Hatsukaichi
廿日市市 | |
|---|---|
 Top:Hayatani Shrine, Itsukushima Shrine, Bottom:Mount Aki Kanmuri, Memorial source in Yuhama Spa, Oze River Dam (all item of left to right) | |
 Flag  Emblem | |
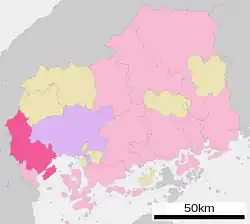
Location of Hatsukaichi in Hiroshima Prefecture | |
 | |
 Hatsukaichi Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 34°20′54″N 132°19′54″E / 34.34833°N 132.33167°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūgoku (San'yō) |
| Prefecture | Hiroshima |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Tarō Matsumoto (from November 2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 489.48 km2 (188.99 sq mi) |
| Population (May 1, 2023) | |
| • Total | 116,087 |
| • Density | 240/km2 (610/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 1-11-1 Shimohera, Hatsukaichi-shi, Hiroshima-ken 738-8501 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Flower | Satsuki azalea |
| Tree | Sakura |

Hatsukaichi (廿日市市, Hatsukaichi-shi) is a city located in Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 May 2023, the city had an estimated population of 116,087 in 53320 households and a population density of 240 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city is 489.48 square kilometres (188.99 sq mi).
Geography
Hatsukaichi is located in far southwestern Hiroshima Prefecture. In the north, the spine of the Chugoku Mountains borders Shimane and Yamaguchi prefectures, and in the south is the coastline of the Seto Inland Sea (Hiroshima Bay). While the coastal areas are becoming more urbanized, the inland rural areas are undergoing marked depopulation.
Adjoining municipalities
Demographics
Per Japanese census data, the population of Hatsukaichi has more than doubled since 1960.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 48,201 | — |
| 1960 | 49,417 | +2.5% |
| 1970 | 57,218 | +15.8% |
| 1980 | 76,592 | +33.9% |
| 1990 | 101,630 | +32.7% |
| 2000 | 114,981 | +13.1% |
| 2010 | 114,062 | −0.8% |
| Hatsukaichi population statistics[2] | ||
Climate
| Climate data for Hatsukaichi (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1978−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.2 (63.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
29.1 (84.4) |
31.5 (88.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.7 (98.1) |
35.4 (95.7) |
29.4 (84.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
19.5 (67.1) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
8.1 (46.6) |
12.2 (54.0) |
18.1 (64.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.8 (78.4) |
29.3 (84.7) |
30.7 (87.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
15.3 (59.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
18.9 (66.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
2.4 (36.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.0 (69.8) |
14.8 (58.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.5 (38.3) |
12.9 (55.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.9 (26.8) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.6 (69.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
7.7 (45.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −11.7 (10.9) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.5 (50.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.5 (2.54) |
80.4 (3.17) |
144.6 (5.69) |
180.0 (7.09) |
212.1 (8.35) |
270.0 (10.63) |
343.0 (13.50) |
189.8 (7.47) |
210.9 (8.30) |
116.7 (4.59) |
82.0 (3.23) |
69.8 (2.75) |
1,963.8 (77.31) |
| Average rainy days | 8.6 | 9.6 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 9.4 | 12.6 | 12.3 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.9 | 117.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 116.9 | 127.6 | 165.0 | 189.2 | 210.0 | 143.3 | 149.8 | 183.3 | 151.9 | 167.6 | 142.2 | 124.5 | 1,871.3 |
| Source: JMA[3][4] | |||||||||||||
History
The area of Hatsukaichi is part of ancient Aki Province. Itsukushima Shrine developed greatly at the end of the Heian period under the patronage of Taira no Kiyomori and gained influence in the region. As the shrine was occasionally destroyed by fire or natural disasters, the Kamakura shogunate, orderd many metal casters moved to the area on the opposite bank (present-day Honmachi, Hatsukaichi City), and the accumulation of living and rebuilding materials such as salt and wood began. Since the last day of the festival held four times a year at Itsukushima Shrine was the 20th, a market began to be held on the 20th of each month as early as the middle of the Kamakura period, and the market on the 20th is called 'Hatsukaichi.' This name appears in official documents from 1454, and since this period, Hatsukaichi has developed as a port and a timber industry town based on the collection of timber from the western Chugoku Mountains. During the Edo Period, the area was part of the holdings of Hiroshima Domain. Following the Meiji restoration, the town of Hatsukaichi was established within Saeki District, Hiroshima on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the modern municipalities system. Hatsukaichi merged with four neighboring villages to become the city of Hatsukaichi on April 1, 1988.
On March 1, 2003, the town of Saeki and the village of Yoshiwa, both from Saeki District, merged into the expanded city of Hatsukaichi. On November 3, 2005, the towns of Miyajima and Ōno (both from Saeki District) were merged into Hatsukaichi. Therefore, Saeki District was dissolved as a result of this merger.
Government
Hatsukaichi has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 28 members. Hatsukaichi contributes two members to the Hiroshima Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of the Hiroshima 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
Hatsukaichi is one of the cities that make up the Hiroshima metropolitan area, and was formerly an industrial city noted for its timber industry, wood processing and food processing, as well as commercial fishing. It is increasing a commuter town for neighboring Hiroshima. However, after the mergers of 2003 and 2005, the city gained a large agricultural hinterland, as well as the major tourist attraction of Itsukushima Shrine.
Education
Hatsukaichi has 16 public elementary schools and seven public junior high schools operated by the city government, and four public high schools operated by the Hiroshima Prefectural Board of Education. There is also one private high school. The prefecture also operates one special education school for the handicapped. The Japanese Red Cross Hiroshima College of Nursing and Sanyo Women's College are located in Hatsukaichi.
Transportation
Railway
![]() JR West (JR West) - San'yō Main Line
JR West (JR West) - San'yō Main Line
- Hatsukaichi - Miyauchikushido - Ajina - Miyajimaguchi - Maezora - Ōnoura
Highways
Ferry
- JR Miyajima Ferry and Miyajima Matsudai Kisen connect between Miyajimaguchi and Miyajima.
Media
Sister city relations
 - Masterton, Greater Wellington, New Zealand, sister city since 1998
- Masterton, Greater Wellington, New Zealand, sister city since 1998 - Mont Saint-Michel, Normandy, France
- Mont Saint-Michel, Normandy, France
Local attractions

- Itsukushima Shrine - an UNESCO World Heritage Site on the island of Itsukushima (also known as Miyajima) - one of the three most beautiful sites in Japan.
- Marine Plaza Miyajima - an aquarium on Miyajima
- Miyajima Natural Botanical Garden
- Miyao Castle ruins, site of the Battle of Miyajima (1555)
- Miyajima Underwater Firework Festival, held in mid-August[5]
- Hatsukaichi City is considered to be the birthplace of kendama, a traditional Japanese toy.
Noted people from Hatsukaichi
- Tadamichi Yamamoto, diplomat
- Yoshirō Edamasa, movie director
References
- ↑ "Hatsukaichi city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- ↑ Hatsukaichi population statistics
- ↑ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ↑ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ↑ "Miyajima Water Fireworks Display". Retrieved July 20, 2012.
External links
 Media related to Hatsukaichi, Hiroshima at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Hatsukaichi, Hiroshima at Wikimedia Commons- Hatsukaichi city official website (in Japanese)
- Le Mont Saint-Michel (in French)
- The 150 year anniversary of France and Japan in 2008 Archived 2008-03-22 at archive.today (in French)
 Geographic data related to Hatsukaichi at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Hatsukaichi at OpenStreetMap
