Ruby Hill | |
|---|---|
 Remains of Ruby Hill, Nevada | |
 Ruby Hill  Ruby Hill | |
| Coordinates: 39°30′17″N 115°59′10″W / 39.50472°N 115.98611°W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
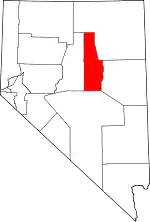
| State | Nevada |
| County | Eureka[1] |
| Elevation | 6,916 ft (2,108 m) |
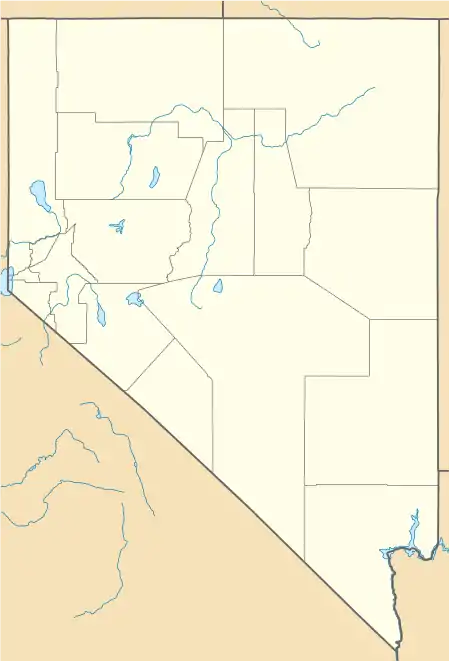
Ruby Hill is a ghost town in Eureka County, in the central part of the U.S. state of Nevada, approximately 2.6 mi (4.2 km) west of the town of Eureka, Nevada. In 1910, the Ruby Hill Railroad was washed out, after which there were only three businesses in town.[2]
History
In 1865, an Indian showed a piece of "mineral-bearing" rock to Owen Farell, M. G. Cough, and Alonzo Monroe. The men recognized that there might be more similar rocks. For ten dollars, they persuaded the Indian to show them where he had found the rock. The Indian directed them to a location about two and a half miles west of the township of Eureka, Nevada.[3] On this site, the northwestern side of Prospect Mountain, the Buckeye and Champion mines were established. In the early 1870s, a mining town followed. The town took its name from the ruby silver discovered there and became known as Ruby Hill.[4] A post office was built and services commenced on September 23, 1873, until its closure on November 30, 1901. The town was served by rail, and the route was named after Ruby Hill. The railroad transported the ore produced to the smelters in Eureka.[2]



Ruby Hill was part of Eureka County. The county was created in 1873 from part of Lander County. It is situated in the middle of the state of Nevada, running north and south in a columnar area, extending "northward from Nye County to the Tuscaroara Mountains, to north of the Humboldt River." The county was formed to help the residents of the township of Eureka. Before the creation of Eureka County, the residents had to travel to Lander County for county government business. For the convenience of the residents of Eureka, the new county was formed, and was named after the town of Eureka.[5] This in turn aided the residents of Ruby Hill.
Mining boomed in Ruby Hill around 1878, when the population grew to its maximum of 2,500 residents. The majority of the 900 residents were miners and their respective families. The town was a bustling center with many stores, schools, churches, a theater, a miner’s union, a brewery, and a printing shop. In the printing shop, the first copies of the Mining Report were produced. It was later renamed the Mining News. By 1880, the population of Ruby Hill had declined, and by 1885, 700 remained. They continued to mine until the end of the 19th century. Miners were able to lease land and prospect for ore. Some of them did find an untouched vein of ore.[2]
By the start of the 20th century, the population of the town was so small that only three businesses remained. In 1910 a powerful storm washed away the railroad and buildings, and many townspeople left. Of the buildings left standing, only one was built in the 19th century.[2]
This small mining camp was active for many years and produced nearly $200,000. The initial location was the Cow and Calf Mine discovered in 1871. The Ruby Hill Mining District was organized in July 1872. By August, Ruby Hill reached its peak population of approximately 150. The town had two restaurants, two stores, a bar, and a boardinghouse. By fall, the smaller mines were depleted and only the four largest mines were producing. Legal problems forced the mines to close and emptied the once bustling camp.
In the early 1880s some mines reopened. That was short lived, and by 1885 only two residents remained. There was intermittent activity until 1928, when all mining activity ended. Because the camp was active for only a few years at a time, few permanent buildings were constructed. Most of the mines are high in the mountains, and access is extremely difficult.
References
- 1 2 3 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Ruby Hill
- 1 2 3 4 Paher, Stanley W. (1970). Nevada Ghost Towns & Mining Camps. p. 185.
- ↑ W. B. Lardner and M. J. Brock, History of Placer and Nevada counties, California : with Biographical Sketches of the Leading Men and Women of the Counties Who Have Been Identified With Their Growth and Development From the Early Days to the Present (Los Angeles: Historic Record Company, 1924).
- ↑ Federal Writers' Project (1941). Origin of Place Names: Nevada (PDF). W.P.A. p. 35.
- ↑ Rufus Wood Leigh, Nevada Place Names: Their Origin and Significance, (Salt Lake City: Deseret News Press, 1964).