.png.webp)
A split pin, also known in the US as a cotter pin or cotter key,[1] is a metal fastener with two tines that are bent during installation, similar to a staple or rivet. Typically made of thick wire with a half-circular cross section, split pins come in multiple sizes and types.
The British definition of "cotter pin" is equivalent to US term "cotter". To avoid confusion, the term split cotter is sometimes used for a split pin. A further use of the term "cotter pin" is the "crank cotter pin" used to lock bicycle pedal cranks to the bottom bracket axle. These are not "split" at all and are wedge shaped.
Construction
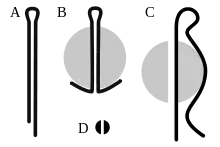
A new split pin (see figure A) has its flat inner surfaces touching for most of its length so that it appears to be a split cylinder (figure D). Once inserted, the two ends of the pin are bent apart, locking it in place (figure B). When they are removed they are supposed to be discarded and replaced, because of fatigue from bending.[2]
Split pins are typically made of soft metal, making them easy to install and remove, but also making it inadvisable to use them to resist strong shear forces. Common materials include mild steel, brass, bronze, stainless steel, and aluminium.[3]
Types
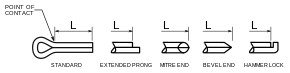
The most common type of split pin is the extended prong with a square cut, but extended prongs are available with all of the other types of ends. The extended prong type is popular because the difference in length of the two tines makes it easier to separate them. To ease insertion into a hole the longer tine may be slightly curved to overlap the tip of the shorter tine or it is beveled.[3]
Hammer lock split pins are properly installed by striking the head with a hammer to secure the pin. This forces the shorter tine forward, spreading the pin.[4]
Types include standard, humped and clinch.
Sizes
The diameters of split pins are standardized.
| Nominal diameter mm |
Hole size mm |
For bolt size mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 1.9 | 6 |
| 2 | 2.4 | 8 |
| 2.5 | 2.8 | 10 |
| 3 | 3.4 | 12, 14 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 20 |
| 5 | 5.6 | 24, 28 |
| 6 | 6.3 | 30, 36, 42 |
| 8 | 8.5 | 48 |
American split pins start at 1⁄32 in and end at 3⁄4 in.[4] Metric conversions in the table below are approximate.
| Nominal diameter | Hole size | For bolt size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in | mm | in | mm | in | mm |
| 1⁄32 | 0.79 | 3⁄64 | 1.19 | ||
| 3⁄64 | 1.19 | 1⁄16 | 1.59 | ||
| 1⁄16 | 1.59 | 5⁄64 | 1.98 | 1⁄4 | 6.35 |
| 5⁄64 | 1.98 | 3⁄32 | 2.38 | 5⁄16 | 7.94 |
| 3⁄32 | 2.38 | 7⁄64 | 2.78 | 3⁄8 | 9.53 |
| 7⁄64 | 2.78 | 1⁄8 | 3.18 | ||
| 1⁄8 | 3.18 | 9⁄64 | 3.57 | 1⁄2 | 12.70 |
| 9⁄64 | 3.57 | 5⁄32 | 3.97 | 5⁄8 | 15.88 |
| 5⁄32 | 3.97 | 11⁄64 | 4.37 | 3⁄4 | 19.05 |
| 3⁄16 | 4.76 | 13⁄64 | 5.16 | 1, 1+1⁄8 | 25.4, 28.58 |
| 7⁄32 | 5.56 | 15⁄64 | 5.95 | 1+1⁄4, 1+3⁄8 | 31.75, 34.93 |
| 1⁄4 | 6.35 | 17⁄64 | 6.75 | 1+1⁄2 | 38.10 |
| 5⁄16 | 7.94 | 5⁄16 | 7.94 | 1+3⁄4 | 44.45 |
| 3⁄8 | 9.53 | 3⁄8 | 9.53 | ||
| 7⁄16 | 11.11 | 7⁄16 | 11.11 | ||
| 1⁄2 | 12.70 | 1⁄2 | 12.70 | ||
| 5⁄8 | 15.88 | 5⁄8 | 15.88 | ||
| 3⁄4 | 19.05 | 3⁄4 | 19.05 | ||
Applications

Split pins are frequently used to secure other fasteners, e.g. clevis pins, or to secure a castellated nut,[6] or, infrequently, as a low-tech shear pin.
Split pins are cheaper but less reusable than linchpins, and provide less strength but easier to install/remove than spring pins.
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,298,299
- ↑ Welsch 2005, p. 141.
- 1 2 Soled 1957, p. 312.
- 1 2 3 Cotter pins, retrieved 2009-08-17.
- 1 2 Jensen 2001, p. 234.
- ↑ Reithmaier 1999, p. 151.
Bibliography
- Jensen, Cecil Howard (2001), Interpreting Engineering Drawings (6th ed.), SteinerBooks, ISBN 978-0-7668-2897-1.
- Reithmaier, Lawrence W. (1999), Standard aircraft handbook for mechanics and technicians (6th ed.), McGraw-Hill Professional, ISBN 978-0-07-134836-2.
- Soled, Julius (1957), Fasteners handbooks, Reinhold Publication Corporation.
- Welsch, Roger (2005), From Tinkering to Torquing: A Beginner's Guide to Tractors and Tools, MBI Publishing Company, ISBN 978-0-7603-2082-2.
External links
 Media related to Split cotter pins at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Split cotter pins at Wikimedia Commons