| Nippon Sharyo P865 & P2020 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| In service |
|
| Manufacturer | Nippon Sharyo |
| Constructed |
|
| Scrapped |
|
| Number built |
|
| Number preserved |
|
| Number scrapped |
|
| Successor | Kinki Sharyo P3010 |
| Formation | Single unit |
| Fleet numbers |
|
| Capacity | 104 standing, 76 seated |
| Operators | |
| Lines served |
|
| Specifications | |
| Car body construction | Low alloy high tensile steel |
| Car length | 87 ft 0 in (26,518 mm) |
| Width | 8 ft 8+3⁄4 in (2,661 mm) |
| Height | 11 ft 6 in (3,505 mm) |
| Floor height | 39.2 in (996 mm) |
| Doors | 8 (4 per side) |
| Articulated sections | 2 (one articulation) |
| Wheel diameter | 2 ft 4.00 in (711.2 mm) |
| Wheelbase | 6 ft 2+13⁄16 in (1.9 m) |
| Maximum speed | 55 mph (89 km/h) |
| Weight | 94,160 lb (42.71 t) |
| Traction system | Chopper control |
| Electric system(s) | Overhead line, 750 V DC |
| Current collector(s) | Brecknell Willis & Faiveley pantographs |
| AAR wheel arrangement | B-2-B |
| Bogies | Inside-bearing type with resilient wheels |
| Braking system(s) | Pulse width controlled electro-pneumatic disc brake |
| Safety system(s) |
|
| Coupling system | Tomlinson |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Notes/references | |
| [1] | |
The P865 and P2020 were articulated light rail vehicles used on the Los Angeles Metro Rail system. They were manufactured by Nippon Sharyo and used on the A, C (P2020), and E lines.
The trains featured air conditioning, emergency intercoms, wheelchair spaces and automated announcements. They are of an air-electric design, with air powered doors, friction brakes, and a pantograph.
Operational history
The P865s were the first urban rail vehicles to run in Los Angeles County since the Pacific Electric Railway ceased operations in 1965 as the first cars were delivered in May 1989. The original 54 railcars, numbered 100–153, were ordered at a cost of $1.17 million each.[2] Prior to entering service, all of the railcars were christened after various cities in Los Angeles County; it was in the same style as christening a ship before being launched.[3][4] Examples include Long Beach (Car 100) and Bell (Car 105).
Nippon Sharyo P2020
The P2020 was the newer version of the P865, which had automated control panels for Green Line service since the C Line was initially intended to be fully automated. 15 vehicles with that model designation were delivered to Metro in 1994.[5] The railcars, numbered 154–168, entered revenue service on the Green Line the following year. In the early 2000s, the railcars were transferred to the Blue Line fleet when the Green Line received newer Siemens P2000 LRVs.
Overhaul
In late 2013, Metro awarded a 60-month fixed price contract to ORX to overhaul the powered axle assemblies for the then twenty-three year old railcars.[6]
Retirement and preservation
The P865s were completely retired in September 2018 after 28 years of service, and were replaced by Kinki Sharyo P3010s.[7] While most of the P865s were dismantled for parts and subsequently scrapped,[7] Cars 100 and 144 were retained. Car 100, christened Long Beach and painted in the original LACTC livery, is being preserved for its namesake city, and will be placed on static display in Downtown Long Beach. Car 144, christened South Gate, was donated to the Southern California Railway Museum in Perris, California.
The P2020s were retired due to exceeding the maximum storage capacity after the final batch of the P3010 were delivered. All 15 railcars were retired throughout early 2021. The last railcars were removed from service on April 23, 2021. In early 2021, the P2020s were towed to Division 16 in Westchester throughout early 2021 via the C and K lines. On March 5, P865 Car 100 assisted in the towing operation. Most of the P2020 fleet was later removed and scrapped, but Car 164 is preserved at the Western Railway Museum in Suisun City, California.
In popular culture
The P865 has made several media appearances other than public service announcements. It was featured in movies such as Lethal Weapon 3, "Heat (1995 film)" , Virtuosity, The Italian Job, "Collateral (film)" and Captain Marvel.
See also
References
- ↑ "Articulated LRV". Nippon Sharyo. Archived from the original on 6 November 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ Ramberg, Anders (July 13, 1990). "Transit: Sleek New Blue Line Will Debut on Saturday". The Los Angeles Times. p. A22. Archived from the original on January 8, 2018. Retrieved January 7, 2018 – via Newspapers.com.
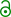
- ↑ Ubaldo, Jose (2017-06-22). "The Metro Blue Line says hello/goodbye to new/old rail cars". The Source. Archived from the original on 2019-07-09. Retrieved 2019-07-09.
- ↑ metrolibrarian (2008-04-18), (1990) "Metro Blue Line Grand Opening and Mobility Promo", archived from the original on 2019-11-15, retrieved 2019-07-09
- ↑ "Overseas USA". Nippon Sharyo. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ "P865/P2020 Light Rail Vehicle Powered Axle Assembly Overhaul" (PDF). media.metro.net. LACMTA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
- 1 2 "End of an era: the last P865 light rail car has been decommissioned". The Source. 2018-09-28. Archived from the original on 2018-10-19. Retrieved 2018-10-19.
External links