 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4-Hydroxy-N,N-didesmethyltamoxifen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
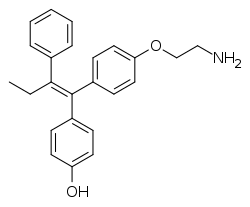
| Formula | C24H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 359.469 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Norendoxifen, also known as 4-hydroxy-N,N-didesmethyltamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (AI) of the triphenylethylene group that was never marketed.[1] It is an active metabolite of the selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) tamoxifen.[1] Unlike tamoxifen, norendoxifen is not a SERM, and instead has been found to act as a potent and selective competitive inhibitor of aromatase (Ki = 35 nM).[1] Drugs with dual SERM and AI activity, such as 4'-hydroxynorendoxifen, have been developed from norendoxifen, and may have therapeutic potential as antiestrogens in the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.[2]
See also
- Afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen)
- Endoxifen (4-hydroxy-N-desmethyltamoxifen)
References
- 1 2 3 Lu WJ, Xu C, Pei Z, Mayhoub AS, Cushman M, Flockhart DA (May 2012). "The tamoxifen metabolite norendoxifen is a potent and selective inhibitor of aromatase (CYP19) and a potential lead compound for novel therapeutic agents". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 133 (1): 99–109. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1699-4. PMID 21814747. S2CID 22096941.
- ↑ Lv W, Liu J, Skaar TC, Flockhart DA, Cushman M (March 2015). "Design and synthesis of norendoxifen analogues with dual aromatase inhibitory and estrogen receptor modulatory activities". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 58 (6): 2623–48. doi:10.1021/jm501218e. PMC 4687028. PMID 25751283.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.