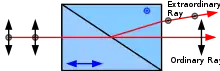
A Rochon Prism
A Rochon prism is a type of polariser. It is made from two prisms of a birefringent material such as calcite, which are cemented together.[1]
The Rochon prism was invented by and is named after Abbé Alexis Marie Rochon. It is in many ways similar to the Wollaston prism, but one ray (the ordinary ray) passes through the prism undeviated. The Sénarmont prism is similar but transmits the s-polarized ray undeviated. In both the Rochon and the Sénarmont prisms the undeviated ray is ordinary on both sides of the interface. Rochon prisms are commercially available, but for many applications other polarisers are preferred.
See also
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.