| RPGR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | RPGR, COD1, CORDX1, CRD, PCDX, RP15, RP3, XLRP3, orf15, Retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 312610 MGI: 1344037 HomoloGene: 55455 GeneCards: RPGR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
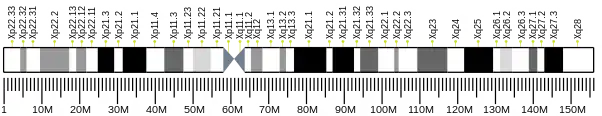
X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator is a GTPase-binding protein that in humans is encoded by the RPGR gene.[5][6][7][8] The gene is located on the X-chromosome and is commonly associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). In photoreceptor cells, RPGR is localized in the connecting cilium which connects the protein-synthesizing inner segment to the photosensitive outer segment and is involved in the modulation of cargo trafficked between the two segments.[9]
Function
This gene encodes a protein with a series of six RCC1-like domains (RLDs), characteristic of the highly conserved guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms of this gene have been reported, but the full-length natures of only some have been determined.[8]
The two major isoforms are RPGRconst, the default isoform, composed of exons 1-19, and RPGRORF15 which retains part of intron 15 as the terminal exon. ORF15 is the terminal exon of RPGRORF15 and is a mutational hotspot accounting for ~60% of RPGR patients with heterogeneous diseases ranging from XLRP to cone-rod degeneration and macular degeneration.[10] Alternatively, the RPGRconst isoform contains a putative prenylation domain on its C-terminal end[10] which is involved in posttranslational modification and allows membrane-association and protein trafficking.[11] The C-terminal domain of the RPGRconst isoform contains a CTIL motif (812CTIL815) which recruits prenyl-binding protein PDE6D which then shuttles the protein to the connecting cilium.[12]
Photoreceptor cells contain an inner segment and an outer segment which are joined by a connecting cilium. Protein synthesis occurs exclusively in the inner segment and all proteins must be trafficked across the connecting cilium to the outer segment where the phototransduction cascade takes place. RPGR is primarily located in a protein complex in the connecting cilium and is involved in regulating the cargo that is trafficked from the inner segment to the outer segment.[9]
Interactions
Retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator has been shown to interact with PDE6D[13] nephronophthisis (NPHP) proteins[14] and RPGRIP1.[15] Binding to PDE6D has been shown to ensure ciliary localization of the RPGRconst isoform.[16] Additionally, the N-terminal of interacts with a PDE6D interacting proetin, INPP5E (inositol polyphosphatase 5E).[12] INPP5E has been shown to regulates phosphoinositide metabolism and may modulate the phosphoinositide content of photoreceptor cells.[9]
RPGR has also been shown to preferentially interact with the GDP-bound form of the small GTPase RAB8A.[17] RAB8A is involved in rhodopsin trafficking in primary cilia.[18] The C-terminal domain of RPGRORF15 has been shown to interact with whirlin, a ciliary protein that is mutated in Usher Syndrome.[19] The RPGRORF15 isoform has been shown to be glutamylated on its N-terminus by tubulin-tyrosine ligase-like 5 (TTLL5).[20] It has also been shown that loss of TTLL5 mimics loss of RPGR in the mouse retina.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000156313 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031174 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Meindl A, Dry K, Herrmann K, Manson F, Ciccodicola A, Edgar A, Carvalho MR, Achatz H, Hellebrand H, Lennon A, Migliaccio C, Porter K, Zrenner E, Bird A, Jay M, Lorenz B, Wittwer B, D'Urso M, Meitinger T, Wright A (May 1996). "A gene (RPGR) with homology to the RCC1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is mutated in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3)". Nature Genetics. 13 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1038/ng0596-35. PMID 8673101. S2CID 31695757.
- ↑ Roepman R, van Duijnhoven G, Rosenberg T, Pinckers AJ, Bleeker-Wagemakers LM, Bergen AA, Post J, Beck A, Reinhardt R, Ropers HH, Cremers FP, Berger W (Jul 1996). "Positional cloning of the gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 3: homology with the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor RCC1". Human Molecular Genetics. 5 (7): 1035–41. doi:10.1093/hmg/5.7.1035. hdl:2066/22748. PMID 8817343.
- ↑ Murga-Zamalloa CA, Atkins SJ, Peranen J, Swaroop A, Khanna H (Sep 2010). "Interaction of retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) with RAB8A GTPase: implications for cilia dysfunction and photoreceptor degeneration". Human Molecular Genetics. 19 (18): 3591–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq275. PMC 2928130. PMID 20631154.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RPGR retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator".
- 1 2 3 Khanna H (October 2015). "Photoreceptor Sensory Cilium: Traversing the Ciliary Gate". Cells. 4 (4): 674–86. doi:10.3390/cells4040674. PMC 4695852. PMID 26501325.
- 1 2 Churchill JD, Bowne SJ, Sullivan LS, Lewis RA, Wheaton DK, Birch DG, et al. (February 2013). "Mutations in the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa genes RPGR and RP2 found in 8.5% of families with a provisional diagnosis of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 54 (2): 1411–6. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-11541. PMC 3597192. PMID 23372056.
- ↑ Glomset JA, Farnsworth CC (1994). "Role of protein modification reactions in programming interactions between ras-related GTPases and cell membranes". Annual Review of Cell Biology. 10: 181–205. doi:10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.001145. PMID 7888176.
- 1 2 Rao KN, Zhang W, Li L, Anand M, Khanna H (2016b) Prenylated retinal ciliopathy protein RPGR interacts with PDE6delta and regulates ciliary localization of Joubert syndrome-associated protein INPP5E. Hum Mol Genet 25(20):4533–4545
- ↑ Linari M, Ueffing M, Manson F, Wright A, Meitinger T, Becker J (Feb 1999). "The retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator, RPGR, interacts with the delta subunit of rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (4): 1315–20. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.1315L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1315. PMC 15460. PMID 9990021.
- ↑ Murga-Zamalloa CA, Desai NJ, Hildebrandt F, Khanna H (July 2010). "Interaction of ciliary disease protein retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator with nephronophthisis-associated proteins in mammalian retinas". Molecular Vision. 16: 1373–81. PMC 2905641. PMID 20664800.
- ↑ Roepman R, Bernoud-Hubac N, Schick DE, Maugeri A, Berger W, Ropers HH, Cremers FP, Ferreira PA (Sep 2000). "The retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) interacts with novel transport-like proteins in the outer segments of rod photoreceptors". Human Molecular Genetics. 9 (14): 2095–105. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.14.2095. PMID 10958648.
- ↑ Rao KN, Zhang W, Li L, Ronquillo C, Baehr W, Khanna H (May 2016). "Ciliopathy-associated protein CEP290 modifies the severity of retinal degeneration due to loss of RPGR". Human Molecular Genetics. 25 (10): 2005–2012. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddw075. PMC 5062589. PMID 26936822.
- ↑ Wang J, Deretic D (January 2014). "Molecular complexes that direct rhodopsin transport to primary cilia". Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 38: 1–19. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.08.004. PMC 3883129. PMID 24135424.
- ↑ Moritz OL, Tam BM, Hurd LL, Peränen J, Deretic D, Papermaster DS (August 2001). "Mutant rab8 Impairs docking and fusion of rhodopsin-bearing post-Golgi membranes and causes cell death of transgenic Xenopus rods". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 12 (8): 2341–51. doi:10.1091/mbc.12.8.2341. PMC 58598. PMID 11514620.
- ↑ Ebermann I, Scholl HP, Charbel Issa P, Becirovic E, Lamprecht J, Jurklies B, et al. (April 2007). "A novel gene for Usher syndrome type 2: mutations in the long isoform of whirlin are associated with retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural hearing loss". Human Genetics. 121 (2): 203–11. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0304-0. PMID 17171570. S2CID 22632047.
- ↑ Sun X, Park JH, Gumerson J, Wu Z, Swaroop A, Qian H, Roll-Mecak A, Li T (2016) Loss of RPGR glutamylation underlies the pathogenic mechanism of retinal dystrophy caused by TTLL5 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E2925–E2934
Further reading
- Jin ZB, Hayakawa M, Murakami A, Nao-i N (2007). "RCC1-like domain and ORF15: essentials in RPGR gene". Retinal Degenerative Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 572. pp. 29–33. doi:10.1007/0-387-32442-9_5. ISBN 978-0-387-28464-4. PMID 17249551.
- Ott J, Bhattacharya S, Chen JD, Denton MJ, Donald J, Dubay C, Farrar GJ, Fishman GA, Frey D, Gal A (Jan 1990). "Localizing multiple X chromosome-linked retinitis pigmentosa loci using multilocus homogeneity tests". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (2): 701–4. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87..701O. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.2.701. PMC 53333. PMID 2300556.
- McGuire RE, Sullivan LS, Blanton SH, Church MW, Heckenlively JR, Daiger SP (Jul 1995). "X-linked dominant cone-rod degeneration: linkage mapping of a new locus for retinitis pigmentosa (RP 15) to Xp22.13-p22.11". American Journal of Human Genetics. 57 (1): 87–94. PMC 1801245. PMID 7611300.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (Jan 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (Sep 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Fujita R, Buraczynska M, Gieser L, Wu W, Forsythe P, Abrahamson M, Jacobson SG, Sieving PA, Andréasson S, Swaroop A (Sep 1997). "Analysis of the RPGR gene in 11 pedigrees with the retinitis pigmentosa type 3 genotype: paucity of mutations in the coding region but splice defects in two families". American Journal of Human Genetics. 61 (3): 571–80. doi:10.1086/515523. PMC 1715956. PMID 9326322.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (Oct 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Buraczynska M, Wu W, Fujita R, Buraczynska K, Phelps E, Andréasson S, Bennett J, Birch DG, Fishman GA, Hoffman DR, Inana G, Jacobson SG, Musarella MA, Sieving PA, Swaroop A (Dec 1997). "Spectrum of mutations in the RPGR gene that are identified in 20% of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". American Journal of Human Genetics. 61 (6): 1287–92. doi:10.1086/301646. PMC 1716085. PMID 9399904.
- Hardcastle AJ, David-Gray ZK, Jay M, Bird AC, Bhattacharya SS (Dec 1997). "Localization of CSNBX (CSNB4) between the retinitis pigmentosa loci RP2 and RP3 on proximal Xp". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 38 (13): 2750–5. PMID 9418727.
- Yan D, Swain PK, Breuer D, Tucker RM, Wu W, Fujita R, Rehemtulla A, Burke D, Swaroop A (Jul 1998). "Biochemical characterization and subcellular localization of the mouse retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (mRpgr)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (31): 19656–63. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.31.19656. PMID 9677393.
- Fishman GA, Grover S, Jacobson SG, Alexander KR, Derlacki DJ, Wu W, Buraczynska M, Swaroop A (Dec 1998). "X-linked retinitis pigmentosa in two families with a missense mutation in the RPGR gene and putative change of glycine to valine at codon 60". Ophthalmology. 105 (12): 2286–96. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(98)91231-3. PMID 9855162.
- Linari M, Ueffing M, Manson F, Wright A, Meitinger T, Becker J (Feb 1999). "The retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator, RPGR, interacts with the delta subunit of rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (4): 1315–20. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.1315L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1315. PMC 15460. PMID 9990021.
- Dry KL, Manson FD, Lennon A, Bergen AA, Van Dorp DB, Wright AF (1999). "Identification of a 5' splice site mutation in the RPGR gene in a family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3)". Human Mutation. 13 (2): 141–5. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:2<141::AID-HUMU6>3.0.CO;2-Q. PMID 10094550. S2CID 34407949.
- Kirschner R, Rosenberg T, Schultz-Heienbrok R, Lenzner S, Feil S, Roepman R, Cremers FP, Ropers HH, Berger W (Aug 1999). "RPGR transcription studies in mouse and human tissues reveal a retina-specific isoform that is disrupted in a patient with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". Human Molecular Genetics. 8 (8): 1571–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.8.1571. PMID 10401007.
- Zito I, Thiselton DL, Gorin MB, Stout JT, Plant C, Bird AC, Bhattacharya SS, Hardcastle AJ (1999). "Identification of novel RPGR (retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator) mutations in a subset of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families segregating with the RP3 locus". Human Genetics. 105 (1–2): 57–62. doi:10.1007/s004390051064. PMID 10480356.
- Miano MG, Testa F, Strazzullo M, Trujillo M, De Bernardo C, Grammatico B, Simonelli F, Mangino M, Torrente I, Ruberto G, Beneyto M, Antinolo G, Rinaldi E, Danesino C, Ventruto V, D'Urso M, Ayuso C, Baiget M, Ciccodicola A (Sep 1999). "Mutation analysis of the RPGR gene reveals novel mutations in south European patients with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa". European Journal of Human Genetics. 7 (6): 687–94. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200352. PMID 10482958.
- Hong DH, Pawlyk BS, Shang J, Sandberg MA, Berson EL, Li T (Mar 2000). "A retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR)-deficient mouse model for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (7): 3649–54. doi:10.1073/pnas.060037497. PMC 16294. PMID 10725384.
- Zito I, Gorin MB, Plant C, Bird AC, Bhattacharya SS, Hardcastle AJ (Apr 2000). "Novel mutations of the RPGR gene in RP3 families". Human Mutation. 15 (4): 386. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200004)15:4<386::AID-HUMU23>3.0.CO;2-4. PMID 10737996.
- Rao KN, Li L, Anand M, Khanna H (2015). "Ablation of retinal ciliopathy protein RPGR results in altered photoreceptor ciliary composition". Scientific Reports. 5: 11137. Bibcode:2015NatSR...511137R. doi:10.1038/srep11137. PMC 4463945. PMID 26068394.