Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Classical Music Portal

Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated notational system, as well as accompanying literature in analytical, critical, historiographical, musicological and philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or groups of composers, whose compositions, personalities and beliefs have fundamentally shaped its history. (Full article...)
Selected articles -
 Image 1
Image 1_by_Elliot_and_Fry_-_02.jpg.webp) Edvard Grieg, in a photograph taken in 1888, by Elliott & Fry
Edvard Grieg, in a photograph taken in 1888, by Elliott & Fry
Peer Gynt, Op. 23, is the incidental music to Henrik Ibsen's 1867 play of the same name, written by the Norwegian composer Edvard Grieg in 1875. It premiered along with the play on 24 February 1876 in Christiania (now Oslo).
Grieg later created two suites from his Peer Gynt music. Some of the music from these suites has received coverage in popular culture. (Full article...) Image 2
Image 2 Mendelssohn in 1846 by Eduard Magnus
Mendelssohn in 1846 by Eduard Magnus
Felix Mendelssohn's Violin Concerto in E minor, Op. 64, MWV O 14, is his last concerto. Well received at its premiere, it has remained among the most prominent and highly-regarded violin concertos. It holds a central place in the violin repertoire and has developed a reputation as an essential concerto for all aspiring concert violinists to master, and usually one of the first Romantic era concertos they learn. A typical performance lasts just under half an hour.
Mendelssohn originally proposed the idea of the violin concerto to Ferdinand David, a close friend and then concertmaster of the Leipzig Gewandhaus Orchestra. Although conceived in 1838, the work took another six years to complete and was not premiered until 1845. During this time, Mendelssohn maintained a regular correspondence with David, who gave him many suggestions. The work itself was one of the foremost violin concertos of the Romantic era and was influential on many other composers. (Full article...) Image 3
Image 3.jpg.webp) Martha Graham, c. 1940
Martha Graham, c. 1940
Appalachian Spring is a ballet created by the American composer Aaron Copland and the choreographer Martha Graham, later arranged as an orchestral work. Commissioned by Elizabeth Sprague Coolidge, Copland composed the ballet for Graham; the original choreography was by Graham, with costumes by Edythe Gilfond and sets by Isamu Noguchi. The music was well-received at the 1944 premiere, earning Copland the Pulitzer Prize for Music after the ballet's 1945 United States tour. The orchestral suite composed in 1945 was played that year by many symphony orchestras; the suite is among Copland's best-known works, and the ballet remains essential in the Martha Graham Dance Company repertoire.
Graham was known for creating the "Graham technique" of dance; in the 1930s, she began commissioning scores from various composers, often related to American history and culture. Around the same time, Copland incorporated relatable and accessible musical characteristics of the Americana style to increase his music's appeal to the general public; he first implemented this in earlier ballets like Billy the Kid and Rodeo. The initial scenario for Appalachian Spring devised by Graham was revised many times by both her and Copland; the title characters' names were changed numerous times and other characters from the early revisions were cut in the final production. Originally orchestrated for a thirteen-piece chamber orchestra, the score was arranged into various suites by Copland for different purposes; the original ballet featured eight episodes, three of which were cut in the well-known orchestral suite. (Full article...)![Image 4Original 1904 poster by Adolfo HohensteinMadama Butterfly (Italian pronunciation: [maˈdaːma ˈbatterflai]; Madame Butterfly) is an opera in three acts (originally two) by Giacomo Puccini, with an Italian libretto by Luigi Illica and Giuseppe Giacosa.It is based on the short story "Madame Butterfly" (1898) by John Luther Long, which in turn was based on stories told to Long by his sister Jennie Correll and on the semi-autobiographical 1887 French novel Madame Chrysanthème by Pierre Loti. Long's version was dramatized by David Belasco as the one-act play Madame Butterfly: A Tragedy of Japan, which, after premiering in New York in 1900, moved to London, where Puccini saw it in the summer of that year. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 4
Image 4 Original 1904 poster by Adolfo Hohenstein
Original 1904 poster by Adolfo Hohenstein
Madama Butterfly (Italian pronunciation: [maˈdaːma ˈbatterflai]; Madame Butterfly) is an opera in three acts (originally two) by Giacomo Puccini, with an Italian libretto by Luigi Illica and Giuseppe Giacosa.
It is based on the short story "Madame Butterfly" (1898) by John Luther Long, which in turn was based on stories told to Long by his sister Jennie Correll and on the semi-autobiographical 1887 French novel Madame Chrysanthème by Pierre Loti. Long's version was dramatized by David Belasco as the one-act play Madame Butterfly: A Tragedy of Japan, which, after premiering in New York in 1900, moved to London, where Puccini saw it in the summer of that year. (Full article...)![Image 5Anton Bruckner wearing the badge of the Order of Franz Joseph (portrait by Josef Büche [de])Josef Anton Bruckner (German: [ˈantoːn ˈbʁʊknɐ] ⓘ; 4 September 1824 – 11 October 1896) was an Austrian composer and organist best known for his symphonies and sacred music, which includes Masses, Te Deum and motets. The symphonies are considered emblematic of the final stage of Austro-German Romanticism because of their rich harmonic language, strongly polyphonic character, and considerable length. Bruckner's compositions helped to define contemporary musical radicalism, owing to their dissonances, unprepared modulations, and roving harmonies.Unlike other musical radicals such as Richard Wagner and Hugo Wolf, Bruckner showed extreme humility before other musicians, Wagner in particular. This apparent dichotomy between Bruckner the man and Bruckner the composer hampers efforts to describe his life in a way that gives a straightforward context for his music. Hans von Bülow described him as "half genius, half simpleton". Bruckner was critical of his own work and often reworked his compositions. There are several versions of many of his works. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 5
Image 5 Anton Bruckner wearing the badge of the Order of Franz Joseph (portrait by Josef Büche)
Anton Bruckner wearing the badge of the Order of Franz Joseph (portrait by Josef Büche)
Josef Anton Bruckner (German: [ˈantoːn ˈbʁʊknɐ] ⓘ; 4 September 1824 – 11 October 1896) was an Austrian composer and organist best known for his symphonies and sacred music, which includes Masses, Te Deum and motets. The symphonies are considered emblematic of the final stage of Austro-German Romanticism because of their rich harmonic language, strongly polyphonic character, and considerable length. Bruckner's compositions helped to define contemporary musical radicalism, owing to their dissonances, unprepared modulations, and roving harmonies.
Unlike other musical radicals such as Richard Wagner and Hugo Wolf, Bruckner showed extreme humility before other musicians, Wagner in particular. This apparent dichotomy between Bruckner the man and Bruckner the composer hampers efforts to describe his life in a way that gives a straightforward context for his music. Hans von Bülow described him as "half genius, half simpleton". Bruckner was critical of his own work and often reworked his compositions. There are several versions of many of his works. (Full article...) Image 6
Image 6 Antonio Vivaldi (engraving by François Morellon de La Cave, from Michel-Charles Le Cène's edition of Vivaldi's Op. 8, 1725)
Antonio Vivaldi (engraving by François Morellon de La Cave, from Michel-Charles Le Cène's edition of Vivaldi's Op. 8, 1725)
The Four Seasons (Italian: Le quattro stagioni) is a group of four violin concerti by Italian composer Antonio Vivaldi, each of which gives musical expression to a season of the year. These were composed around 1718−1720, when Vivaldi was the court chapel master in Mantua. They were published in 1725 in Amsterdam, together with eight additional concerti, as Il cimento dell'armonia e dell'inventione (The Contest Between Harmony and Invention).
The Four Seasons is the best known of Vivaldi's works. Though three of the concerti are wholly original, the first, "Spring", borrows patterns from a sinfonia in the first act of Vivaldi's contemporaneous opera Il Giustino. The inspiration for the concertos is not the countryside around Mantua, as initially supposed, where Vivaldi was living at the time, since according to Karl Heller they could have been written as early as 1716–1717, while Vivaldi was engaged with the court of Mantua only in 1718. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7
The violin, sometimes known as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone (string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular use. The violin typically has four strings (some can have five), usually tuned in perfect fifths with notes G3, D4, A4, E5, and is most commonly played by drawing a bow across its strings. It can also be played by plucking the strings with the fingers (pizzicato) and, in specialized cases, by striking the strings with the wooden side of the bow (col legno).
Violins are important instruments in a wide variety of musical genres. They are most prominent in the Western classical tradition, both in ensembles (from chamber music to orchestras) and as solo instruments. Violins are also important in many varieties of folk music, including country music, bluegrass music, and in jazz. Electric violins with solid bodies and piezoelectric pickups are used in some forms of rock music and jazz fusion, with the pickups plugged into instrument amplifiers and speakers to produce sound. The violin has come to be incorporated in many non-Western music cultures, including Indian music and Iranian music. The name fiddle is often used regardless of the type of music played on it. (Full article...)![Image 8Otello and Desdemonaby Alexandre-Marie Colin, 1829Otello (Italian pronunciation: [oˈtɛllo]) is an opera in four acts by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Arrigo Boito, based on Shakespeare's play Othello. It was Verdi's penultimate opera, first performed at the Teatro alla Scala, Milan, on 5 February 1887.The composer was reluctant to write anything new after the success of Aida in 1871, and he retreated into retirement. It took his Milan publisher Giulio Ricordi the next ten years, first to encourage the revision of Verdi's 1857 Simon Boccanegra by introducing Boito as librettist and then to begin the arduous process of persuading and cajoling Verdi to see Boito's completed libretto for Otello in July/August 1881. However, the process of writing the first drafts of the libretto and the years of their revision, with Verdi all along not promising anything, dragged on. It wasn't until 1884, five years after the first drafts of the libretto, that composition began, with most of the work finishing in late 1885. When it finally premiered in Milan on 5 February 1887, it proved to be a resounding success, and further stagings of Otello soon followed at leading theatres throughout Europe and America. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 8
Image 8 Otello and Desdemona
Otello and Desdemona
by Alexandre-Marie Colin, 1829
Otello (Italian pronunciation: [oˈtɛllo]) is an opera in four acts by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Arrigo Boito, based on Shakespeare's play Othello. It was Verdi's penultimate opera, first performed at the Teatro alla Scala, Milan, on 5 February 1887.
The composer was reluctant to write anything new after the success of Aida in 1871, and he retreated into retirement. It took his Milan publisher Giulio Ricordi the next ten years, first to encourage the revision of Verdi's 1857 Simon Boccanegra by introducing Boito as librettist and then to begin the arduous process of persuading and cajoling Verdi to see Boito's completed libretto for Otello in July/August 1881. However, the process of writing the first drafts of the libretto and the years of their revision, with Verdi all along not promising anything, dragged on. It wasn't until 1884, five years after the first drafts of the libretto, that composition began, with most of the work finishing in late 1885. When it finally premiered in Milan on 5 February 1887, it proved to be a resounding success, and further stagings of Otello soon followed at leading theatres throughout Europe and America. (Full article...) Image 9
Image 9 1820 portrait
1820 portrait
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 1770 – 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire and span the transition from the Classical period to the Romantic era in classical music. Beethoven's career has conventionally been divided into early, middle, and late periods. His early period, during which he forged his craft, is typically considered to have lasted until 1802. From 1802 to around 1812, his middle period showed an individual development from the styles of Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and is sometimes characterized as heroic. During this time, he began to grow increasingly deaf. In his late period, from 1812 to 1827, he extended his innovations in musical form and expression.
Born in Bonn, Beethoven displayed his musical talent at a young age. He was initially taught intensively by his father, Johann van Beethoven, and later by Christian Gottlob Neefe. Under Neefe's tutelage in 1783, he published his first work, a set of keyboard variations. He found relief from a dysfunctional home life with the family of Helene von Breuning, whose children he loved, befriended, and taught piano. At age 21, he moved to Vienna, which subsequently became his base, and studied composition with Haydn. Beethoven then gained a reputation as a virtuoso pianist, and was soon patronised by Karl Alois, Prince Lichnowsky for compositions, which resulted in his three Opus 1 piano trios (the earliest works to which he accorded an opus number) in 1795. (Full article...) Image 10
Image 10
An orchestra (/ˈɔːrkɪstrə/; OR-ki-strə) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:- bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass
- woodwinds, such as the flute, oboe, clarinet, and bassoon (occasional saxophone)
- brass instruments, such as the horn, trumpet, trombone, cornet, euphonium, and tuba
- percussion instruments, such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, triangle, tambourine, tam-tam and mallet percussion instruments
Other instruments such as the piano, harpsichord, and celesta may sometimes appear in a fifth keyboard section or may stand alone as soloist instruments, as may the concert harp and, for performances of some modern compositions, electronic instruments, and guitars. (Full article...) Image 11
Image 11 Performance on period instruments is a key aspect of HIP, such as this baroque orchestra (Photo: Josetxu Obregón and the Spanish ensemble La Ritirata, 2013).
Performance on period instruments is a key aspect of HIP, such as this baroque orchestra (Photo: Josetxu Obregón and the Spanish ensemble La Ritirata, 2013).
Historically informed performance (also referred to as period performance, authentic performance, or HIP) is an approach to the performance of classical music, which aims to be faithful to the approach, manner and style of the musical era in which a work was originally conceived.
It is based on two key aspects: the application of the stylistic and technical aspects of performance, known as performance practice; and the use of period instruments which may be reproductions of historical instruments that were in use at the time of the original composition, and which usually have different timbre and temperament from their modern equivalents. A further area of study, that of changing listener expectations, is increasingly under investigation. (Full article...) Image 12
Image 12 Davies in 2012
Davies in 2012
Sir Peter Maxwell Davies CH CBE (8 September 1934 – 14 March 2016) was an English composer and conductor, who in 2004 was made Master of the Queen's Music.
As a student at both the University of Manchester and the Royal Manchester College of Music, Davies formed a group dedicated to contemporary music called the New Music Manchester with fellow students Harrison Birtwistle, Alexander Goehr, Elgar Howarth and John Ogdon. Davies's compositions include eight works for the stage—from the monodrama Eight Songs for a Mad King, which shocked the audience in 1969, to Kommilitonen!, first performed in 2011—and ten symphonies, written between 1973 and 2013. (Full article...)
General images -

 Image 2Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes. (from Baroque music)
Image 2Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes. (from Baroque music) Image 3Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music))
Image 3Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music)) Image 4Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music)
Image 4Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music) Image 5Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music)
Image 5Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music) Image 6A group of Renaissance musicians in The Concert (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst (from Renaissance music)
Image 6A group of Renaissance musicians in The Concert (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst (from Renaissance music) Image 7Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music))
Image 7Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music)) Image 81875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music))
Image 81875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music)) Image 9Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music)
Image 9Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music) Image 10Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)
Image 10Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)

 Image 13A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music)
Image 13A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music) Image 14Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music)
Image 14Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music) Image 15A young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))
Image 15A young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))

 Image 18Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))
Image 18Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))

.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp) Image 22Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music)
Image 22Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music) Image 23Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music))
Image 23Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music)) Image 24Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music)
Image 24Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music) Image 25The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music))
Image 25The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music)) Image 26A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music))
Image 26A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music)) Image 27Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music))
Image 27Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music)) Image 28The Mozart family c. 1780. The portrait on the wall is of Mozart's mother. (from Classical period (music))
Image 28The Mozart family c. 1780. The portrait on the wall is of Mozart's mother. (from Classical period (music))
Quotes -
| “ | Music is enough for a life — but a life is too short for music. | ” |
| — Richard Strauss | ||
Related portals
WikiProjects
| WikiProject Classical music | WikiProject Composers | WikiProject Contemporary music |
|---|---|---|
| WikiProject Opera | WikiProject Richard Wagner | WikiProject Gilbert and Sullivan |
 Selected composers -
Selected composers - 
 Image 1
Image 1 Leo Ornstein as a young man, c. 1918
Leo Ornstein as a young man, c. 1918
Leo Ornstein (born Лев Орнштейн, Lev Ornshteyn; c. December 11, 1895 – February 24, 2002) was an American experimental composer and pianist of the early twentieth century. His performances of works by avant-garde composers and his own innovative and even shocking pieces made him a cause célèbre on both sides of the Atlantic. The bulk of his experimental works were written for piano.
Ornstein was the first important composer to make extensive use of the tone cluster. As a pianist, he was considered a world-class talent. By the mid-1920s, he had walked away from his fame and soon disappeared from popular memory. Though he gave his last public concert before the age of forty, he continued writing music for another half-century and beyond. Largely forgotten for decades, he was rediscovered in the mid-1970s. Ornstein completed his eighth and final piano sonata in September 1990 at the age of ninety-four, making him the oldest published composer in history at the time (a mark since passed by Elliott Carter). (Full article...) Image 2Yasunori Mitsuda (光田 康典, Mitsuda Yasunori, born January 21, 1972) is a Japanese composer and musician. He is best known for his work in video games, primarily for the Chrono, Xeno, Shadow Hearts, and Inazuma Eleven franchises, among various others. Mitsuda began composing music for his own games in high school, later attending a music college in Tokyo. While still a student, he was granted an intern position at the game development studio Wolf Team.
Image 2Yasunori Mitsuda (光田 康典, Mitsuda Yasunori, born January 21, 1972) is a Japanese composer and musician. He is best known for his work in video games, primarily for the Chrono, Xeno, Shadow Hearts, and Inazuma Eleven franchises, among various others. Mitsuda began composing music for his own games in high school, later attending a music college in Tokyo. While still a student, he was granted an intern position at the game development studio Wolf Team..jpg.webp) Mitsuda in 2019
Mitsuda in 2019
Mitsuda joined Square upon graduation in 1992 and worked there as a sound effects designer for two years before telling Square's vice president Hironobu Sakaguchi he would quit unless he could write music for their games. Shortly after, Sakaguchi assigned him to work on the soundtrack for Chrono Trigger (1995), whose music has since been cited as among the best in video games. (Full article...)![Image 3Frederik Magle conducting on 20 September 2011, in the DRs Koncerthuset.Frederik Reesen Magle (Danish pronunciation: [ˈfʁeðˀʁek ˈmɑwlə]; born 17 April 1977) is a Danish composer, concert organist, and pianist. He writes contemporary classical music as well as fusion of classical music and other genres. His compositions include orchestral works, cantatas, chamber music, and solo works (mainly for organ), including several compositions commissioned by the Danish royal family. Magle has gained a reputation as an organ virtuoso, and as a composer and performing artist who does not refrain from venturing into more experimental projects – often with improvisation – bordering jazz, electronica, and other non-classical genres.His best-known works include his concerto for organ and orchestra The Infinite Second, his brass quintet piece Lys på din vej (Light on your path), composed for the christening of Prince Nikolai, The Hope for brass band and choir, his symphonic suite Cantabile, a collection of improvisations for organ titled Like a Flame, and his fanfare for two trumpets and organ The Fairest of Roses. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 3
Image 3.jpg.webp) Frederik Magle conducting on 20 September 2011, in the DRs Koncerthuset.
Frederik Magle conducting on 20 September 2011, in the DRs Koncerthuset.
Frederik Reesen Magle (Danish pronunciation: [ˈfʁeðˀʁek ˈmɑwlə]; born 17 April 1977) is a Danish composer, concert organist, and pianist. He writes contemporary classical music as well as fusion of classical music and other genres. His compositions include orchestral works, cantatas, chamber music, and solo works (mainly for organ), including several compositions commissioned by the Danish royal family. Magle has gained a reputation as an organ virtuoso, and as a composer and performing artist who does not refrain from venturing into more experimental projects – often with improvisation – bordering jazz, electronica, and other non-classical genres.
His best-known works include his concerto for organ and orchestra The Infinite Second, his brass quintet piece Lys på din vej (Light on your path), composed for the christening of Prince Nikolai, The Hope for brass band and choir, his symphonic suite Cantabile, a collection of improvisations for organ titled Like a Flame, and his fanfare for two trumpets and organ The Fairest of Roses. (Full article...) Image 4Nobuo Uematsu (植松 伸夫, Uematsu Nobuo, born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese composer and keyboardist best known for his contributions to the Final Fantasy video game series by Square Enix. A self-taught musician, he began playing the piano at the age of twelve, with English singer-songwriter Elton John as one of his biggest influences.
Image 4Nobuo Uematsu (植松 伸夫, Uematsu Nobuo, born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese composer and keyboardist best known for his contributions to the Final Fantasy video game series by Square Enix. A self-taught musician, he began playing the piano at the age of twelve, with English singer-songwriter Elton John as one of his biggest influences. Uematsu in 2011
Uematsu in 2011
Uematsu joined Square in 1986, where he first met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. The two later worked together on many games at the company, most notably in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly two decades with Square, Uematsu left in 2004 to create his own production company and music label, Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for other games, including ones developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's development studio, Mistwalker. (Full article...) Image 5
Image 5
Percy Aldridge Grainger (born George Percy Grainger; 8 July 1882 – 20 February 1961) was an Australian-born composer, arranger and pianist who moved to the United States in 1914 and became an American citizen in 1918. In the course of a long and innovative career he played a prominent role in the revival of interest in British folk music in the early years of the 20th century. Although much of his work was experimental and unusual, the piece with which he is most generally associated is his piano arrangement of the folk-dance tune "Country Gardens".
Grainger left Australia at the age of 13 to attend the Hoch Conservatory in Frankfurt. Between 1901 and 1914 he was based in London, where he established himself first as a society pianist and later as a concert performer, composer, and collector of original folk melodies. As his reputation grew he met many of the significant figures in European music, forming important friendships with Frederick Delius and Edvard Grieg. He became a champion of Nordic music and culture, his enthusiasm for which he often expressed in private letters, sometimes in crudely racial or anti-Semitic terms. (Full article...)![Image 6Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna HofoperGustav Mahler (German: [ˈɡʊstaf ˈmaːlɐ]; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism of the early 20th century. While in his lifetime his status as a conductor was established beyond question, his own music gained wide popularity only after periods of relative neglect, which included a ban on its performance in much of Europe during the Nazi era. After 1945 his compositions were rediscovered by a new generation of listeners; Mahler has since become one of the most frequently performed and recorded of all composers.Born in Bohemia (then part of the Austrian Empire) to Jewish parents of humble origins, the German-speaking Mahler displayed his musical gifts at an early age. After graduating from the Vienna Conservatory in 1878, he held a succession of conducting posts of rising importance in the opera houses of Europe, culminating in his appointment in 1897 as director of the Vienna Court Opera (Hofoper). During his ten years in Vienna, Mahler—who had converted to Catholicism to secure the post—experienced regular opposition and hostility from the anti-Semitic press. Nevertheless, his innovative productions and insistence on the highest performance standards ensured his reputation as one of the greatest of opera conductors, particularly as an interpreter of the stage works of Wagner, Mozart, and Tchaikovsky. Late in his life he was briefly director of New York's Metropolitan Opera and the New York Philharmonic. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 6
Image 6 Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper
Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper
Gustav Mahler (German: [ˈɡʊstaf ˈmaːlɐ]; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism of the early 20th century. While in his lifetime his status as a conductor was established beyond question, his own music gained wide popularity only after periods of relative neglect, which included a ban on its performance in much of Europe during the Nazi era. After 1945 his compositions were rediscovered by a new generation of listeners; Mahler has since become one of the most frequently performed and recorded of all composers.
Born in Bohemia (then part of the Austrian Empire) to Jewish parents of humble origins, the German-speaking Mahler displayed his musical gifts at an early age. After graduating from the Vienna Conservatory in 1878, he held a succession of conducting posts of rising importance in the opera houses of Europe, culminating in his appointment in 1897 as director of the Vienna Court Opera (Hofoper). During his ten years in Vienna, Mahler—who had converted to Catholicism to secure the post—experienced regular opposition and hostility from the anti-Semitic press. Nevertheless, his innovative productions and insistence on the highest performance standards ensured his reputation as one of the greatest of opera conductors, particularly as an interpreter of the stage works of Wagner, Mozart, and Tchaikovsky. Late in his life he was briefly director of New York's Metropolitan Opera and the New York Philharmonic. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7 Wall at a Video Games Live event in 2009
Wall at a Video Games Live event in 2009
Jack Wall (born 1964) is an American video game music composer. He has worked on video game music for over 20 games including the Myst franchise, Splinter Cell, Jade Empire, Mass Effect, and Call of Duty. Wall earned a degree in civil engineering from Drexel University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and, after a brief stint working in civil engineering, transitioned into music production. He worked with musicians such as John Cale, David Byrne, and Patti Smith, and, after performing increasingly complex production and sound engineering tasks, moved into music composition in 1995.
Wall immediately began working in the video game industry, composing the soundtrack to Vigilance. Primarily composing in an orchestral style, by 2001 he composed the soundtrack to Myst III: Exile, which was the title he says put him on the map as a video game composer. In 2002, Wall became one of around 20 co-founders of the Game Audio Network Guild (G.A.N.G.) as well as senior director. In 2005, Wall, along with G.A.N.G. founder and fellow composer Tommy Tallarico, produced the Video Games Live concert series, having served as the conductor for the international concert tour. His latest released soundtrack is that of 2020's Black Ops Cold War. His soundtracks for Myst III: Exile, Myst IV: Revelation, Rise of the Kasai, Jade Empire, Mass Effect, and Mass Effect 2 were nominated for and won multiple awards. (Full article...) Image 8
Image 8 Fanny Hensel, 1842, by Moritz Daniel Oppenheim
Fanny Hensel, 1842, by Moritz Daniel Oppenheim
Fanny Mendelssohn (14 November 1805 – 14 May 1847) was a German composer and pianist of the early Romantic era who was known as Fanny Hensel after her marriage. Her compositions include a piano trio, a piano quartet, an orchestral overture, four cantatas, more than 125 pieces for the piano and over 250 lieder, most of which were unpublished in her lifetime. Although lauded for her piano technique, she rarely gave public performances outside her family circle.
She grew up in Berlin and received a thorough musical education from teachers including her mother, as well as the composers Ludwig Berger and Carl Friedrich Zelter. Her younger brother Felix Mendelssohn, also a composer and pianist, shared the same education and the two developed a close relationship. Owing to her family's reservations and to social conventions of the time about the roles of women, six of her songs were published under her brother's name in his Opus 8 and 9 collections. In 1829, she married artist Wilhelm Hensel and, in 1830, they had their only child, Sebastian Hensel. In 1846, despite the continuing ambivalence of her family towards her musical ambitions, Fanny Hensel published a collection of songs as her Opus 1. She died of a stroke in 1847, aged 41. (Full article...) Image 9
Image 9 A 1611 woodcut of Josquin des Prez, possibly copied from a now-lost oil painting made during his lifetime. There have been doubts concerning whether this depiction is an accurate likeness, see § Portraits.
A 1611 woodcut of Josquin des Prez, possibly copied from a now-lost oil painting made during his lifetime. There have been doubts concerning whether this depiction is an accurate likeness, see § Portraits.
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez (c. 1450–1455 – 27 August 1521) was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a central figure of the Franco-Flemish School and had a profound influence on the music of 16th-century Europe. Building on the work of his predecessors Guillaume Du Fay and Johannes Ockeghem, he developed a complex style of expressive—and often imitative—movement between independent voices (polyphony) which informs much of his work. He further emphasized the relationship between text and music, and departed from the early Renaissance tendency towards lengthy melismatic lines on a single syllable, preferring to use shorter, repeated motifs between voices. Josquin was a singer, and his compositions are mainly vocal. They include masses, motets and secular chansons.
Josquin's biography has been continually revised by modern scholarship, and remains highly uncertain. Little is known of his early years; he was born in the French-speaking area of Flanders, and he may have been an altar boy and have been educated at the Cambrai Cathedral, or taught by Ockeghem. By 1477 he was in the choir of René of Anjou and then probably served under Louis XI of France. Now a wealthy man, in the 1480s Josquin traveled Italy with the Cardinal Ascanio Sforza, may have worked in Vienna for the Hungarian king Matthias Corvinus, and wrote the motet Ave Maria ... Virgo serena, and the popular chansons Adieu mes amours and Que vous ma dame. He served Pope Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI in Rome, Louis XII in France, and Ercole I d'Este in Ferrara. Many of his works were published by Ottaviano Petrucci in the early 16th century, including the Missa Hercules Dux Ferrariae. In his final years in Condé, Josquin produced some of his most admired works, including the masses Missa de Beata Virgine and Missa Pange lingua; the motets Benedicta es, Inviolata, Pater noster–Ave Maria and Praeter rerum seriem; and the chansons Mille regretz, Nimphes, nappés and Plus nulz regretz. (Full article...) Image 10Alan Dudley Bush (22 December 1900 – 31 October 1995) was a British composer, pianist, conductor, teacher and political activist. A committed communist, his uncompromising political beliefs were often reflected in his music. He composed prolifically across a range of genres, but struggled through his lifetime for recognition from the British musical establishment, which largely ignored his works.
Image 10Alan Dudley Bush (22 December 1900 – 31 October 1995) was a British composer, pianist, conductor, teacher and political activist. A committed communist, his uncompromising political beliefs were often reflected in his music. He composed prolifically across a range of genres, but struggled through his lifetime for recognition from the British musical establishment, which largely ignored his works.
Bush, from a prosperous middle-class background, enjoyed considerable success as a student at the Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in the early 1920s, and spent much of that decade furthering his compositional and piano-playing skills under distinguished tutors. A two-year period in Berlin in 1929 to 1931, early in the Nazi Party's rise to power, cemented Bush's political convictions and moved him from the mainstream Labour Party to the Communist Party of Great Britain which he joined in 1935. He wrote several large-scale works in the 1930s, and was heavily involved with workers' choirs for whom he composed pageants, choruses and songs. His pro-Soviet stance led to a temporary ban on his music by the BBC in the early years of the Second World War, and his refusal to modify his position in the postwar Cold War era led to a more prolonged semi-ostracism of his music. As a result, the four major operas he wrote between 1950 and 1970 were all premiered in East Germany. (Full article...) Image 11
Image 11 Rossini as a young man, c. 1810–1815
Rossini as a young man, c. 1810–1815
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards for both comic and serious opera before retiring from large-scale composition while still in his thirties, at the height of his popularity.
Born in Pesaro to parents who were both musicians (his father a trumpeter, his mother a singer), Rossini began to compose by the age of twelve and was educated at music school in Bologna. His first opera was performed in Venice in 1810 when he was 18 years old. In 1815 he was engaged to write operas and manage theatres in Naples. In the period 1810–1823, he wrote 34 operas for the Italian stage that were performed in Venice, Milan, Ferrara, Naples and elsewhere; this productivity necessitated an almost formulaic approach for some components (such as overtures) and a certain amount of self-borrowing. During this period he produced his most popular works, including the comic operas L'italiana in Algeri, Il barbiere di Siviglia (known in English as The Barber of Seville) and La Cenerentola, which brought to a peak the opera buffa tradition he inherited from masters such as Domenico Cimarosa and Giovanni Paisiello. He also composed opera seria works such as Tancredi, Otello and Semiramide. All of these attracted admiration for their innovation in melody, harmonic and instrumental colour, and dramatic form. In 1824 he was contracted by the Opéra in Paris, for which he produced an opera to celebrate the coronation of Charles X, Il viaggio a Reims (later cannibalised for his first opera in French, Le comte Ory), revisions of two of his Italian operas, Le siège de Corinthe and Moïse, and in 1829 his last opera, Guillaume Tell. (Full article...)![Image 12A l’arme A l’arme by Grimace, verso 55 from the Chantilly CodexGrimace (fl. mid-to-late 14th century; French: [ɡʁi.mas]; also Grymace, Grimache or Magister Grimache) was a French composer-poet in the ars nova style of late medieval music. Virtually nothing is known about Grimace's life other than speculative information based on the circumstances and content of his five surviving compositions of formes fixes; three ballades, a virelai and rondeau. His best known and most often performed work in modern-times is the virelai and proto-battaglia: A l’arme A l’arme.He is thought to have been a younger contemporary of Guillaume de Machaut and based in southern France. Three of his works were included in the Chantilly Codex, which is an important source of ars subtilior music. However, along with P. des Molins, Jehan Vaillant and F. Andrieu, Grimace was one of the post-Machaut generation whose music shows few distinctly ars subtilior features, leading scholars to recognize Grimace's work as closer to the ars nova style of Machaut. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 12
Image 12 A l’arme A l’arme by Grimace, verso 55 from the Chantilly Codex
A l’arme A l’arme by Grimace, verso 55 from the Chantilly Codex
Grimace (fl. mid-to-late 14th century; French: [ɡʁi.mas]; also Grymace, Grimache or Magister Grimache) was a French composer-poet in the ars nova style of late medieval music. Virtually nothing is known about Grimace's life other than speculative information based on the circumstances and content of his five surviving compositions of formes fixes; three ballades, a virelai and rondeau. His best known and most often performed work in modern-times is the virelai and proto-battaglia: A l’arme A l’arme.
He is thought to have been a younger contemporary of Guillaume de Machaut and based in southern France. Three of his works were included in the Chantilly Codex, which is an important source of ars subtilior music. However, along with P. des Molins, Jehan Vaillant and F. Andrieu, Grimace was one of the post-Machaut generation whose music shows few distinctly ars subtilior features, leading scholars to recognize Grimace's work as closer to the ars nova style of Machaut. (Full article...)![Image 13Tōru Takemitsu (武満 徹, pronounced [takeꜜmitsɯ̥ toːɾɯ]; 8 October 1930 – 20 February 1996) was a Japanese composer and writer on aesthetics and music theory. Largely self-taught, Takemitsu was admired for the subtle manipulation of instrumental and orchestral timbre. He is known for combining elements of oriental and occidental philosophy and for fusing sound with silence and tradition with innovation.He composed several hundred independent works of music, scored more than ninety films and published twenty books. He was also a founding member of the Jikken Kōbō (Experimental Workshop) in Japan, a group of avant-garde artists who distanced themselves from academia and whose collaborative work is often regarded among the most influential of the 20th century. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 13Tōru Takemitsu (武満 徹, pronounced [takeꜜmitsɯ̥ toːɾɯ]; 8 October 1930 – 20 February 1996) was a Japanese composer and writer on aesthetics and music theory. Largely self-taught, Takemitsu was admired for the subtle manipulation of instrumental and orchestral timbre. He is known for combining elements of oriental and occidental philosophy and for fusing sound with silence and tradition with innovation.
Image 13Tōru Takemitsu (武満 徹, pronounced [takeꜜmitsɯ̥ toːɾɯ]; 8 October 1930 – 20 February 1996) was a Japanese composer and writer on aesthetics and music theory. Largely self-taught, Takemitsu was admired for the subtle manipulation of instrumental and orchestral timbre. He is known for combining elements of oriental and occidental philosophy and for fusing sound with silence and tradition with innovation.
He composed several hundred independent works of music, scored more than ninety films and published twenty books. He was also a founding member of the Jikken Kōbō (Experimental Workshop) in Japan, a group of avant-garde artists who distanced themselves from academia and whose collaborative work is often regarded among the most influential of the 20th century. (Full article...) Image 14
Image 14.jpg.webp) Britten in 1968, by Hans Wild
Britten in 1968, by Hans Wild
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten OM CH (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976, aged 63) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, other vocal music, orchestral and chamber pieces. His best-known works include the opera Peter Grimes (1945), the War Requiem (1962) and the orchestral showpiece The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra (1945).
Born in Lowestoft, Suffolk, the son of a dentist, Britten showed talent from an early age. He studied at the Royal College of Music in London and privately with the composer Frank Bridge. Britten first came to public attention with the a cappella choral work A Boy was Born in 1934. With the premiere of Peter Grimes in 1945, he leapt to international fame. Over the next 28 years, he wrote 14 more operas, establishing himself as one of the leading 20th-century composers in the genre. In addition to large-scale operas for Sadler's Wells and Covent Garden, he wrote chamber operas for small forces, suitable for performance in venues of modest size. Among the best known of these is The Turn of the Screw (1954). Recurring themes in his operas include the struggle of an outsider against a hostile society and the corruption of innocence. (Full article...) Image 15
Image 15 Merrill Bradshaw in 1963
Merrill Bradshaw in 1963
Merrill Bradshaw (June 18, 1929 – July 12, 2000) was an American composer and professor at Brigham Young University (BYU), where he was composer-in-residence from 1967 to 1994.
Bradshaw grew up in Lyman, Wyoming; Salt Lake City, Utah; and Portland, Oregon. He was a member of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). He studied music theory at BYU with John R. Halliday and others, after which he continued his studies in composition at the University of Illinois. He became a faculty member at BYU in 1957. He was chairman of composition and theory from 1973 to 1983, and the executive director of the Barlow Endowment for Music Composition from 1983 to 1999. From 1973 to 1978 he chaired an LDS Church committee to revise the hymnbook, although the committee was suspended before they published their intended hymnal. A different committee authored the 1985 hymnal. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) -
- ... that gas lighting inspired Stephen Gunzenhauser to start a classical music festival?
- ... that the founders of the Turkish Republic despised Turkish classical music and tried to censor it?
- ... that the conductor Im Won-sik is considered the "father of Korea's classical music world"?
- ... that in 1994, Anthony Pople created two computer programs to analyse classical music?
- ... that the Stadthalle Hannover, the largest classical music concert hall in Germany by capacity, was modelled after the Pantheon in Rome and completed by 1914?
- ... that the choral music of Artemy Vedel, who is regarded as one of the Golden Three composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, was censored but performed from handwritten copies?
Selected image
 Image 1Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf.
Image 1Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf. Image 2Photograph: Augustus Binu; edit: Chris WoodrichKuchipudi is a Classical Indian dance from Andhra Pradesh, India. According to legend, an orphan named Siddhendra Yogi established the Kuchipudi dance-drama tradition in the seventh century. The performance usually begins with stage rites, after which each character comes onto the stage and introduces herself with a small composition of both song and dance. The drama then begins, and the dance is typically accompanied by Carnatic music.
Image 2Photograph: Augustus Binu; edit: Chris WoodrichKuchipudi is a Classical Indian dance from Andhra Pradesh, India. According to legend, an orphan named Siddhendra Yogi established the Kuchipudi dance-drama tradition in the seventh century. The performance usually begins with stage rites, after which each character comes onto the stage and introduces herself with a small composition of both song and dance. The drama then begins, and the dance is typically accompanied by Carnatic music. Image 3
Image 3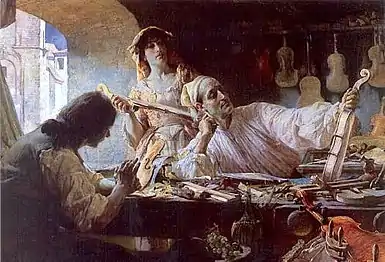 Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari. Image 4Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes.
Image 4Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes. Image 5Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.
Image 5Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.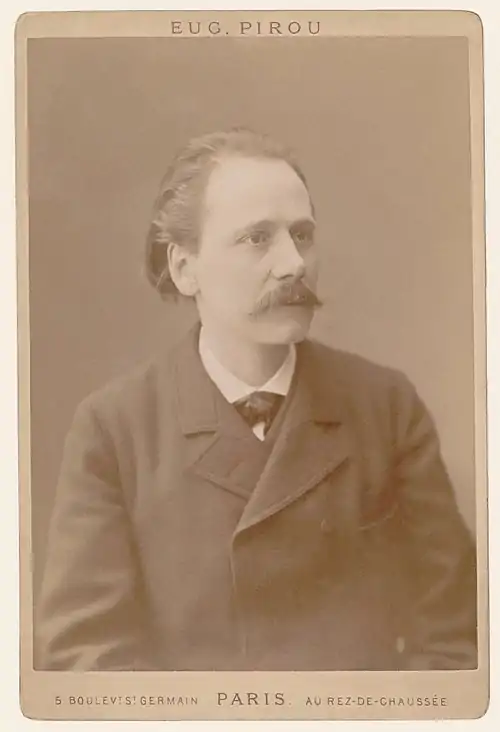 Image 6Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875.
Image 6Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875..jpg.webp) Image 7Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s.
Image 7Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s. Image 8
Image 8 A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in the London district of Covent Garden. The large building, often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. Image 9
Image 9 The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta.
The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta. Image 10
Image 10 Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form.
Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form. Image 11Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
Image 11Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
This portrait of Bach was painted in 1776 by Thomas Gainsborough, as part of a collection started by Bach's former teacher Padre Martini. It now hangs in the National Portrait Gallery, London. Image 12Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
Image 12Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
Topics
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Categories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals
