IntroductionA star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and trace heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime, its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time. Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars orbit closely, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy. (Full article...) Selected star -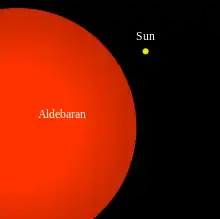 Size comparison between Aldebaran and the Sun Photo credit: commons:user:Riffsyphon1024 and commons:user:Mysid
Aldebaran (α Tau, α Tauri, Alpha Tauri) is a red giant star located about 65 light years away in the zodiac constellation of Taurus. With an average apparent magnitude of 0.87 it is the brightest star in the constellation and is one of the brightest stars in the nighttime sky. The name Aldebaran is Arabic (الدبران al-dabarān) and translates literally as "the follower", presumably because this bright star appears to follow the Pleiades, or "Seven Sisters" star cluster in the night sky. In 1997 a substellar companion was reported but subsequent observations have not confirmed this claim. Aldebaran is classified as a type K5III star. It is an orange giant star that has moved off the main sequence line of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. It has exhausted the hydrogen fuel in its core and hydrogen fusion has ceased there. Although not yet hot enough for fusing helium, the core temperature of the star has greatly increased due to gravitational pressure and the star has expanded to a diameter of 44.2 times the diameter of the Sun,Richichi & Roccatagliata (2005) derived an angular diameter of 20.58±0.03 milliarcsec, which given a distance of 65 light years yields a diameter of 61 million km.</ref> approximately 61 million kilometres (see 10 gigametres for similar sizes). The Hipparcos satellite has measured it as 65.1 light-years (20.0 pc) away, and it shines with 150 times the Sun's luminosity. Aldebaran is a slightly variable star, of the slow irregular variable type LB. It varies by about 0.2 in apparent magnitude. Selected article - Supernova Cassiopeia A Photo credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
A supernova (plural supernovae) is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova. Supernovae are extremely luminous and cause a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months. During this short interval a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun is expected to emit over its entire life span. The explosion expels much or all of a star's material at a velocity of up to 30,000 km/s (a tenth the speed of light), driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. This shock wave sweeps up an expanding shell of gas and dust called a supernova remnant. Several types of supernovae exist. Types I and II can be triggered in one of two ways, either turning off or suddenly turning on the production of energy through nuclear fusion. After the core of an aging massive star ceases to generate energy from nuclear fusion, it may undergo sudden gravitational collapse into a neutron star or black hole, releasing gravitational potential energy that heats and expels the star's outer layers. Alternatively a white dwarf star may accumulate sufficient material from a stellar companion (either through accretion or via a merger) to raise its core temperature enough to ignite carbon fusion, at which point it undergoes runaway nuclear fusion, completely disrupting it. Stellar cores whose furnaces have permanently gone out collapse when their masses exceed the Chandrasekhar limit, while accreting white dwarfs ignite as they approach this limit (roughly 1.38 times the mass of the sun). White dwarfs are also subject to a different, much smaller type of thermonuclear explosion fueled by hydrogen on their surfaces called a nova. Solitary stars with a mass below approximately nine solar masses, such as the Sun, evolve into white dwarfs without ever becoming supernovae. Selected image - Pinwheel Galaxy Photo credit: NASA
The Pinwheel Galaxy (also known as Messier 101 or NGC 5457) is a face-on spiral galaxy about 27 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major, discovered by Pierre Méchain. On February 28, 2006, NASA and the ESA released a very detailed image of Pinwheel Galaxy, which was the largest and most detailed image of a galaxy by Hubble Space Telescope at the time. The image was composed from 51 individual exposures, plus some extra ground-based photos. M101 is a relatively large galaxy compared to the Milky Way. With a diameter of 170,000 light-years it is nearly twice the size of the Milky Way. It has a disk mass on the order of 100 billion solar masses, along with a small bulge of about 3 billion solar masses. Did you know?
SubcategoriesTo display all subcategories click on the ►
Stars Stars by luminosity class Stars by metallicity Stars by spectral type Stars by type Stars with proper names Lists of stars Star types Astronomical catalogues of stars Star atlases Coats of arms with stars Star symbols Stars in the Andromeda Galaxy Star clusters Fiction about stars Stellar groupings Hypothetical stars Star images Stellar dynamics Sun Star systems Wikipedia categories named after stars Star stubs Sun Atmospheric radiation Solar calendars Coats of arms with sunrays Coats of arms with suns Sun in culture Day Horizontal coordinate system Missions to the Sun Solar observatories Solar phenomena Solar alignment Solar eclipses Solar energy Sun tanning Sundials Sun stubs Galaxies Astronomical catalogues of galaxies Galaxies discovered by year Fiction about galaxies Galaxy clusters Galaxy filaments Galaxy superclusters Lists of galaxies Galaxy morphological types Active galaxies Barred galaxies Dark galaxies Dwarf galaxies Elliptical galaxies Field galaxies Hypothetical galaxies Galaxy images Interacting galaxies Irregular galaxies Lenticular galaxies Low surface brightness galaxies Overlapping galaxies Peculiar galaxies Polar-ring galaxies Protogalaxies Ring galaxies Seyfert galaxies Spiral galaxies Starburst galaxies Supermassive black holes Galaxy stubs Wikipedia categories named after galaxies Black holes Fiction about black holes Intermediate-mass black holes Stellar black holes Supermassive black holes White holes Supernovae Fiction about supernovae Historical supernovae Hypernovae Discoverers of supernovae Supernova remnants Selected biography - Galileo Galilei's portrait painted in 1636 Photo credit: By Justus Sustermans
Galileo Galilei (Italian pronunciation: [galiˈlɛo galiˈlɛi]; 15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations, and support for Copernicanism. Galileo has been called the "father of modern observational astronomy", the "father of modern physics", the "father of science", and "the father of modern science". Stephen Hawking says: "Galileo, perhaps more than any other single person, was responsible for the birth of modern science." The motion of uniformly accelerated objects, taught in nearly all high school and introductory college physics courses, was studied by Galileo as the subject of kinematics. His contributions to observational astronomy include the telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, the discovery of the four largest satellites of Jupiter (named the Galilean moons in his honour), and the observation and analysis of sunspots. Galileo also worked in applied science and technology, inventing an improved military compass and other instruments. Galileo's championing of Copernicanism was controversial within his lifetime, when a large majority of philosophers and astronomers still subscribed (at least outwardly) to the geocentric view that the Earth is at the centre of the universe. After 1610, when he began publicly supporting the heliocentric view, which placed the Sun at the centre of the universe, he met with bitter opposition from some philosophers and clerics, and two of the latter eventually denounced him to the Roman Inquisition early in 1615. In February 1616, although he had been cleared of any offence, the Catholic Church nevertheless condemned heliocentrism as "false and contrary to Scripture", and Galileo was warned to abandon his support for it—which he promised to do. When he later defended his views in his most famous work, Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems, published in 1632, he was tried by the Inquisition, found "vehemently suspect of heresy", forced to recant, and spent the rest of his life under house arrest. TopicsWikiProjects
More science WikiProjects...
Things to do
Related portalsMore science portals...
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|