Valley Metro Rail (styled as METRO) is a 28.2-mile (45 km)[3] light rail line serving the cities of Phoenix, Tempe, and Mesa in Arizona, USA. The network, which is part of the Valley Metro public transit system, began operations on December 27, 2008. In 2022, the system had a ridership of 9,108,600, or about 30,400 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2023.
In the years since it opened in 2008, the system has undergone four expansions (including the Tempe Streetcar), with at least three more scheduled. Furthermore, extensions are planned into West Phoenix at Desert Sky Mall and to South Phoenix at Baseline Road, all of which were expanded as a direct result of obtaining funding under the Proposition 104 sales tax increase.
Cost and infrastructure
The expected construction cost for the initial 20 miles (32 km) was $1.4 billion, or $70 million per mile.[4] In 2008, Valley Metro estimated the train would cost $184 million to operate over the following five years with fares covering $44 million (24%) of the operation costs and tax subsidies covering the remaining costs.[5]
Trains operate on city streets in a "center reservation", similar to the Red Line of the METRORail light rail system in Houston, the surface sections of the MBTA subway's Green Line in Boston, and some surface sections of the Muni Metro in San Francisco and TRAX in Salt Lake City. Some parts of the line, such as the bridge over Tempe Town Lake (near State Route 202), have no contact with other traffic. The vehicles used are rated for a maximum speed of 58 miles per hour (93 km/h), and have to complete the 28 miles (45 km) route in just over 90 minutes, including station stops.[6] The system is powered by an overhead catenary that supplies power at 750 V DC.[7]
History

Numerous plans preceded the implementation of light rail. The Phoenix Street Railway provided streetcar service from 1887 to 1948. Historic vehicles may be seen at the Phoenix Trolley Museum, with Car #116 celebrating her 80th birthday on December 25, 2008, just days before the opening of modern rail service. In 1989, the ValTrans elevated rail proposal was turned down by voters in a referendum due to cost and feasibility concerns.[8] Subsequent initiatives during the 1990s failed over similar reasons.
Metro was created by the Transit 2000 Regional Transportation Plan (RTP), also called the Transit 2000 plan, which involved a 0.5 per cent sales tax, and was approved by Phoenix voters in 2000. Transit 2000 aimed at improving the local bus service (considered unacceptably inadequate compared to other major US cities) and the formation of bus rapid transit and light rail, among other things, which was seen as a more affordable approach. It used the route placing and color designations from the 1989 ValTrans plan.
Construction on the new light rail line began in March 2005. In March 2008, cracks in the system's rails were discovered. The cause of the cracks was determined to be improper use of plasma cutting torches by contractors.[9] The affected track was repaired by May at a cost of $600,000 with still no word on which parties will be held financially responsible.[10] The last of the concrete and rail for the system was installed in the end of April, with the CEO declaring the system to be on time and on budget.[11]
.jpg.webp)
There are 28 stations on the initial twenty-mile (32 km) starter segment. The line celebrated its grand opening on December 27, 2008, with official ribbon-cutting ceremonies and community celebrations throughout Phoenix, Tempe, and Mesa. The event was produced by Arizona's Entertainment Solutions, Inc.[12] and was attended by thousands of local residents who waited as long as an hour or more to ride the vehicles.[13][14] The stations have been designed to complement their immediate surroundings.[15] Station platform areas are approximately 16 feet (4.9 m) wide by 300 feet (91 m) long.
As of early 2014, income has exceeded Metro's stated goal with 44.6% farebox recovery, partially due to the light rail ridership far exceeding original projections. The light rail has also led to rapid urban development in downtown Phoenix and Tempe, generating additional revenue through taxes.
Valley Metro had its busiest month in April 2017, with a total passenger count of 1,514,456 and an average weekday ridership of 52,910. On the weekend of March 31, 2017, through April 2, 2017, the light rail system saw 275,615 passengers board the train due to several large events including Final Four Fan Fest, March Madness Music Festival, Arizona Diamondbacks home opener, Phoenix Pride Festival, Phoenix Suns game, and Tempe Festival of the Arts. That Sunday, April 2, 2017, they saw 80,210 passengers board the train thanks to fans attending the Arizona Diamondbacks home opening game as well as the other large events occurring that weekend.[16]
Central Mesa Extension
The Central Mesa Extension extended rail service 3.1 miles (5.0 km) from the line's original eastern terminus at Sycamore Street in the median of Main Street to Mesa Drive.[17] It added four stations at Alma School Road, Country Club Drive, Center Street, and Mesa Drive. In March 2012, Valley Metro selected a design-build joint venture between Kiewit Corporation and Mass. Electric to construct the extension.[18] Construction began in July 2012 and passenger service began on August 22, 2015.[19] Mesa held a summit in early 2012 to have urban developers give their ideas on how to revitalize Downtown Mesa.[20] The extension cost $200 million, paid for from a combination of Proposition 400 sales tax revenues and federal air quality and New Starts grants, and is estimated to have added 5,000 daily riders.[17]
Northwest Extension Phase I

The system was extended north from the previous terminus at Montebello Avenue along the median of 19th Avenue to a new terminus and park and ride at the southwest corner of 19th Avenue and Dunlap Avenue in the City of Phoenix in 2016. The extension features 3.2 miles of track, three additional stations, and prior to opening was predicted to serve 5,000 riders per day in its first full year of operation.
As an original part of the Transit 2000 plan, this extension was originally scheduled to open by 2012.[21] However, a combination of lower than expected sales tax revenues, combined with uncertainty surrounding the availability of federal funds to support the project resulted in the opening date being pushed back initially to 2014, and then by 9 years, to fiscal year 2023, by the Phoenix City Council in June 2009.[22]
In July 2012, a vote was held to reschedule this extension to open in 2016. Under this plan, the city of Phoenix advanced $60 million of local funds to Valley Metro Rail, who would then fund the remaining cost of the project (approximately $267 million) with both Transit 2000 and Proposition 400 funds,[23] thereby allowing work on the project to begin.

The design-build contract was awarded to a joint venture of Sundt and Stacy and Witbeck, for the 3.2-mile (5.1 km) extension.[24] Construction began in January 2013,[25] with a celebration to mark the laying of the first track section being held in July 2014.[26] Construction work continued until December 2015, when it was announced that testing along the new stretch would begin.[27][28] The extension opened on March 19, 2016.
50th Street infill station
The 50th Street infill station project adds a new station to the existing alignment at 50th Street and Washington. The project aimed to enable better connectivity with nearby businesses, and recent commercial and residential development projects in the area.[29]
The project, funded entirely by the city of Phoenix, began construction in June 2017; service to the new station started on April 25, 2019.[30]
Gilbert Road Extension
An extension further eastward, 1.9 miles (3.1 km) past the terminus at Mesa Drive to Gilbert Road, began construction in October 2016,[31] and began operating on May 18, 2019.[32][33] The line, budgeted at approximately $184 million, travels in the median of Main Street and has one intermediate stop at Stapley Drive. The design-build contract for this project was awarded to Sundt/Stacy and Witbeck, with Jacobs Engineering providing design services for the project.[34][35] Service to the new stations started on May 18, 2019.
Tempe Streetcar

Tempe Streetcar consist of 14 stations, running from Dorsey Lane west on Apache Boulevard, then north on Mill Avenue.[36] From there, it loops around Downtown Tempe along Mill and Ash avenues.[37] The route continues along Rio Salado Parkway to Marina Heights, with a possible extension to Mesa to connect with the Chicago Cubs’ new spring training facility, as well as Tempe Marketplace.[38][39] Service began on May 20, 2022.[40]
Proposition 105 and South Extension
After voters approved a tax measure in August 2015 to fund transportation, the City of Phoenix moved the timeline of the light rail extension to South Phoenix up by a decade. Outreach to the residents and business owners of South Phoenix became strained when the extension called for the reduction of lanes from four to two along Central Avenue.[41] In February 2019, opponents were able to gather enough signatures to require the city to hold a referendum on future light rail expansion.[42] The referendum to stop light rail expansion, known as Proposition 105, failed to pass in a special election on August 27, 2019.[43] Construction on the South Central extension began in October 2019[44] and it is expected to be operational by 2024.[45]
Operations
Route description
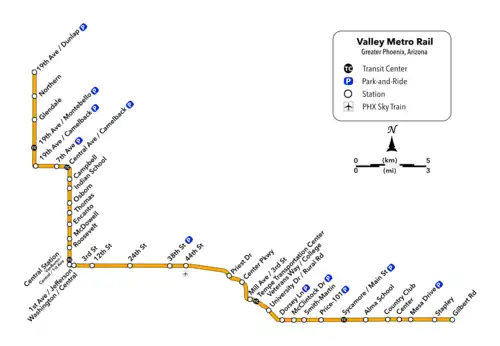
As of 2019, the Valley Metro Rail system consists of one single line serving all 38 stations total, and denoted with a gold-yellow color on Valley Metro publications.[46] The line starts in Phoenix at the 19th Avenue/Dunlap station on its own right-of-way south of Dunlap Avenue, before turning south on 19th Avenue for 4 miles (6.4 km). It then turns eastward on Camelback Road for 2.5 miles (4.0 km), then turns south onto Central Avenue where it continues all the way into Downtown Phoenix. At Roosevelt, the line splits into one-way segments: Mesa-bound service runs on First Avenue south before turning east on Jefferson Street; likewise, Dunlap-bound one-way service starts at 26th Street on Washington Street before turning north on Central Avenue.

After both tracks rejoin east of 24th Street on Washington Street, it continues past Sky Harbor Airport – which is connected by the PHX Sky Train at 44th Street/Washington – then turns southeast toward Tempe. The line leaves Washington Street and crosses Tempe Town Lake on its own bridge parallel to the Union Pacific Railroad before turning east along Mill Avenue (where the Tempe Streetcar connects at Mill Avenue/3rd St) and then proceeding via its own right-of-way near ASU. Going southward, it joins Apache Boulevard headed eastward, which becomes Main Street in the city of Mesa, where the light rail line ends at an intersection with Gilbert Road.

Hours and headways
Full service on the line begins Monday through Friday at approximately 4:30 a.m., while Saturday and Sunday service begins at approximately 4:50 a.m.[47] Service ends at approximately 1 a.m. Monday through Thursday nights, weekend service ends at 3:25 a.m. Friday and Saturday mornings, with Sunday service ending at approximately 12:30 a.m. Monday morning.[47]
Due to the fact a complete light rail trip takes approximately 90 minutes from end to end, trains departing at 11 p.m. for example end by 12:25 a.m. In the early morning and late night hours, limited service operates eastbound service from Priest Drive/Washington to Gilbert Road and westbound from 50th Street/Washington to Dunlap Avenue. This limited service extends the line's operating hours to as early as 3:30 a.m. all days, as late as 1:20 a.m. Sunday through Thursday, and as late as 4:20 a.m. on Friday and Saturday.[47] Every day, 1–4 eastbound PM rush hour trips short-turn at 44th Street/Washington and 1–4 westbound PM rush hour trips short-turn at Priest Drive/Washington.[47]
Weekday frequencies consist of every 12 minutes, Saturday daytime service every 15 minutes, and Sunday and evening service every 20 minutes.[47]
Rolling stock
As of 2020, Valley Metro Rail operates a fleet of 50 Kinki Sharyo Low Floor Light Rail Vehicles (LRVs), which were built exclusive to VMR. Each vehicle has a seated capacity of 66.[48] Due to the desert climate of the Phoenix area the units were designed with more insulation and solar reflective windows as well as larger air conditioner units.[49] The vehicles are accessible with space for four wheelchairs and four bicycles, per vehicle with addition to a hydraulic levelling system to remove potential vertical gap, to ease loading.[50] Up to three vehicles may operate together in a single train set but are typically in sets of two.[51] The vehicles have a maximum speed of 58 mph (93 km/h).[52] The LF-LRVs are also equipped with energy absorbent bumpers to reduce the effects of road vehicle collision, measures warranted due to the light rail mostly running in the center of streets.[53]
In 2017, Valley Metro contracted Brookville Equipment Corporation and Siemens Mobility for six and 11 light rail vehicles, respectively, with the Brookville fleet planned to be used for Tempe Streetcar service.[54] The first Siemens car arrived in March 2020[55] and the first Brookville car for Tempe in March 2021.[56]
| Manufacturer | Model | Quantity | Fleet numbers | Years in service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinki Sharyo | Low Floor Light Rail Vehicle[48] | 50 | 101–150 | 2008–present |
| Brookville | Liberty Streetcar[57] | 6[54] | 180–185 | 2022–present[58] |
| Siemens | S700[59][lower-alpha 1] | 25 (53 options)[54][61] | 201–225 | 2022–present[62] |
Fares
Valley Metro Rail shares its fare system with the Valley Metro Bus system, but uses a proof-of-payment system to allow for simplified boarding and platform access. Passes can be purchased from ticket vending machines at the entrance to all stations, or purchased in the Valley Metro App, but must be validated or scanned before boarding the train.[63] Passes can also be purchased on board buses, or in select retailers.
Fare inspections are conducted throughout the system at random to ensure compliance. As of 2015, the system has a fare-compliance rate of 94%.[64]
Future extensions and improvements
South Central Extension (2024)
The South Central Extension will run from Downtown Phoenix, south along Central Avenue to Baseline Road, adding 4.9 miles (7.9 km) and seven stations, while connecting with two park and ride locations.[65] Additionally, this project will form a light rail hub in Downtown Phoenix, between Central and First avenues to the west and east, and Washington and Jefferson streets to the north and south. Also included are new tracks for turn-around / staging purposes at both Third Avenue and Fifth Street for enhanced flexibility during peak service.[66] Trains along the segment are planned to operate as a new line, originating at Baseline Road and running to the Downtown Hub before interlining with the existing light rail system and continuing north to the terminus at Dunlap Avenue/19th Avenue.[67] Construction began in 2019, with completion expected in 2024.
Northwest Extension Phase II (2024)
Upon completion of Northwest Phase I, focus shifted to Phase II of the project. This extension will continue west on Dunlap Avenue before turning to head north along 25th Avenue. From there, the system will head west on Mountain View Road, before crossing Interstate 17 and terminating on the east side of Metrocenter Mall. The extension is expected to include three new stations, one in the vicinity of 25th Avenue and Dunlap, another adjacent to the Rose Mofford Sports Complex and a relocated transit center on the east side of Metrocenter Mall.[34]
By October 2017, the project had entered the environmental assessment (EA) phase.[68][69] The construction contract was awarded to Kiewit-McCarthy in July 2020 and was scheduled to break ground in the Fall.[70] Service is planned to begin on January 27, 2024.[71]
Capitol Extension (2027)
Capitol/I-10 West | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Capitol Extension will run from Central Station and 1st Avenue/Jefferson in Downtown Phoenix west to the Arizona State Capitol. As of 2023 the project team has begun the environmental assessment.[72][73]
I-10 West Extension (2030)
The I-10 West Extension would run from the state capitol west to Interstate 17 before turning north to the interchange of Interstate 10 and I-17 ("The Stack"). Then the line will turn west and continue down I-10 in the median past 43rd Avenue. It will then go over the westbound lanes of I-10 to continue alongside the highway to Desert Sky Mall, adding 11 miles (18 km) and 8 stations to connect the West Valley and ease congestion on Interstate 10. The line will transfer over I-10 from the median to the shoulder to accommodate Loop 202, which will connect with I-10 around 51st Avenue.[74][75] In fall 2021, the Phoenix City Council approved extending the project corridor to the Desert Sky Transit Center, adjacent to the Desert Sky Mall. As of 2023 preliminary engineering work is underway.[76][77]
West Phoenix

Starting in 2013, Valley Metro along with the cities of Glendale and Phoenix approved a project to study the potential extension of light rail, bus rapid transit or streetcar to Glendale. Initially, three different route options were proposed, all of which headed west from the current light rail system and featured a shared terminus in the Downtown Glendale area. Options included travel directly across Glendale Avenue, as well as routes that travel along Camelback Road and a combination of 43rd and 51st avenues, before entering the shared downtown terminus area.
In February 2016, a community working group recommend a route for this project, this route travels along Camelback Road until 43rd Avenue, at which point light rail would travel north along 43rd Avenue until Glendale Avenue, from there it would continue west until it reaches 56th Avenue, where the route is likely to shift approximately 500 feet (150 m) north to Glenn Drive, where it will continue to the downtown terminus. Light rail was selected as the preferred type of transit for the route, as opposed to bus rapid transit or streetcar.[78]
On October 17, 2017, Glendale City Council directed staff against moving forward on a route into downtown Glendale, effectively killing the plans for the Glendale portion of the extension.[79] At the beginning of 2019, Phoenix City Council voted to indefinitely delay the remaining Phoenix portion of the project.[80]
Starting in 2022, Valley Metro opened talks again about the West Phoenix Extension. The West Phoenix Extension will run from 91st Avenue and Thomas Road to 75th Avenue and Thomas then turn north to Indian School Road and connect to the Indian School Road and Central Avenue station. As of 2023 the project is in the locally preferred alternative adoption process. The West Phoenix Extension will also connect with the I-10 Extension on 79th Avenue and Thomas Road and the Phoenix BRT on 35th Avenue and Indian School Road.[81][82]
Other
As of 2019, an extension was planned to occur to Arizona State University's West campus in 2044.[34] A previous study into a Northeast light rail corridor has been suspended indefinitely, with Phoenix City Council directing funds towards street maintenance instead.[83]
As of 2019, extensions of streetcar and light rail in Tempe, Mesa, and Chandler were being studied.[84][85][86]
A northeast extension to Paradise Valley Mall, closely following Arizona State Route 51 is also being considered.[87]
See also
References
Informational notes
Citations
- ↑ "Transit Ridership Report Third Quarter 2023" (PDF). American Public Transportation Association. November 30, 2023. Retrieved December 6, 2023.
- ↑ "Transit Ridership Report Fourth Quarter 2022" (PDF). American Public Transportation Association. March 1, 2023. Retrieved March 29, 2023.
- 1 2 "Light rail to reach eastern end of the line with opening of Mesa extension". azcentral. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2019.
- ↑ "FAQs and Fast Facts" (pdf). – ValleyMetro.org. Archived December 17, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Coping with light-rail costs". archive.azcentral.com. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Rail – Timetable". March 19, 2016. Archived from the original on March 22, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Fast facts" (PDF). ValleyMetro.org. September 14, 2011. p. 6. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ↑ Phoenix Transit Elections. – Arizona Rail Passenger Association. Archived August 12, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Light-rail cracks: Who is at fault? Archived February 20, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. – Arizona Republic. – AZCentral.com.
- ↑ "30 light-rail sections fixed at cost of $600K" Archived February 20, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. – Arizona Republic. – AZCentral.com. – May 16, 2008.
- ↑ "Light-rail construction: The end is near?" Archived February 20, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. – Arizona Republic. – AZCentral.com. – April 29, 2008.
- ↑ "Entertainment Solutions Inc". Solutionsaz.com. Archived from the original on October 17, 2013. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- ↑ "Long waits greet riders along stops on light-rail lines". archive.azcentral.com. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved July 10, 2021.
- ↑ "Phoenix Light Rail Grand Opening 12/27/08 08:00 AM". Valley Metro. December 27, 2008. Archived from the original on February 9, 2009. Retrieved December 25, 2008.
- ↑ "Light Rail Station Design". Valley Metro. Archived from the original on December 17, 2007. Retrieved February 20, 2008.
- ↑ "Rail Weekend Ridership Up 79 Percent" (Press release). Valley Metro. April 3, 2017. Archived from the original on June 19, 2017. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- 1 2 "Central Mesa Light Rail Extension" (PDF). Valley Metro. December 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 18, 2015. Retrieved May 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Design-Build Contractor Selected for Central Mesa Extension" (Press release). Valley Metro. March 22, 2012. Archived from the original on May 18, 2015. Retrieved May 9, 2015.
- ↑ Mitchell, Garrett (August 22, 2015). "Mesa light rail expansion debuts to thousands of riders". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved August 25, 2015.
- ↑ Groff, Garin (February 16, 2012). "Downtown Mesa summit to tackle urban development along light rail – East Valley Tribune: Mesa". East Valley Tribune. Archived from the original on February 18, 2012. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- ↑ "Valley Metro – RTP Brochure" (PDF). p. 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 27, 2015. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Holstege, Sean (June 25, 2009). "Light-rail extension planned for 19th Ave. delayed until 2014". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Bui, Lynh (July 21, 2012). "Phoenix OKs plan to accelerate light-rail extension". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Sundt Construction-Stacy and Witbeck Joint Venture Chosen To Extend Valley Metro Light Rail Line". April 5, 2013. Archived from the original on April 3, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Sundt Partnership Breaks Ground on Phoenix Light Rail Project". January 15, 2013. Archived from the original on April 3, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Community Celebrates Progress of the Northwest Light Rail Extension". Archived from the original on April 1, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Northwest Extension Marks Arrival of Trains". Valley Metro. Archived from the original on April 1, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Goth, Brenna (December 10, 2015). "Northwest Phoenix light-rail extension to open in March". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Goth, Brenna (September 28, 2016). "New $23 million Phoenix light-rail station to serve riders with disabilities". AZCentral. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "50th Street Station (Fact Sheet, Q2 2017)" (PDF). Valley Metro Rail. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Groundbreaking ceremony for light rail extension to Gilbert Road". City of Mesa. October 15, 2016. Archived from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Gilbert Road Extension (Fact Sheet, Q3 2017)" (PDF). Valley Metro Rail. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 22, 2020. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Celebrate with us on May 18! Two more miles of light rail open in Mesa. | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. May 20, 2019. Archived from the original on May 13, 2019. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- 1 2 3 Goth, Brenna (February 9, 2016). "South Phoenix light rail on fast track, to come a decade early". Arizona Republic. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved February 15, 2016.
- ↑ "Gilbert Road Light Rail Extension" (PDF). Valley Metro. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 23, 2015. Retrieved June 5, 2015.
- ↑ "Tempe Streetcar" (PDF). Valley Metro. December 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 18, 2015. Retrieved May 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Valley Metro – Tempe Streetcar". Valley Metro. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ "South Bank – Mixed Use Urban Community Development – Tempe Town Lake, Tempe, AZ". Southbanktempe.com. Archived from the original on January 4, 2014. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- ↑ "Downtown Tempe – Hayden Ferry Lakeside". Haydenferry.com. Archived from the original on October 17, 2013. Retrieved October 17, 2013.
- ↑ "Streetcar is now open in Tempe" (Press release). Valley Metro. May 2022. Retrieved May 20, 2022.
- ↑ Estes, Christina; Goldstein, Steve; Gilger, Lauren (August 13, 2019). "Proposition 105: A Light Rail Fact Check For Phoenix Voters". KJZZ. Archived from the original on August 29, 2019. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
Christina Estes: Well, this started with some residents and business owners in south Phoenix who didn't want to see Central Avenue reduced from four lanes to two lanes to make room for light rail. It has since morphed into a full anti-light rail initiative. If voters approved Prop 105 it will stop the South Central extension as well as other future light rail projects.
- ↑ Boehm, Jessica (February 6, 2019). "Phoenix voters will decide future of light rail in August". Arizona Republic. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
- ↑ Goldstein, Steve; Brodie, Mark (August 28, 2019). "Phoenix Leaders React To Overwhelming Rejection Of Proposition 105, Proposition 106". KJZZ. Archived from the original on August 29, 2019. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
- ↑ "Construction Begins on South Central Extension Downtown Hub Light Rail Project". Mass Transit Mag. October 21, 2019. Archived from the original on October 22, 2019. Retrieved October 21, 2019.
- ↑ "South Central Extension/Downtown Hub". Valley Metro. November 22, 2019. Archived from the original on April 14, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2020.
- ↑ http://www.valleymetro.org/images/uploads/Valley_Metro_System_Map_April_2016.pdf Archived May 8, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Valley Metro System Map (April 2016)
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Valley Metro Rail" (PDF). Valley Metro. October 28, 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 29, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2020.
- 1 2 "Valley Metro Rail Low Floor Light Rail Vehicle Technical Data" (PDF). Kinki Sharyo. Retrieved November 28, 2022.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Rail Facts" (PDF). Valley Metro. August 19, 2021. p. 10. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Rail Facts" (PDF). Valley Metro. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- ↑ Holle, Gina. "Phoenix Light Rail: On Track" (PDF). Community Transportation Association of America. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 15, 2015. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Rail – Technical Data" (PDF). Kinkisharyo International. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Phoenix, AZ Valley Metro Rail (VMR)". Kinkisharyo. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved February 20, 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Valley Metro contracts with Siemens, Brookville for new rail fleet". Progressive Railroading. Archived from the original on December 3, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2020.
- ↑ Valley Metro (March 18, 2020). "Siemens rail car delivery". Facebook. Archived from the original on November 16, 2020. Retrieved November 16, 2020.
- ↑ "Brookville Delivers First of Six Off-Wire Capable Streetcars to Valley Metro". Metro Magazine. March 15, 2021. Archived from the original on April 10, 2021. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ↑ "Brookville catches $33M Tempe streetcar contract". Railway Age. June 19, 2017. Archived from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ West, Bryan (January 22, 2018). "Rails delivered to Tempe for 3-mile streetcar project". KPNX. Archived from the original on September 13, 2020. Retrieved July 6, 2018.
- ↑ "Siemens to build eleven light rail vehicles for Phoenix". Siemens AG. June 14, 2017. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Siemens rebadges North American low-floor cars". Tramways & Urban Transit. No. 993. UK: Mainspring Enterprises Ltd. September 2020. p. 336. ISSN 1460-8324.
- ↑ Clark, Douglas (October 6, 2020). "Valley Metro Regional Public Transportation Authority to expand light rail fleet in Phoenix, Arizona". Transportation Today. Archived from the original on October 14, 2020. Retrieved October 7, 2020.
- ↑ "Valley Metro adds new light rail transit to fleet". Yahoo News. January 11, 2022. Archived from the original on January 18, 2022. Retrieved January 16, 2022.
- ↑ "Proof of Payment – Valley Metro". Archived from the original on March 6, 2016. Retrieved February 22, 2016.
- ↑ "Valley Metro RMC Minutes (February 3, 2016)" (PDF). Valley Metro. pp. 198–199. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 2, 2016. Retrieved February 22, 2016.
- ↑ "South Central (Fact Sheet, Q2 2017)" (PDF). Valley Metro Rail. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Light Rail Hub Coming to Downtown Phoenix". City of Phoenix. September 27, 2017. Archived from the original on December 18, 2018. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "South Central Light Rail Expansion Environmental Assessment" (PDF). Valley Metro. Federal Transit Administration. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Rail Board Packet (September 2017)" (PDF). Valley Metro Rail. p. 85. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Northwest Phase II (Fact Sheet, Q2 2017)" (PDF). Valley Metro Rail. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Valley Metro awards Northwest Extension Phase II construction contract to Kiewit-McCarthy JV". Mass Transit Magazine. July 17, 2020. Archived from the original on July 19, 2020. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Opening date set for Valley Metro light rail extension to Metrocenter area in Phoenix". KTAR. December 21, 2023. Retrieved December 22, 2023.
- ↑ Goodman, Jessica (May 27, 2020). "City of Phoenix, Valley Metro want your input on Capitol and I-10 West Light Rail Extension". AZFamily. Archived from the original on July 9, 2021. Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- ↑ "Capitol Extension". www.valleymetro.org. Retrieved December 13, 2022.
- ↑ "Loop 202 South Mountain Freeway Project". Arizona DOT. Archived from the original on October 5, 2017. Retrieved October 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Capitol/I-10 West Fact Sheet" (PDF). Valley Metro. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved September 25, 2020.
- ↑ "I-10 West Extension". www.valleymetro.org. Retrieved December 13, 2022.
- ↑ Jensen, Audrey (April 27, 2023). "Phoenix proposes high-capacity transit through Maryvale to Loop 101 in the West Valley". Phoenix Business Journal. Retrieved July 10, 2023.
- ↑ Giblin, Paul (February 11, 2016). "Valley Metro picks preferred light-rail route through west Phoenix into downtown Glendale". The Arizona Republic. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved March 20, 2016.
- ↑ Vandell, Perry (October 23, 2017). "Glendale City Council kills plans for downtown light rail". azcentral. Archived from the original on February 20, 2022. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "West Phoenix Transit Corridor Study | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Valley Metro Launches West Phoenix Transit Alternatives Study". RT&S. March 7, 2023.
- ↑ "West Phoenix High-Capacity Transit Alternatives Analysis". Valley Metro. October 10, 2023.
- ↑ "Northeast | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Arizona Avenue Alternatives Analysis | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. May 9, 2018. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Fiesta District Alternatives Analysis | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. January 6, 2018. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Tempe/Mesa Streetcar Feasibility Study | Valley Metro". www.valleymetro.org. January 13, 2018. Archived from the original on August 5, 2019. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 30, 2020. Retrieved March 31, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
- Official website
- Article on Valley Metro Rail and preemptive urban revitalization
- Slideshow of photos on light rail construction and progress – from azcentral.com
- A BRIEF HISTORY OF PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION IN METRO PHOENIX
- South Phoenix light rail on fast track, to come a decade early
- Allhands: No, transit STILL doesn't go there | Phoenix
