longer used after the end of the Argaric civilization.
Recently, archaeologists have suggested that these structures are mainly connected with water management, and agricultural production:
"Motilla del Azuer contains the oldest well known from the Iberian Peninsula and the archaeologists suspect that the walled enclosures were therefore used to protect and manage the livelihood of the people living in the settlement: To secure the well’s water, to store and process cereals on a large scale, to occasionally keep the livestock, and to produce pottery and other domestic artefacts."[2]
Analysis by Moreno et al. (2014) verified a relationship between the geological substrate and the spatial distribution of the “motillas”[1] who reported the first paleohydrogeological interdisciplinary research in La Mancha. According to the authors:
"Recent studies show that the “motilla” sites from the Bronze Age in La Mancha may be the most ancient system of groundwater collection in the Iberian Peninsula. ... These were built during the Climatic Event 4.2 ka cal BP, in a time of environmental stress due to a period of severe, prolonged drought."[1]
Gallery
 Motilla del Azuer
Motilla del Azuer Motilla del Azuer
Motilla del Azuer Motilla del Azuer
Motilla del Azuer
See also
Notes
- 1 2 3 Mejías Moreno, M.; Benítez de Lugo Enrich, L.; Pozo Tejado, J.; del y Moraleda Sierra, J. (2014). "Los primeros aprovechamientos de aguas subterráneas en la Península Ibérica. Las motillas de Daimiel en la Edad del Bronce de La Mancha" (PDF). Boletín Geológico y Minero. 125 (4): 455–474. ISSN 0366-0176.
- ↑ "Motilla del Azuer - A Bronze Age Wonder". eyeonspain.com. 2015.
External links
References
- Fundación Dalpa, "Patrimonio de Castilla la Mancha, La Motilla del Azuer: la Edad de Bronce en la Mancha", Memoria Historia, XVII, 2009, pgs. 93-96