 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
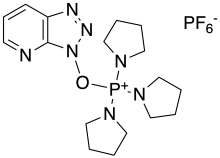
| IUPAC name
(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Other names
PyAOP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.575 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H27F6N7OP2 | |
| Molar mass | 521.389 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 163–168 °C (325–334 °F; 436–441 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
PyAOP ((7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate) is a coupling reagent used in solid phase peptide synthesis. It is a derivative of the HOAt family of coupling reagents. It is preferred over HATU, because it does not side react at the N-terminus of the peptide.[1] Compared to the HOBt derivates, PyAOP (and HOAt in general) are more reactive due to the additional nitrogen.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Albericio, F.; Cases, M.; Alsina, J.; Triolo, S. A.; Carpino, L. A; Kates, S. (1997). "On the use of PyAOP, a phosphonium salt derived from HOAt, in solid-phase peptide synthesis". Tetrahedron Letters. 38 (27): 4853–4856. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(97)01011-3.
- ↑ Albericio, Fernando; Bofill, Josep M.; El-Faham, Ayman; Kates, Steven A. (1998). "Use of Onium Salt-Based Coupling Reagents in Peptide Synthesis1". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. American Chemical Society. 63 (26): 9678–9683. doi:10.1021/jo980807y. ISSN 0022-3263.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.