 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rubidium bromide | |
| Other names
Rubidium(I) bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.238 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| RbBr | |
| Molar mass | 165.372 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Density | 3.350 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 693 °C (1,279 °F; 966 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,340 °C (2,440 °F; 1,610 K) |
| 98 g/100 mL | |
| −56.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Rubidium fluoride Rubidium chloride Rubidium iodide Rubidium astatide |
Other cations |
Lithium bromide Sodium bromide Potassium bromide Caesium bromide Francium bromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
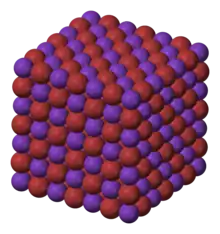
Rubidium bromide is the bromide of rubidium. It has a NaCl crystal structure, with a lattice constant of 685 picometres.[1]
There are several methods for synthesising rubidium bromide. One involves reacting rubidium hydroxide with hydrobromic acid:
- RbOH + HBr → RbBr + H2O
Another method is to neutralize rubidium carbonate with hydrobromic acid:
- Rb2CO3 + 2 HBr → 2 RbBr + H2O + CO2
Rubidium metal would react directly with bromine to form RbBr, but this is not a sensible production method, since rubidium metal is substantially more expensive than the carbonate or hydroxide; moreover, the reaction would be explosive.
References
- ↑ G. Chern; J. G. Skofronick; W. P. Brug; S. A. Safron (1989). "Surface phonon modes of the RbBr(001) crystal surface by inelastic He-atom scattering". Phys. Rev. B. 39 (17): 12838–12844. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.39.12838. PMID 9948158.
- WebElements. URL accessed March 1, 2006.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.