 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
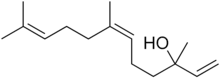
3,7,11-Trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol | |
| Other names
Peruviol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.816 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H26O | |
| Molar mass | 222.37 g/mol |
| Density | 0.872 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 122 °C (252 °F; 395 K) at 3 mmHg |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4898 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Nerolidol, also known as peruviol and penetrol , is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alcohol. A colorless liquid, it is found in the essential oils of many types of plants and flowers.[1] There are four isomers of nerolidol', which differ in the geometry about the central double bond and configuration of the hydroxyl-bearing carbon, but most applications use such a mixture. The aroma of nerolidol is woody and reminiscent of fresh bark. It is used as a flavoring agent and in perfumery as well as in non-cosmetic products such as detergents and cleansers.[2] Nerolidyl derivatives include nerolidyl diphosphate[3] and the fragrance nerolidyl acetate.[4]
Synthesis and occurrence
Nerolidol is produced commercially from geranylacetone by the addition of vinyl Grignard reagent. It is used as a source of farnesol, vitamin E, and vitamin K1.[4]
Significant sources of natural nerolidol is Cabreuva oil and the oil of Dalbergia parviflora.[4] It is also present in neroli, ginger, jasmine, lavender, tea tree, Cannabis sativa, and lemon grass, and is a dominant scent compound in Brassavola nodosa.[5]
Further reading
- Miguel, M.G.; Dandlen, S.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Duarte, A.; Faisca, J. (2008). "ESSENTIAL OILS OF FLOWERS OF CITRUS SINENSIS AND CITRUS CLEMENTINA CULTIVATED IN ALGARVE, PORTUGAL". Acta Horticulturae (773): 89–94. doi:10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.773.12. hdl:10400.1/2788. ISSN 0567-7572.
See also
References
- 1 2 Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6388.
- ↑ Chan, Weng-Keong; Tan, Loh Teng-Hern; Chan, Kok-Gan; Lee, Learn-Han; Goh, Bey-Hing (2016-04-28). "Nerolidol: A Sesquiterpene Alcohol with Multi-Faceted Pharmacological and Biological Activities". Molecules. 21 (5): 529. doi:10.3390/molecules21050529. PMC 6272852. PMID 27136520.
- ↑ Benedict, C. R. (1 April 2001). "The Cyclization of Farnesyl Diphosphate and Nerolidyl Diphosphate by a Purified Recombinant delta-Cadinene Synthase". Plant Physiology. 125 (4): 1754–1765. doi:10.1104/pp.125.4.1754. PMC 88832. PMID 11299356.

- 1 2 3 Sell, Charles S. (2006). "Terpenoids". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2005181602120504.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ↑ Kaiser, Roman (1993). The Scent of Orchids. Elsevier. pp. 58, 199–200. ISBN 978-0-444-89841-8.