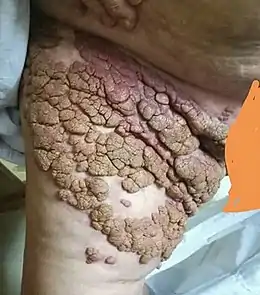
Nevus lipomatosus (cutaneous) superficialis (NLS or NLCS, also known as "Nevus lipomatosis of Hoffman and Zurhelle"[1]) is characterized by soft, yellowish papules or cerebriform plaques, usually of the buttock or thigh, less often of the ear or scalp, with a wrinkled rather than warty surface.[1][2]: 625 It is usually congenital in origin or appears within the first three decades.[3]
A pedunculated lipofibroma is a solitary variant of nevus lipomatosus superficialis.[3] It usually appears in adult life, and usually on the axilla, knee, ear, arm, scalp and the lower trunk.[3]
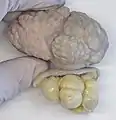 Pedunculated lipofibroma, gross pathology
Pedunculated lipofibroma, gross pathology.jpg.webp) Micrograph of pedunculated lipofibroma, low magnification, with dermal expansion of fatty tissue.
Micrograph of pedunculated lipofibroma, low magnification, with dermal expansion of fatty tissue..jpg.webp) Intermediate magnification, showing mature lipocytes with absence of capsule.
Intermediate magnification, showing mature lipocytes with absence of capsule.
In both multiple and solitary variants, the histopathology shows variable amounts of mature lipocytes within the dermis. Occasionally, there is an excessive fibrocollagenous tissue proliferation. The main differential diagnoses are acrochordon, seborrheic keratosis, intradermal melanocytic nevi, neurofibromas, verrucae and fibroepithelioma of Pinkus.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1840. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- 1 2 3 4 Das, Anupam; Chandra, Somodyuti; Mohanty, Swosti; Gharami, RameshC; Podder, Indrashis (2015). "Solitary pedunculated growth in a child". Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology: 0. doi:10.4103/2319-7250.165641. ISSN 2319-7250.