Sidoarjo
Kabupaten Sidoarjo | |
|---|---|
| Sidoarjo Regency | |
.jpg.webp) | |
 Seal | |
| Motto: Sidoarjo Bersih Hatinya | |
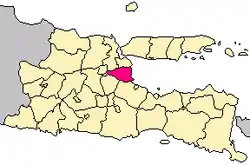 Location within East Java | |
Interactive map outlining Sidoarjo Regency | |
| Coordinates: 7°27′S 112°42′E / 7.450°S 112.700°E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Capital | Sidoarjo |
| Government | |
| • Regent | H.Ahmad Muhdlor Ali |
| • Vice Regent | Subandi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 719.34 km2 (277.74 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 2,033,760 |
| • Density | 2,800/km2 (7,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (IWST) |
| Area code | (+62) 31 |
| Website | sidoarjokab.go.id |
Sidoarjo Regency (Javanese: ꦑꦧꦸꦥꦠꦺꦤ꧀ꦱꦶꦢꦲꦂꦗ, romanized: Kabupatèn Sidaharja) is a regency in East Java, Indonesia. It is bordered by Surabaya city and Gresik Regency to the north, by Pasuruan Regency to the south, by Mojokerto Regency to the west and by the Madura Strait to the east. It has an area of 719.34 km2, making it the smallest regency in East Java.[1]
As at the 2010 census, Sidoarjo Regency had a population of 2,191,489[2] while the 2020 census showed a small decline to 2,033,760,[3] notably in the northern part of the regency immediately bordering Surabaya; the official estimate as at mid 2022 showed a further decline to 1,955,002 (comprising 979,567 males and 975,435 females).[1] The regency is part of the urban region surrounding Surabaya, known as 'Gerbangkertosusila' area.[4]
Administrative districts
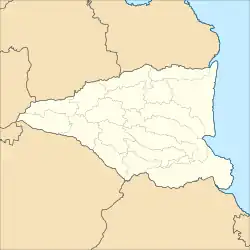
The Sidoarjo Regency is divided into eighteen administrative districts (kecamatan). The districts are tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 census[2] and the 2020 census,[3] together with the official estimates as at mid 2022.[1] The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (totaling 322 rural desa and 31 urban kelurahan), and its post code.
| Kode Wilayah | Name of District (kecamatan) | Area in km2 | Pop'n census 2010 | Pop'n census 2020 | Pop'n estimate mid 2022 | Admin centre | No. of villages | Post code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.15.01 | Tarik | 39.73 | 61,032 | 69,189 | 66,144 | Mergosari | 20 | 61265 |
| 35.15.02 | Prambon | 29.89 | 68,576 | 79,952 | 76,446 | Prambon | 20 | 61264 |
| 35.15.03 | Krembung | 27.90 | 58,336 | 69,887 | 66,858 | Mojoruntul | 19 | 61275 |
| 35.15.04 | Porong | 30.71 | 64,390 | 73,446 | 69,271 | Juwetkenongo | 19 (a) | 61274 |
| 35.15.05 | Jabon | 82.92 | 49,567 | 56,266 | 54,054 | Dukuhsari | 15 | 61276 |
| 35.15.06 | Tanggulangin | 29.78 | 83,304 | 89,804 | 85,476 | Kalitengah | 19 | 61272 |
| 35.15.07 | Candi | 42.86 | 145,155 | 153,423 | 149,219 | Gelam | 24 | 61271 |
| 35.15.09 | Tulangan | 31.31 | 84,582 | 102,339 | 97,960 | Kenongo | 22 | 61273 |
| 35.15.10 | Wonoayu | 30.29 | 71,822 | 85,586 | 81,395 | Wonoayu | 23 | 61261 |
| 35.15.14 | Sukodono | 32.85 | 110,596 | 121,859 | 118,447 | Anggaswangi | 19 | 61216 - 61258 |
| 35.15.08 | Sidoarjo | 62.03 | 193,469 | 201,120 | 191,247 | Sidokumpul | 24 (b) | 61212 - 61234 |
| 35.15.15 | Buduran | 43.65 | 91,931 | 98,710 | 96,580 | Banjarkemantren | 15 | 61252 |
| 35.15.17 | Sedati | 79.23 | 92,786 | 96,636 | 93,061 | Pulungan | 16 | 61253 |
| 35.15.18 | Waru | 30.59 | 231,309 | 200,754 | 192,613 | Janti | 17 | 61256 |
| 35.15.16 | Gedangan | 24.01 | 132,971 | 120,003 | 116,034 | Keboansikep | 15 | 61254 |
| 35.15.13 | Taman | 31.36 | 213,224 | 207,815 | 197,892 | Bebekan | 24 (c) | 61212 - 61257 |
| 35.15.11 | Krian | 25.89 | 131,281 | 130,930 | 126,718 | Kraton | 22 (d) | 61262 |
| 35.15.12 | Balongbendo | 44.34 | 66,841 | 76,050 | 72,587 | Wonokupang | 20 | 61263 |
| Totals | 719.34 | 2,191,489 | 2,033,764 | 1,955,002 | Sidoarjo | 353 |
Notes: (a) comprising 6 kelurahan (Gedang, Jatirejo, Juwetkenongo, Mindi, Porong and Siring) and 13 desa.
(b) comprising 14 kelurahan (Bulusidokare, Celep, Cemengkalang, Gebang, Lemahputro, Magersari, Pekauman, Pucang,
Pucanganom, Sekardangan, Sidokare, Sidoklumpuk, Sidokumpul and Urangagung) and 8 desa.
(c) comprising 8 kelurahan (Bebekan, Geluran, Kalijaten, Ketegan, Ngelom, Sepanjang, Taman and Wonocolo) and 16 desa.
(d) including 3 kelurahan (Kemasan, Krian and Tambak Kemerakan).
Economy
As a satellite region and part of Greater Surabaya, Sidoarjo economy is valued at 197.24 Trillion IDR in 2020 and is the second-largest[5] in East Java after Surabaya.
Primary Sector
Although Sidoarjo Regency's land area is relatively small and densely populated, the primary sector still maintains a role in Sidoarjo's economy. Agriculture is mainly produced in western and south-western part of Sidoarjo mainly Tulangan District, Krembung District, and Balongbendo District. During colonial era, Sidoarjo was famous for sugarcane production and it was hosted several sugar mills owned by Colonial government. After Independence, Indonesia government nationalised all of sugar mills in Sidoarjo. Sugarcane production sector peaked in 70s and gradually declining since then, due to inflows of manufacturing investment and rapid urbanization that reduced sugarcane planting area. Today, agricultural crops that still produced in Sidoarjo are Rice, Banana, Papaya, Cassava, and several lowland vegetables.
Fisheries also still maintain a role. In the past, Sidoarjo was known as a fishing town, but the fishing sector was slowly declining as Sidoarjo became more urbanized. Today, fishing has been replaced by aquaculture as the main source of fish in Sidoarjo. Highly productive aquaculture is mainly produced in the eastern part of Sidoarjo Regency, and the main product is Milkfish and farmed shrimp which are mostly exported to the US and Japan. Sidoarjo is also famous for its processed fishery products, such as prawn cracker, fish cracker, shrimp paste and petis.
Mining sector could be neglected as it contributes very small to Sidoarjo economy. The main mining sector is natural gas, which is produced in Porong District. There are also several sand miners that operate in Jabon District.
Secondary Sector
Manufacturing is a main sector of Sidoarjo economy with contribution nearly 40%. Sidoarjo manufacturing production is diversified and range from furniture to electronics products. There are numerous manufacturing plants in Sidoarjo. Among this are : Jatim Taman Steel (Steel Manufacturer), Avian (Paints and building material), Tunggal Djaja (Paints Production), Maspion (Household durable goods), Japfa Comfeed (Feedmills and poultry), Interbat (Pharmaceuticals), Integra (Furniture), Tjiwi Kimia (Paper), Kimberly-Clark's Softex (Non-durable consumer goods), Unicharm (Non-durable consumer goods), Polygon Bikes (Bikes), Alumindo (Aluminium products), Sekar Group (Food processing), Hisamitsu (Pharmaceutical), Lighting Solutions (Lamp), ECCO (Footwear), Samator (Industrial gas and chemicals), Bernofarm (Pharmaceutical), Muntjul Diamond (Vehicle body), Charoen Pokphand (Agribusiness) and many more.
There are thousands small and medium manufacturers established in Sidoarjo. Garments, Food Processing, Footwear, Apparel, and Furniture are products that usually produced by small and medium manufacturers in Sidoarjo. There are also many small and medium manufacturers that produces Traditional Herbs, Machinery, Packaging, and Metal products.
During colonial era, there are ten sugarmills in Sidoarjo and the oldest is Watu Tulis Sugarmills that built in 1838.[6] Today, there are remain three sugarmills that still operated in Sidoarjo. Among this are New Candi Sugarmills that built in 1911, Krembung Sugarmills, and Watu Tulis Sugarmills.
Tertiary Sector
The main tertiary sectors in Sidoarjo are wholesaling and retailing, food services, education, and financial services. As Sidoarjo is getting more urbanized, the tertiary sector is predicted to grow significantly. The fastest growth in the tertiary sector is recording in experience-related services, such as food services (notably restaurant, cafe) and movie theater. Education Services are also predicted to grow, as several private tutoring companies are opening a branch in Sidoarjo and private schools are gaining more students, due to increasingly population, income, and lack of capacity in state schools.
Lapindo Mud flow
Since May 2006, more than 10,000 people in the Porong District have been displaced by the hot mud flowing from a natural gas well being drilled by Lapindo Brantas, an oil well company that is part of a conglomerate owned by Coordinating Minister for the People's Welfare Aburizal Bakrie.[7] Gas and hot mud started spewing from the well on May 28, when the drill penetrated a layer of liquid sediment. Attempts to pump concrete down the well did not stop the flow. While some scientists have speculated that the earthquake that struck Yogyakarta on May 27, the day before the well erupted, may have cracked the ground, creating potential pathways for the mud to reach the surface, others have suggested that the drilling procedure was faulty by not using a casing. This is likely to be incorrect as technical papers on the subject showed that there were up to four sets of casing installed and cemented in the well. Some 50,000 cubic metres of hot mud were erupting every day as of August; in September, the amount increased to some 125,000 cubic metres daily.[8] On September 26 barriers built to hold back the mud failed, resulting in the flooding of more villages. Gus Maksum, one of the thousands of Sidoarjo villagers displaced by the mud flow gives a detailed first-hand account of the first year of the disaster in his memoir Titanic Made By Lapindo.[9] As of late September 2006 scientists are saying that the eruption may be a mud volcano forming, and may be impossible to stop.[10][11][12]
Climate
Sidoarjo has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) with moderate to little rainfall from May to November and heavy rainfall from December to April.
| Climate data for Sidoarjo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.8 (87.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.9 (91.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.7 (89.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.7 (80.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.0 (80.6) |
26.8 (80.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.7 (72.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.6 (69.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.0 (71.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 303 (11.9) |
296 (11.7) |
268 (10.6) |
174 (6.9) |
116 (4.6) |
66 (2.6) |
40 (1.6) |
10 (0.4) |
7 (0.3) |
30 (1.2) |
110 (4.3) |
232 (9.1) |
1,652 (65.2) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[13] | |||||||||||||
References
- 1 2 3 4 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023, Kabupaten Sidoarjo Dalam Angka 2023 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.3515)
- 1 2 Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- 1 2 Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ↑ Mega Urbanization Archived 2007-10-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Perekonomian Kota Surabaya Terbesar di Jawa Timur pada 2020 | Databoks". databoks.katadata.co.id (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2021-12-09.
- ↑ Hadi, Lukman. "Pabrik Gula di Sidoarjo Sudah Ada Jauh Sebelum Indonesia Merdeka - Surabaya Network". Pabrik Gula di Sidoarjo Sudah Ada Jauh Sebelum Indonesia Merdeka - Surabaya Network (in Indonesian). Retrieved 2021-12-09.
- ↑ The Jakarta Post: Bakrie name at stake - URL retrieved October 13, 2006
- ↑ Katastrophen: Sintflut aus Matsch (Spiegel Online, in German) - URL retrieved October 13, 2006
- ↑ Gus Maksum's Titanic Made By Lapindo spotlights Sidoarjo - URL retrieved September 15, 2010
- ↑ Mud volcano floods Java - URL retrieved September 28, 2006
- ↑ Indonesia mudflow breaks barriers, injures six - URL retrieved September 28, 2006
- ↑ New Indonesia Calamity: A Man-Made Mud Bath - URL retrieved October 6, 2006
- ↑ "Climate: Sidoarjo". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
{Culinary} Sidoarjo has lots of worth to culinary tastes, from sour and spicy, to sweet culinary. Sour food in Sidoarjo can be described as a fruity dish called Rujak, and the most famous ones are Lontong Kupang, Sate Kerang, and Lontong Balap which are very spicy. And Klepon is a sweet dessert wrapped by a coconut zest.