| Sinus tarsi syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | STS |
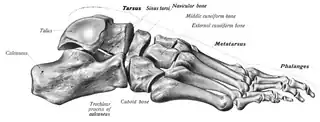 | |
| A medical diagram of the foot bones, with the sinus tarsi labeled (upper right; next to Tarsus label) | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics, podiatry |
| Symptoms | Pain or tenderness in the sinus tarsi |
| Causes | Ankle sprain; pronation; flat foot; excessive physical activity; PTTD |
| Diagnostic method | Physical examination |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, orthotics, anti-inflammatories, steroids |
Sinus tarsi syndrome is the clinical disorder of pain and tenderness in the sinus tarsi, which is a lateral tunnel in the foot at the junction of the hindfoot and the midfoot, between the ankle and the heel.[1][2] Most of the time, sinus tarsi syndrome onsets after ankle sprains, however there can be other causes.[3] There are a variety of treatments, divided into conservative treatments such as physical and orthotic therapy, and more invasive ones such as cortisone injections.[4] The condition is somewhat poorly understood and is subject to heavy debate in the medical community.[5]
Causes
Sinus tarsi syndrome can have a variety of causes. The most common is an inversion (rolling out) ankle sprain, which makes up 70-80% of cases, followed by pronation of the foot, which is responsible for about 20-30% of cases.[3] More rarely, excessive physical activity and other forms of foot trauma/chronic ankle injury are thought to be the cause.[1][6]
In the case of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction causing flatfoot, sinus tarsi syndrome can also develop due to the disruption in the entire structure of the foot.[4]
The condition is also thought to be caused by ankle/subtalar joint instability causing inflammation in the area.[7]
Symptoms
Sinus tarsi syndrome is characterized by pain, tenderness, and instability/aggravation of the pain when walking on uneven surfaces or during weight-bearing activity. The pain will be also aggravated by inversion (turning in) and eversion (turning out). Looseness of the ankle and foot joints can also occur.[3] There is also often the presence of ligament tears, arthrofibrosis, ganglion cysts, or degeneration of the joints. Occasionally, peroneal spasms, valgus hindfoot, and limited varus motion can also be present.[8]
Diagnosis
X-ray can show some impingement in the sinus tarsi area.[4] Other diagnostic tests include: bone scans, CT scans, and MRI evaluation. Doctors may inject local anesthetic to localize the problem to the sinus tarsi.[3] Radiopharmaceuticals can also be used to identify inflammation.[1] Ankle arthroscopy may also be used to locate damaged tissue. Diagnosis is often a process of elimination as sinus tarsi syndrome is rarely a definitive disorder.[3]
Treatment
Conservative treatments
Conservative (non-surgical) treatments are often considered first. Possible treatments include:[3][4][9]
- Period of immobilization (rest)
- Activity moderation
- Supportive footwear
- Ankle sleeves/braces
- Orthotic therapy
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Physical therapy
However, while conservative treatments are often effect, resistant cases may require more invasive treatments such as:[1][3][4][9]
- Corticosteroid injections into the tarsal canal
- Oral steroids
- Custom orthoses
- Cryotherapy
These forms of treatment, while being invasive and expensive, are known to be very effective.
Surgical treatments
Surgical treatments are very rare and reserved for highly resistant cases. Surgery can be open (via an incision) or closed (via arthroscopy).[3] In cases of flatfoot, sinus tarsi syndrome is complicated by the collapse of the arches. In these cases, surgery includes debridement (cleaning out) of the sinus tarsi and possible reconstruction of the foot. Surgery can also include debridement of bone spurs as well.[4]
In cases where joint insufficiency causes the syndrome, surgery is often very effective.[7]
Prognosis
If treated, sinus tarsi syndrome has an excellent prognosis.[10] Full recovery is to be expected, though some patients will need rehabilitation.[1] However, relapse can occasionally occur, especially if only conservative treatments are undergone.[8] Sinus tarsi syndrome can be misdiagnosed as a chronic ankle sprain. Untreated sinus tarsi syndrome can develop into chronic ankle pain and disability.[9]
History
Sinus tarsi syndrome was first studied by Dr. Denis O'Connor in 1957. O'Connor claimed conservative treatment was ineffective and surgery was the only effective option, describing a surgery in which the surgeon resects the superficial ligamentous floor and cleans out the fat pad. O'Connor claimed all 14 patients this surgery was performed on reported relief of their symptoms. While there is not a lot of consensus in the medical community (and the disorder continues to be understudied), other treatment options, including conservative treatments, have been to proven to be viable in the time since.[5]
Since its first description, the causes of the syndrome have also been in dispute. In 1960, Brown proposed that herniation caused the pain and discomfort associated with the syndrome. In 1981, Taillard et al describes ligament tearing as a cause. Further on, Schwarzenbach et al described scarring around the veins to be the source of pain.[11]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Schubert, Roberto. "Sinus tarsi syndrome | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. doi:10.53347/rid-16623. Retrieved 2022-12-22.
- ↑ Khan, Imran; Peters, Jonathan; Welck, Matt; Saifuddin, Asif (April 2023). "Sinus tarsi and sinus tarsi syndrome: An imaging review". European Journal of Radiology. 161: 110725. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.110725. ISSN 0720-048X. PMID 36773427. S2CID 256591305.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "What is Sinus Tarsi Syndrome, Testing and Treatment". www.aapsm.org. Retrieved 2022-12-22.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Sinus Tarsi Syndrome". The Foot and Ankle Clinic. Retrieved 2022-12-22.
- 1 2 Arshad, Z; Bhatia, M (August 2021). "Current concepts in sinus tarsi syndrome: A scoping review". Foot and Ankle Surgery. 27 (6): 615–21. doi:10.1016/j.fas.2020.08.013. PMID 32978087. S2CID 221937877.
- ↑ Helgeson, Kevin (February 2009). "Examination and intervention for sinus tarsi syndrome". North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 4 (1): 29–37. ISSN 1558-6162. PMC 2953318. PMID 21509118.
- 1 2 Pisani, Giacomo; Pisani, Pier Carlo; Parino, Enrico (January 2005). "Sinus tarsi syndrome and subtalar joint instability". Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery. 22 (1): 63–77. doi:10.1016/j.cpm.2004.08.005. PMID 15555844.
- 1 2 Yang, C; Huang, Q; Cao, Y; Li, X; Zhu, Y; Xu, X (August 2021). "Staged surgical management of sinus tarsi syndrome: our experience of 273 cases". Annals of Palliative Medicine. 10 (8): 8909–18. doi:10.21037/apm-21-1694. ISSN 2224-5839. PMID 34488378. S2CID 237431608.
- 1 2 3 Klausner, VB; McKeigue, ME (May 2000). "The sinus tarsi syndrome: a cause of chronic ankle pain". The Physician and Sportsmedicine. 28 (5): 75–80. doi:10.3810/psm.2000.05.900. ISSN 0091-3847. PMID 20086641. S2CID 207670085.
- ↑ "Sinus Tarsi Syndrome". FootCareMD. Retrieved 2022-12-22.
- ↑ Akiyama, Koichi; Takakura, Yoshinori; Tomita, Yasuharu; Sugimoto, Kazuya; Tanaka, Yasuhito; Tamai, Susumu (July 1999). "Neurohistology of the sinus tarsi and sinus tarsi syndrome". Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 4 (4): 299–303. doi:10.1007/s007760050107. PMID 10436278. S2CID 24051350.