 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
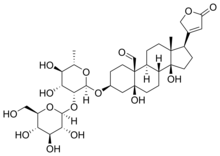
| IUPAC name
3β-[β-D-Glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy]-5,14-dihydroxy-19-oxo-5β-card-20-enolide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,5aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-7-{[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-4,5-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3a,5a-dihydroxy-11a-methyl-1-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)hexadecahydro-9aH-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-9a-carbaldehyde | |
| Other names
Strophanthidin 3-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H50O16 | |
| Molar mass | 714.758 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 162 to 170 °C (324 to 338 °F; 435 to 443 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Neoconvalloside is a cardenolide glycoside extracted from Convallaria majalis.[2]
References
- ↑ Viqar Uddin Ahmad & Anwer Basha (2006). Spectroscopic Data of Steroid Glycosides: Cardenolides and Pregnanes. Vol. 4. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-39576-0_386. ISBN 978-0-387-31162-3.
- ↑ Komissarenko, N. F.; Stupakova, E. P. (1986). "Neoconvalloside - a cardenolide glycoside from plants of the genus Convallaria". Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii (2): 201–204.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.