 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Resatorvid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
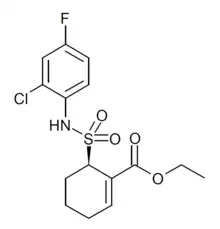
| Formula | C15H17ClFNO4S |
| Molar mass | 361.8 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Resatorvid (TAK-242) is a cyclohexane derivative that was invented by scientists at Takeda in a drug discovery campaign to identify inhibitors of the receptor TLR4.[1] It binds directly to cysteine residue 747[1] intracellularly, preventing TLR4 binding with TIRAP and thus preventing downstream signal transduction.[2]
A randomized, double-blinded Phase III trial of resatorvid in sepsis was halted early due to lack of efficacy, and the compound has become a widely used tool compound in biological research.[1]
It has antiinflammatory and neuroprotective effects in preclinical models.[3] It has been explored in preclinical studies of several forms of cancer, including multiple myeloma, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer,[4] and has been suggested for study in skin cancers.[5]
Efforts have been made to improve resatorvid by making prodrugs and deuterated derivatives.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Wang X, Smith C, Yin H (June 2013). "Targeting Toll-like receptors with small molecule agents". Chemical Society Reviews. 42 (12): 4859–4866. doi:10.1039/c3cs60039d. PMC 3665707. PMID 23503527.
- ↑ Karimy JK, Reeves BC, Kahle KT (June 2020). "Targeting TLR4-dependent inflammation in post-hemorrhagic brain injury". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets. 24 (6): 525–533. doi:10.1080/14728222.2020.1752182. PMC 8104018. PMID 32249624.
- 1 2 Miller S, Blanco MJ (June 2021). "Small molecule therapeutics for neuroinflammation-mediated neurodegenerative disorders". RSC Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (6): 871–886. doi:10.1039/d1md00036e. PMC 8221257. PMID 34223157.
- ↑ Innao V, Rizzo V, Allegra AG, Musolino C, Allegra A (February 2021). "Promising Anti-Mitochondrial Agents for Overcoming Acquired Drug Resistance in Multiple Myeloma". Cells. 10 (2): 439. doi:10.3390/cells10020439. PMC 7922387. PMID 33669515.
- ↑ Dickinson SE, Wondrak GT (2018). "TLR4-directed Molecular Strategies Targeting Skin Photodamage and Carcinogenesis". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 25 (40): 5487–5502. doi:10.2174/0929867324666170828125328. PMID 28847267. S2CID 670318.
Further reading
- Matsunaga N, Tsuchimori N, Matsumoto T, Ii M (January 2011). "TAK-242 (resatorvid), a small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 signaling, binds selectively to TLR4 and interferes with interactions between TLR4 and its adaptor molecules". Molecular Pharmacology. 79 (1): 34–41. doi:10.1124/mol.110.068064. PMID 20881006. S2CID 7818996.
- Samarpita S, Kim JY, Rasool MK, Kim KS (January 2020). "Investigation of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 inhibitor TAK-242 as a new potential anti-rheumatoid arthritis drug". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 22 (1): 16. doi:10.1186/s13075-020-2097-2. PMC 6979396. PMID 31973752.
- Feng Y, Gao J, Cui Y, Li M, Li R, Cui C, Cui J (January 2017). "Neuroprotective Effects of Resatorvid Against Traumatic Brain Injury in Rat: Involvement of Neuronal Autophagy and TLR4 Signaling Pathway". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. 37 (1): 155–168. doi:10.1007/s10571-016-0356-1. PMID 26961544. S2CID 21583205.
- Dickinson SE, Wondrak GT (2019). "TLR4-directed Molecular Strategies Targeting Skin Photodamage and Carcinogenesis". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 25 (40): 5487–5502. doi:10.2174/0929867324666170828125328. PMID 28847267. S2CID 670318.
- Kashani B, Zandi Z, Karimzadeh MR, Bashash D, Nasrollahzadeh A, Ghaffari SH (December 2019). "Blockade of TLR4 using TAK-242 (resatorvid) enhances anti-cancer effects of chemotherapeutic agents: a novel synergistic approach for breast and ovarian cancers". Immunologic Research. 67 (6): 505–516. doi:10.1007/s12026-019-09113-8. PMID 32026322. S2CID 211048929.
- Zandi Z, Kashani B, Bashash D, Poursani EM, Mousavi SA, Chahardoli B, Ghaffari SH (February 2020). "The anticancer effect of the TLR4 inhibition using TAK-242 (resatorvid) either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy: A novel therapeutic potential for breast cancer". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 121 (2): 1623–1634. doi:10.1002/jcb.29397. PMID 31535397. S2CID 202689986.</ref>