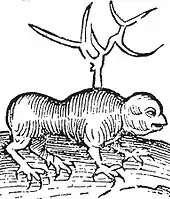
The Myrmecoleon or Ant-lion[1] is a fantastical animal from classical times, possibly derived from an error in the Septuagint version of the book of Job, reappearing in the Greek Christian Physiologus of the 3rd or 4th century A.D.[2][3][4]
It is found in Medieval bestiaries such as the Hortus Sanitatis of Jacob Meydenbach.[5] It is also referenced in some sources as a Formicaleon (Antlion), Formicaleun or Mirmicioleon.[6][7][8][9] Myrmecoleon comes from the Greek words for ant (μύρμηξ [myrmeks]) and lion (λέων [leon]).
Note that the Aberdeen Bestiary describes "There is a stone in the sea which is called in Greek mermecoleon and in Latin concasabea, because it is both hollow and round. It is, moreover, divided into two parts, so that if it wants to, it can close up. The stone lies at the bottom of the sea and comes to life early in the morning. When it rises from its resting-place to the surface of the sea, it opens its mouth and takes in some heavenly dew, and the rays of the sun shine around it; thus there grows within the stone a most precious, shining pearl indeed, conceived from the heavenly dew and given lustre by the rays of the sun."[10]
Interpretations

There are two interpretations of what a Myrmecoleon is. In one version, the antlion is so called because it is the "lion of ants", a large ant or small animal that hides in the dust and kills ants. In the other version, it is a beast that is the result of a mating between a lion and an ant. It has the face of a lion and the body of an ant, with each part having its appropriate nature. Because the lion part will only eat meat and the ant part can only digest grain, the ant-lion starves.[11]
The ant-lion story may come from a mistranslation of a word in the Septuagint version of the Old Testament, from the book of Job. The word in Hebrew is la'ish (ליש), an uncommon word for lion, which in other translations of Job is rendered as either lion or tiger; in the Septuagint it is translated as mermecolion, ant-lion.[6]
References
- ↑ "Ant-lion". The Medieval Bestiary. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- ↑ Swanson, Mark. ""Ant-lion" in the Physiologus".
- ↑ Kevan, D. K. McE. 1992. Antlion ante Linné: [Myrmekoleon] to Myrmeleon (Insecta: Neuroptera: Myrmeleonidae [sic]). Pp. 203-232 in Current Research in Neuropterology. Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Neuropterology [Symposium held in Bagnères-de-Luchon, France, 1991.] M. Canard, H. Aspöck, and M. W. Mansell, eds. Toulouse.
- ↑ Gerhardt, M. I. 1965. The ant-lion nature study on the interpretation of a biblical text, from the Physiologus to Albert the Great. Vivarium. 3: p.1-23
- ↑ Ortus sanitatis. Open Library. OL 25129180M.
- 1 2 "Ant-lion". Retrieved 28 February 2016.
- ↑ Swanson, Mark. "Bestiary: Creatures of Myth and Psyche". Retrieved 28 February 2016.
- ↑ Druce, G. C. 1923. [Myrmekoleon] or Ant-Lion. Pp. 347-363 in The Antiquaries Journal. Vol. III, No. 4. Oxford University Press, London.
- ↑ Kevan, D. K. McE. 1992. Antlion ante Linné: [Myrmekoleon] to Myrmeleon (Insecta: Neuroptera: Myrmeleonidae [sic]). Pp. 203-232 in Current Research in Neuropterology. Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Neuropterology [Symposium held in Bagnères-de-Luchon, France, 1991.] M. Canard, H. Aspöck, and M. W. Mansell, eds. Toulouse.
- ↑ "Folio 96r - the adamas stone, continued. De lapide qui dicitur mermecoleon; Of the stone called mermecoleon | The Aberdeen Bestiary | The University of Aberdeen". www.abdn.ac.uk. Retrieved 2019-10-05.
- ↑ Swanson, Mark. ""Ant-lion" in Medieval Bestiaries". Retrieved 28 February 2016.