Srobotnik | |
|---|---|
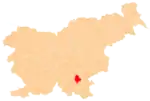
 Srobotnik Location in Slovenia | |
| Coordinates: 45°42′14.84″N 15°4′3.33″E / 45.7041222°N 15.0675917°E | |
| Country | |
| Traditional region | Lower Carniola |
| Statistical region | Southeast Slovenia |
| Municipality | Dolenjske Toplice |
| Elevation | 377.4 m (1,238.2 ft) |
| Population (2002) | |
| • Total | none |
Srobotnik (pronounced [sɾɔˈboːtnik]; German: Gutenberg,[1] sometimes Guttenberg,[2] Gottscheerish: Liəlochpargəl[3]) is a remote abandoned settlement in the Municipality of Dolenjske Toplice in southern Slovenia. The area is part of the traditional region of Lower Carniola and is now included in the Southeast Slovenia Statistical Region.[4] Its territory is now part of the village of Občice.
Name
The name Srobotnik is based on the common Slovene noun srobot 'clematis' with the addition of the associative suffix '-nik'. The Gottschee German name Liəlochpargəl is semantically similar, derived from the dialect word Lieloch 'clematis'[5][6] (from Middle High German liele[7]) + pargəl 'little mountain'. The names thus refer to the local vegetation. The standard German name Gutenberg (literally, 'good mountain') may simply be an optimistic name expressing wishes for a good harvest.[3]
History
Srobotnik was a Gottschee German village. The settlement was not mentioned in the land registry of 1574 or the census of 1770, and so it was probably a more recent settlement.[3] In 1931 it had 10 houses and a population of 31. The inhabitants were evicted in the fall of 1941. During the Rog Offensive in the summer of 1942, Italian forces burned the village and it was never rebuilt.[8]
References
- ↑ Ferenc, Mitja. 2007. Nekdanji nemški jezikovni otok na kočevskem. Kočevje: Pokrajinski muzej, p. 4.
- ↑ Glonar, Joža. 1931. Poučni slovar. Ljubljana: Umetniška propaganda, p. 459.
- 1 2 3 Petschauer, Erich. 1980. "Die Gottscheer Siedlungen – Ortsnamenverzeichnis." In Das Jahrhundertbuch der Gottscheer (pp. 181–197). Klagenfurt: Leustik.
- ↑ Dolenjske Toplice municipal site
- ↑ Hegi, Gustav. 1907. Illustrierte Flora von Mittel-Europa: Dicotyledons. Munich: J. F. Lehmann, p. 511.
- ↑ Bayerischer Forstverein. 1998. Sträucher in Wald und Flur: Bedeutung für Ökologie und Forstwirtschaft: natürliche Vorkommen in Wald- und Feldgehölzen: Einzeldarstellungen der Straucharten. Landsberg: Ecomed, p. 335.
- ↑ Snoj, Marko (2009). Etimološki slovar slovenskih zemljepisnih imen. Ljubljana: Modrijan. pp. 233–234.
- ↑ Savnik, Roman, ed. 1971. Krajevni leksikon Slovenije, vol. 2. Ljubljana: Državna založba Slovenije, p. 532.
External links