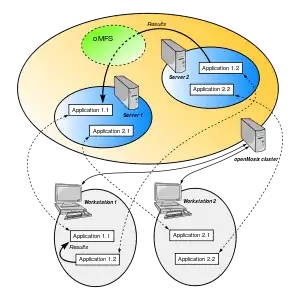
openMosix was a free cluster management system that provided single-system image (SSI) capabilities, e.g. automatic work distribution among nodes. It allowed program processes (not threads) to migrate to machines in the node's network that would be able to run that process faster (process migration). It was particularly useful for running parallel applications having low to moderate input/output (I/O).[1] It was released as a Linux kernel patch, but was also available on specialized Live CDs. openMosix development has been halted by its developers, but the LinuxPMI project is continuing development of the former openMosix code.
History
openMosix was originally forked from MOSIX by Moshe Bar on February 10, 2002 when MOSIX became proprietary software.
openMosix was considered stable on Linux kernel 2.4.x for the x86 architecture, but porting to Linux 2.6 kernel remained in the alpha stage. Support for the 64-bit AMD64 architecture only started with the 2.6 version.
On July 15, 2007, Bar announced that the openMOSIX project would reach its end of life on March 1, 2008, due to the decreasing need for single system image (SSI) clustering as low-cost multi-core processors increase in availability.[2]
OpenMosix used to be distributed as a Gentoo Linux kernel choice, but it was removed from Gentoo Linux's Portage tree in February 2007.[3]
As of March 1, 2008, openMosix read-only source code is still hosted at SourceForge.[4] The OpenPMIx project is continuing development of the former openMosix code.
ClusterKnoppix
| Developer | Wim Vandersmissen[5] |
|---|---|
| OS family | Linux distribution |
| Working state | discontinued |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | 10 May 2003 |
| Latest release | 3.6 / 1 September 2004[6] |
| Update method | APT (several front-ends available) |
| Package manager | dpkg |
| Platforms | i486 |
| Kernel type | Linux kernel |
| Userland | GNU Core Utilities |
| License | Debian Free Software Guidelines and others |
| Official website | openmosix |
ClusterKnoppix is a specialized Linux distribution based on the Knoppix distribution, but which uses the openMosix kernel.
Traditionally, clustered computing could only be achieved by setting up individual rsh keys, creating NFS shares, editing host files, setting static IPs, and applying kernel patches manually. ClusterKnoppix effectively renders most of this work unnecessary. The distribution contains an autoconfiguration system where new ClusterKnoppix-running computers attached to the network automatically join the cluster.
ClusterKnoppix is a modified Knoppix distro using the OpenMosix kernel.
See also
Live CDs
Linux Live CDs with openMosix include:
- CHAOS (a very small boot CD)
- dyne:bolic
- Quantian, a scientific distribution based on clusterKnoppix
References
- ↑ "About MOSIX". Retrieved 2017-07-20.
- ↑ Knox, Bruce (2007-07-15). "openMosix Project End of Life Announcement". SourceForge.net. Archived from the original on 2009-08-09. Retrieved 2017-07-20.
- ↑ Gianelloni, Chris; Kowarsky, Mark; Berkholz, Donnie; Black, Daniel; Pettenò, Diego Elio; Gable, Keith (2007-02-19). "Gentoo package moves". Gentoo Weekly Newsletter. Gentoo Foundation, Inc. Archived from the original on 2014-12-25. Retrieved 2017-07-20.
- ↑ "the openMosix Project". 2008-03-01. Retrieved 2008-03-01.
- ↑ "ClusterKnoppix". Slashdot. 2003-05-29.
- ↑ "clusterKNOPPIX". DistroWatch. 2017-08-26. Retrieved 2018-01-07.
External links
- Official website
- openMosixWiki
- Original page at wayback archive
- ClusterKnoppix at sourceforge.net
- Clusterknoppix at distrowatch
- Load-Balancing cluster HowTo using ClusterKnoppix
- http://ftp.fi.muni.cz/pub/linux/clusterKnoppix/
- http://ftp.linux.cz/pub/linux/clusterKnoppix/
- OpenPMIx