 The cover of the paperback edition of The Return of the Shadow | |
| Editor | Christopher Tolkien |
|---|---|
| Author | J. R. R. Tolkien |
| Cover artist | Roger Garland (paperbacks) John Howe (paperbacks) |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Language | English |
| Series | The History of Middle-earth |
| Subject | Tolkien's legendarium |
| Genre | High fantasy Literary analysis |
| Publisher | George Allen & Unwin (UK) |
Publication date | 1988 (The Return of the Shadow) 1989 (The Treason of Isengard) 1990 (The War of the Ring) 1992 (Sauron Defeated) |
| Media type | Print (hardback and paperback) |
| Pages | 512 (The Return of the Shadow) 512 (The Treason of Isengard) 496 (The War of the Ring) 496 (Sauron Defeated) |
| ISBN | 978-0261102248 (The Return of the Shadow) ISBN 978-0261102200 (The Treason of Isengard) ISBN 978-0261102231 (The War of the Ring) ISBN 978-0261103054 (Sauron Defeated) |
| Preceded by | The Lost Road and Other Writings |
| Followed by | Morgoth's Ring |
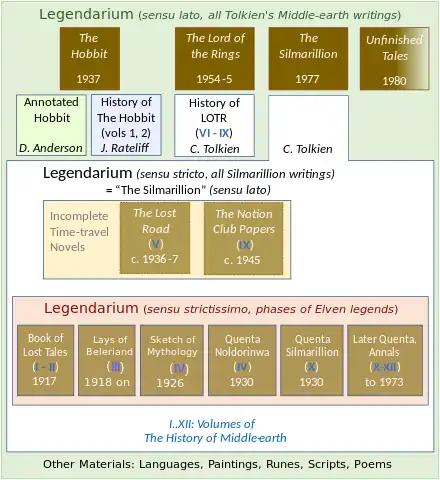
The History of The Lord of the Rings is a four-volume work by Christopher Tolkien published between 1988 and 1992 that documents the process of J. R. R. Tolkien's writing of The Lord of the Rings. The History is also numbered as volumes six to nine of The History of Middle-earth ("HoME").
Contents
The volumes are:
- (HoME 6) The Return of the Shadow (1988)
- (HoME 7) The Treason of Isengard (1989)
- (HoME 8) The War of the Ring (1990)
- (HoME 9) Sauron Defeated (1992)[lower-alpha 1]
The first volume of The History encompasses three initial stages of composition or, as Christopher Tolkien calls them, "phases", including what Tolkien later called "the crucial chapter" which sets up the central plot, "The Shadow of the Past".[T 1] It finishes with the Fellowship of the Ring entering the Mines of Moria.
The second volume continues to the meeting with Théoden king of Rohan, and includes the invention and evolution of Lothlórien and Galadriel; plans for Frodo and Sam's progress to Mordor; the invention and evolution of Treebeard, the Ents, and Fangorn; discussions of the original map of Middle-earth at the end of the Third Age; and of the evolution of Cirth in an appendix.
The third volume, The War of the Ring continues to the opening of the Black Gate.
The last volume finishes the story and features the rejected Epilogue, in which Sam answers his children's questions. It also includes The Notion Club Papers (a time-travel story related to Númenor), a draft of the Drowning of Anadûnê, and the only extant account of Tolkien's fictional language Adûnaic.
Some paperback editions of the fourth volume, retitled The End of the Third Age, include only the materials for The Lord of the Rings.[lower-alpha 2]
The original idea was to release The History of The Lord of the Rings in three volumes, not four. When The Treason of Isengard was first published in paperback Volume 8 was to be called Sauron Defeated and was to be the last volume.
Some information concerning the appendices and a soon-abandoned sequel to the novel can also be found in volume 12, The Peoples of Middle-earth.
Titles
The titles of the volumes derive from discarded titles for the separate books of The Lord of the Rings. J. R. R. Tolkien conceived the latter as a single volume comprising six "books" plus extensive appendices, but the original publisher split the work into three, publishing two books per volume with the appendices included in the third. The titles proposed by Tolkien for the six books were: Book 1, The First Journey or The Ring Sets Out; Book 2, The Journey of the Nine Companions or The Ring Goes South; Book 3, The Treason of Isengard; Book 4, The Journey of the Ring-Bearers or The Ring Goes East; Book 5, The War of the Ring; and Book 6, The End of the Third Age. The title The Return of the Shadow was a discarded title for Volume 1.
Three of the titles of the volumes of The History of The Lord of the Rings were also used as book titles for the seven-volume edition of The Lord of the Rings: The Treason of Isengard for Book 3, The War of the Ring for Book 5, and The End of the Third Age for Book 6.
Tengwar inscriptions
There is an inscription in Fëanorian characters (Tengwar, an alphabet Tolkien devised for the High-Elves) on the title page of each of the volumes of History of Middle-earth, written by Christopher Tolkien and describing the contents of the book.
| Vol. | Title | Inscription |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | The Return of the Shadow | In the Return of the Shadow are traced the first forms of the story of the Lord of the Rings; herein the journey of the Hobbit who bore the Great Ring, at first named Bingo but afterwards Frodo, is followed from Hobbiton in the Shire through the Old Forest to Weathertop and Rivendel, and ends in this volume before the Tomb of Balin, the Dwarf-lord of Moria. |
| 7 | The Treason of Isengard | In The Treason of Isengard the story of the Fellowship of the Ring is traced from Rivendell through Moria and the Land of Lothlórien to the time of its ending at Salembel beside Anduin the Great river, then is told of the return of Gandalf Mithrandir, of the meeting of the hobbits with Fangorn and of the war upon the Riders of Rohan by the traitor Saruman. |
| 8 | The War of the Ring | In the War of the Ring is traced the story of the history at Helm's Deep and the drowning of Isengard by the Ents, then is told of the journey of Frodo with Samwise and Gollum to the Morannon, of the meeting with Faramir and the stairs of Cirith Ungol, of the Battle of the Pelennor Fields and of the coming of Aragorn in the fleet of Umbar. |
| 9 | Sauron Defeated | In this book is traced first the story of the destruction of the One Ring and the Downfall of Sauron at the End of the Third Age. Then follows an account of the intrusion of the Cataclysm of the West into the deliberations of certain scholars of Oxford and the Fall of Sauron named Zigûr in the Drowning of Anadûne. |
Tolkien's creativity
The History of The Lord of the Rings reveals much of the slow, aggregative nature of Tolkien's creativity. As Christopher Tolkien noted of the first two volumes, Tolkien had eventually brought the story up to Rivendell, but still "without any clear conception of what lay before him".[T 2] He also noted how, on the way, his father could get caught up in a "spider's web of argumentation"[T 3] – what Tom Shippey described as getting "bogged down in sometimes strikingly unnecessary webs of minor causation".[1] Thus (for example) the character eventually known as Pippin Took was, in a series of rewriting and of deleted adventures, variously known as Odo, Frodo, Folco, Faramond, Peregrin, Hamilcar, Fredegar, and Olo – the figures also being Boffins and Bolgers, as well as Tooks.[T 4]
Only with the Breaking of the Fellowship did fluency finally arrive for Tolkien, his son recording how chapters were suddenly "achieved with far greater facility than any previous part of the story".[T 5] Thereafter Tolkien's problem was rather one of selecting between alternative accounts, so as to produce the best effect – two episodes in the "fascinating study"[2] Sauron Defeated that were eventually deleted being the pardoning of Saruman, and an awards ceremony at the book's close.[1]
Notes
- ↑ Volume 9 is also published as The End of the Third Age; that edition omits material not related to The Lord of the Rings.
- ↑ Editions by HarperCollins and Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
References
Primary
- ↑ The Lord of the Rings, 2nd edition, "Foreword".
- ↑ Christopher Tolkien (ed.) The Treason of Isengard (London 1989) p. 18
- ↑ Christopher Tolkien (ed.) The Treason of Isengard (London 1989) p. 52
- ↑ Christopher Tolkien (ed.) The Treason of Isengard (London 1989) p. 31
- ↑ Christopher Tolkien (ed.) The Treason of Isengard (London 1989) p. 410 and compare p. 411-14
Secondary
- 1 2 Tom Shippey, The Road to Middle-Earth (London 1992) pp. 282-285
- ↑ "Reviews: Sauron Defeated by JRR Tolkien (The History of The Lord of the Rings: Part 4)". Fantasy Book Review. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
Sources
- Shippey, Tom (2005) [1982]. The Road to Middle-Earth (Third ed.). HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-26110-275-0.
- Whittingham, Elizabeth A. (2017). The Evolution of Tolkien's Mythology: A Study of the History of Middle-earth. McFarland. ISBN 978-1-47661-174-7.

