 Progressive Alliance logo | |
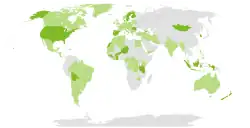 Light green: Countries with a political party affiliated with the Progressive Alliance Dark green: Countries with the ruling party affiliated with the Progressive Alliance | |
| Abbreviation | PA |
|---|---|
| Formation |
|
| Purpose | Global network of social democratic and progressive political parties and organisations |
| Headquarters | Berlin, Germany |
Region served | Worldwide |
Membership | 118 political parties and 28 associated organisations |
Main organ | Conference of the Progressive Alliance |
| Website | progressive-alliance |
| Part of a series on |
| Social democracy |
|---|
 |
The Progressive Alliance (PA) is a political international of progressive and social democratic political parties and organisations founded on 22 May 2013 in Leipzig, Germany.[1] The alliance was formed as an alternative to the existing Socialist International, of which many of its member parties are former or current members.[2][3] The Progressive Alliance claims 140 participants from around the world.
History
The first step towards the creation of the Progressive Alliance was the decision in January 2012 by Sigmar Gabriel, then chairman of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), to cancel payment of the SPD's £100,000 yearly membership fee to the Socialist International. Gabriel had been critical of the Socialist International's admittance and continuing inclusion of undemocratic political movements into the organisation.[4][5][6]
An initial Conference of the Progressive Alliance was held in Rome, Italy, on 14–15 December 2012, with representatives of 42 political parties attending.[7][8] They included Pier Luigi Bersani, leader of the Democratic Party of Italy; Harlem Désir, Chair of the French Socialist Party; Hermes Binner, Chair of the Argentine Socialist Party; Peter Shumlin, Democratic Governor of Vermont; and Mustapha Ben Jafar, Secretary General of the Tunisian Democratic Forum for Labour and Liberties.[9] Also present were representatives of the Indian National Congress, the Workers' Party of Brazil, and PASOK of Greece.[10][11] The Dutch Labour Party also supported the formation of the organisation,[12] as did the Swiss Socialist Party,[13] and the Social Democratic Party of Austria.[14]
During the Council of the Socialist International in Cascais, Portugal, on 4–5 February 2013, 50 political parties discussed on the sidelines the formation of the Progressive Alliance, including the Movement for Democratic Change of Zimbabwe.[15]
The official foundation of the organisation was held on 22 May 2013 in Leipzig, Germany, on the 150th anniversary of the formation of the General German Workers' Association (ADAV), the predecessor of the SPD.[16][17][18][19][20] The organisation stated the aim of becoming the global network of "the progressive, democratic, social-democratic, socialist and labour movement".[21][22] It was reported that representatives of approximately 70 social-democratic political parties from across the world attended the event.[23][24][25] The Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats (S&D) group in the European Parliament joined the organisation upon its official foundation.[26] Many member parties are also affiliated to the Socialist International.[27] In September 2013 the Democratic Party of Cyprus (DIKO) announced that it was negotiating to join the Progressive Alliance and that its representatives were to attend a seminar of the international in Stockholm on 24 October.[28] The Democratic Party of Korea was a founding member but withdrew in 2016. The Korean Justice Party currently participates as an observer.
On 4–5 December 2014, a Progressive Alliance conference was held in Lisbon for member parties of the S&D group.[29] A regional seminar was held on 25 September 2015 in Batu Ferringhi, Malaysia, which also hosted delegates from the Democratic Action Party of Malaysia, Democratic Party of Japan and Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle.[30] On 25 April 2016 the organisation held a seminar in São Paulo hosted by the Workers' Party of Brazil.[31]
Participants
The Progressive Alliance lists 118 parties and 28 organisations which participate in the network, rather than claiming members.[32]
| Country | Party/Organization | Abbreviation | National Lower Houses | Government | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socialist Forces Front | FFS | 0 / 407 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Socialist Party | PS | 2 / 257 [33] | In opposition | |||
| Generation for a National Encounter | GEN | 1 / 257 | In opposition | |||
| Australian Labor Party | ALP | 78 / 151 | In government | In government in New South Wales, Northern Territory, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia. In coalition in the Australian Capital Territory. | ||
| Social Democratic Party of Austria | SPÖ | 40 / 183 | In opposition | Ruling at state-level in Burgenland, Carinthia, Vienna. | ||
| National Democratic Action Society | Waad | 0 / 40 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | Banned in its country as a terrorist organisation as of 2017. | ||
| Belarusian Social Democratic Party | Hramada | 0 / 110 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Socialist Party | PS | 20 / 150 | In coalition | |||
| Forward | Vooruit[34] | 9 / 150 | In coalition | |||
| Movement for Socialism | MAS | 75 / 130 | In government | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Bosnia and Herzegovina | SDP | 5 / 42 | In government | |||
| Workers' Party | PT | 67 / 513 | In government | In government in Bahia, Ceará, Piauí and Rio Grande do Norte. | ||
| Brazilian Socialist Party | PSB | 14 / 513 | In coalition | In government in Espírito Santo, Maranhão and Paraíba. | ||
| Bulgarian Socialist Party | BSP | 26 / 240 | In opposition | |||
| People's Movement for Progress | MPP | Dissolved | Extra-parliamentary opposition | President Roch Marc Christian Kaboré, a member of the party, was deposed in a midterm coup d'état. | ||
| Social Democratic Front | SDF | 5 / 180 | In opposition | |||
| New Democratic Party | NDP/NPD | 25 / 338 | Confidence and supply | Has supply and confidence agreement in federal parliament.[35] In government in the province of British Columbia. In government in the province of Manitoba. Supply and confidency agreement in the territory of Yukon. | ||
| Movement for the Liberation of the Central African People | MLPC | 9 / 100 | In opposition | |||
| Socialist Party of Chile | PS | 13 / 155 | In coalition | |||
| Party for Democracy | PPD | 7 / 155 | In coalition | |||
| Citizens' Action Party | PAC | 0 / 57 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Croatia | SDP | 34 / 151 | In opposition | |||
| Movement for Social Democracy | EDEK | 4 / 56 | In opposition | |||
| Democratic Party | Diko | 9 / 56 | In opposition | |||
| Social Democracy | SOCDEM | 0 / 200 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Union for Democracy and Social Progress | UDPS | 32 / 500 | In coalition | |||
| Social Democratic Party | 50 / 179 | In coalition | ||||
| Modern Revolutionary Party | PRM | 88 / 190 | In government | |||
| Revolutionary Front for an Independent East Timor | FRETILIN | 19 / 65 | In opposition | |||
| Egyptian Social Democratic Party | ESDP | 7 / 596 | In opposition | |||
| Convergence for Social Democracy | CPDS | 1 / 100 | In opposition | |||
| Eritrean People's Democratic Front | EPDF | 0 / 150 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | Banned as a legal party due to country being a one-party state. | ||
| People's United Democratic Movement | PUDEMO | 0 / 66 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Swazi Democratic Party | SWADEPA | 0 / 66 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Finland | SDP | 43 / 200 | In opposition | |||
| Socialist Party | PS | 27 / 577 | In opposition | |||
| Georgian Dream | 84 / 150 | In government | ||||
| Social Democratic Party of Germany | SPD | 206 / 736 [36] | In government | |||
| National Democratic Congress | NDC | 137 / 275 | In opposition | |||
| PASOK – Movement for Change | PASOK-KINAL | 22 / 300 [37] | In opposition | |||
| National Democratic Congress | NDC | 9 / 15 | In government | |||
| Guinean People's Assembly | RPG | 1 / 81 | In opposition | President Alpha Condé, a member of the party, was deposed in a midterm coup d'état. Moreover, the National Assembly, where it held a supermajority, was replaced by the junta-appointed National Transitional Council.[38] | ||
| Hungarian Socialist Party | MSzP | 10 / 199 | In opposition | |||
| Indian National Congress | INC | 49 / 543 | In opposition | In government in Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Karnataka . | ||
| Samajwadi Party | SP | 3 / 543 | In opposition | |||
| Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle | PDI-P | 128 / 575 | In government | |||
| National Democratic Party | NasDem | 59 / 575 | In government | |||
| Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan | PDKI | 0 / 290 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Komala Party of Iranian Kurdistan | KPIK | 0 / 290 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Patriotic Union of Kurdistan | PUK | 18 / 329 | In opposition | |||
| Kurdistan Socialist Democratic Party | KSDP | 0 / 329 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Labour Party | 7 / 160 | In opposition | ||||
| Israeli Labor Party | HaAvoda | 4 / 120 | In opposition | |||
| Meretz | 0 / 120 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | ||||
| Democratic Party | PD | 69 / 400 | In opposition | |||
| Cap Union for Democracy and Development | CAP-UDD | 0 / 255 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Freedom and Democracy for the Republic | LIDER | 0 / 255 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Jordanian Social Democratic Party | KPK | 0 / 130 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Labour Party of Kenya | KLP | 0 / 320 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Vetëvendosje | LV | 59 / 120 | In government | |||
| Social Democratic Party "Harmony" | SDPS | 0 / 100 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Progressive Socialist Party | PSP | 9 / 128 | In coalition | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Lithuania | LSDP | 13 / 141 | In opposition | |||
| Luxembourg Socialist Workers' Party | LSAP | 10 / 60 | In coalition | |||
| Democratic Action Party | DAP | 40 / 222 | In coalition | In coalition in Negeri Sembilan, Penang, Perak, Pahang and Selangor. | ||
| Rally of Democratic Forces | RFD | 6 / 95 | In opposition | |||
| Mauritius Militant Movement | MMM | 9 / 69 | In opposition | |||
| Citizens' Movement | MC | 23 / 500 | In opposition | In government in Jalisco and Nuevo León in coalition Guanajuato and Yucatan . | ||
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | PRD | 15 / 500 | In opposition | in coalition Aguascalientes Chihuahua Durango Guanajuato | ||
| Democratic Party of Moldova | PDM | 0 / 101 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Mongolian People's Party | MPP | 62 / 76 | In government | |||
| Democratic Party of Socialists of Montenegro | DPS | 29 / 81 | In opposition | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Montenegro | SDP | 2 / 81 | In opposition | |||
| Socialist Union of Popular Forces | USFP | 34 / 395 | In opposition | |||
| Democratic Party for a New Society | DPNS | 0 / 440 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Nepali Congress | NC | 63 / 275 | In government | |||
| Labour Party | PvdA | 9 / 150 | In opposition | |||
| New Zealand Labour Party | LAB | 34 / 123 | In opposition | |||
| Sandinista Renovation Movement (Unamos) | MRS | 0 / 92 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Nigerien Party for Democracy and Socialism | PNDS | 79 / 171 | In coalition | |||
| Social Democratic Union of Macedonia | SDSM | 31 / 120 | In coalition | |||
| Republican Turkish Party | CTP | 18 / 50 | In opposition | Northern Cyprus is not a UN-recognized state. | ||
| Labour Party | Ap | 48 / 169 | In coalition | |||
| Fatah | 45 / 132 | In government | ||||
| Palestinian National Initiative | PNI | 2 / 132 | In opposition | |||
| Party for a Country of Solidarity | PPS | 0 / 80 | In opposition | Affiliated with Guasú Front in national parliament. | ||
| Akbayan Citizens' Action Party | 0 / 304 | In opposition | One senator in the popularly-elected upper chamber, Senate of the Philippines. | |||
| Socialist Party | PS | 120 / 230 | In government | |||
| Citizens' Convergence | CC | 0 / 151 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Social Democratic Party | PSD | 110 / 330 | In coalition | |||
| Saint Lucia Labour Party | SLP | 13 / 17 | In government | |||
| Movement for the Liberation of São Tomé and Príncipe/Social Democratic Party | MLSTP-PSD | 18 / 55 | In opposition | |||
| Socialist Party of Senegal | PS | 0 / 150 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Democratic Party | DS | 10 / 250 | In opposition | |||
| Direction – Slovak Social Democracy | Smer-SD | 42 / 150 | In government | |||
| Social Democrats | SD | 12 / 90 | In coalition | |||
| Spanish Socialist Workers' Party | PSOE | 120 / 350 | In coalition | |||
| Swedish Social Democratic Party | SAP | 107 / 349 | In opposition | |||
| Social Democratic Party of Switzerland | SP | 39 / 200 | In coalition | |||
| Syrian Democratic People's Party | 0 / 250 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | ||||
| Chama Cha Mapinduzi | CCM | 365 / 393 | In government | |||
| Democratic Forum for Labour and Liberties | Ettakatol | 0 / 217 | Extra-parliamentary opposition | |||
| Republican People's Party | CHP | 136 / 600 | In opposition | |||
| Peoples' Democratic Party | HDP | 55 / 600 | In opposition | |||
| Labour Party | 199 / 650 | In opposition | In Government in Wales | |||
| Democratic Party | 213 / 435 | In government | Minority party in the House of Representatives, majority party in the Senate, and holds the presidency. | |||
| Socialist Party of Uruguay | PSU | 3 / 99 | In opposition | Affiliated with the Broad Front in the national parliament. | ||
| Movimiento al Socialismo | MAS | 0 / 277 | In opposition | Affiliated with the Democratic Alliance in the national parliament. | ||
| Polisario Front | 53 / 53 | One-party state | Western Sahara is not a UN-recognized state. | |||
| Yemeni Socialist Party | YSP | 8 / 301 | In opposition | |||
| Movement for Democratic Change | MDC | 0 / 210 | In opposition | |||
| Africa | Central African Progressive Alliance | APAC | ||||
| The Americas | Center for American Progress | CAP | ||||
| Trade Union Confederation of the Americas | CSA | |||||
| Asia | Network of Social Democracy in Asia | SOCDEM | ||||
| Arab Social Democratic Forum | ASDF | |||||
| Europe | Party of European Socialists | PES | ||||
| Party of European Socialists Women | PES Women | |||||
| Young European Socialists | YES | |||||
| Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats | S&D | |||||
| Foundation for European Progressive Studies | FEPS | |||||
| Socialist Group in the Council of Europe | SOC | |||||
| European Forum for Democracy and Solidarity | ||||||
| International | Socialist International Women | SIW | ||||
| International Union of Socialist Youth | IUSY | |||||
| International Trade Union Confederation | ITUC | |||||
| National Democratic Institute for International Affairs | NDI | |||||
| Olof Palme International Center | OPIC | |||||
| Trade Union Advisory Committee to the OECD | TUAC | |||||
| Association for Democratic Socialism | ||||||
| CEE Gender Network | ||||||
| Global Progressive Forum | ||||||
| Industrial Global Union | ||||||
| Just Jobs Network | ||||||
| Solidar |
References
- ↑ Jean-Jacques Lambin (2014). Rethinking the Market Economy: New Challenges, New Ideas, New Opportunities. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 269. ISBN 978-1-137-39291-6.
- ↑ Talbot C. Imlay (2018). The Practice of Socialist Internationalism: European Socialists and International Politics, 1914–1960. Oxford University Press. p. 465. ISBN 978-0-19-964104-8.
- ↑ Nathan Gilbert Quimpo (2020). "The Post-war Rise and Decline of the Left". In Toby Carroll; Shahar Hameiri; Lee Jones (eds.). The Political Economy of Southeast Asia: Politics and Uneven Development Under Hyperglobalisation. Springer Nature. p. 150. ISBN 978-3-03-028255-4.
- ↑ "SPD will Sozialistischer Internationale den Geldhahn zudrehen und den Mitgliedsbeitrag nicht zahlen". Der Spiegel. 22 January 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Sigmar Gabriel (3 February 2011). "Gastbeitrag: Keine Kumpanei mit Despoten". Frankfurter Rundschau (in German). Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Christian Salm (2016). Transnational Socialist Networks in the 1970s: European Community Development Aid and Southern Enlargement. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. xiv. ISBN 978-1-137-55120-7.
- ↑ Redaktion neues deutschland. "16.12.2012: Sozialdemokraten gründen neue Internationale". NeuesDeutschland. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Progressive Alliance Conference". Partito Democratico. Archived from the original on 19 April 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Sigmar Gabriel in Rom" (in German). Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands (SPD). Archived from the original on 10 March 2014. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Progressive Allianz" (in German). Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands (SPD). 22 February 1999. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Tense Pasok leadership meeting concludes". Eleftherotypia. 9 May 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "PvdA steunt oprichting Progressive Alliance". PvdA. 19 December 2012. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Masmejan, Denis (16 May 2013). "Le PS suisse rompt avec l'Internationale socialiste". Le Temps (in French). Archived from the original on 28 June 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "Sozialdemokraten wollen Sozialistische Internationale entmachten". Kurier. 17 May 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe: Socialist International Calls for Reforms in Zimbabwe". allAfrica.com. 6 February 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Social Democrats Seek Revival on 150th b-day". The Local. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Borriss, Gernot (10 May 2013). "Sozialistisch war gestern, progressiv ist heute: SPD lädt zur Gründung eines internationalen Parteiennetzwerkes nach Leipzig". Leipziger Zeitung. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ Von Aert van Riel (16 April 2013). "07.05.2013: SPD spaltet Internationale". Neues Deutschland. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Quadbeck, Eva (17 May 2013). "Berlin: Kanzlerin kommt zur 150-Jahr-Feier der SPD". Nachrichten.rp-online.de. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Gabriel hofft durch Parteijubiläum auf Motivationsschub". Donaukurier.de. 16 May 2013. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Basic document". Progressive Alliance. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "A Progressive Network for the 21st Century" (PDF). Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands (SPD). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2014.
- ↑ "Sozialdemokratische Parteien gründen neues Bündnis". Deutsche Welle. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- ↑ "Bruderzwist unter Sozialisten". Süddeutsche Zeitung. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "Geschichte: Mehr als 70 sozialdemokratische Parteien bilden Progressive Alliance". Die Welt. 23 November 2011. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ "S&D Group joins new Progressive Alliance – 'the network of progressive forces for the 21st century'". Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats. 24 January 2013. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ↑ Lamb, Peter, ed. (2015). Historical Dictionary of Socialism. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 436. ISBN 978-1-4422-5827-3.
- ↑ "Το ΔΗ.ΚΟ. συνδέεται με την "Προοδευτική Συμμαχία"". DIKO. Archived from the original on 9 November 2013. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ↑ "Progressive Alliance Parliamentarian Conference – Decent Work and Education: Investing in Equal Opportunities for All". Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ↑ "Global democratic leaders demand Anwar's release, persecution of government critics to stop". 25 September 2015. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- ↑ "Lula Promises to Fight Rousseff's Impeachment at Progressive Alliance Seminar". Folha de S.Paulo. 26 April 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2016.
- ↑ "Parties & Organisations". Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- ↑ Argentine Chamber of Deputies, 2021 Argentine legislative election
- ↑ "Vooruit". Vooruit. Retrieved 14 March 2023.
- ↑ "Delivering for Canadians Now". Prime Minister of Canada. 22 March 2022. Retrieved 25 April 2022.
- ↑ 2021 German federal election
- ↑ 2019 Greek legislative election.
- ↑ AfricaNews (23 January 2022). "Head of Guinea's ruling junta appoints members of transitional council". Africanews. Retrieved 31 May 2022.