Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics:
- Maritime Guinea (La Guinée Maritime) covers 34% of the country
- Middle Guinea (La Moyenne-Guinée) covers 20% of the country
- Upper Guinea (La Haute-Guinée) covers 38% of the country
- Forested Guinea (Guinée Forestière) covers 23% of the country, and is both forested and mountainous
Government divisions
Regions
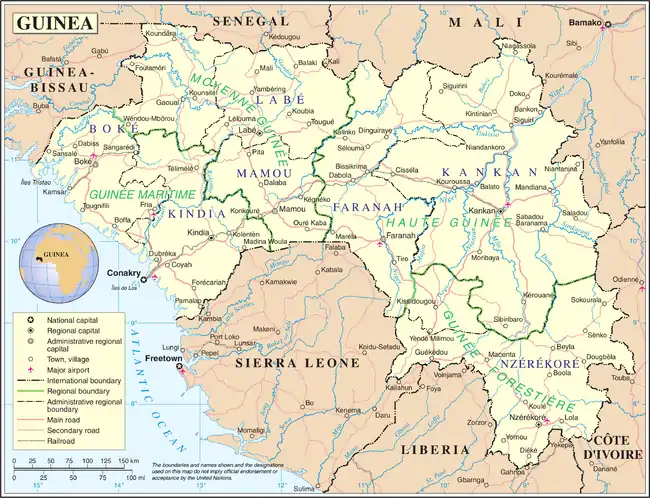
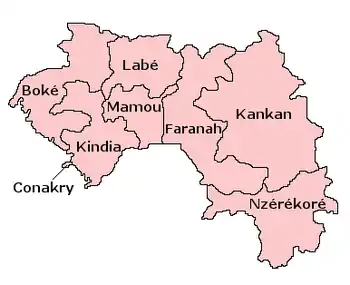
Guinea is divided into seven administrative regions. The national capital, Conakry, ranks as a special zone.
| Region | Capital | Area (km2 | Population (2014 census) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conakry Region | Conakry | 450 | 1,660,973 |
| Nzérékoré Region | Nzérékoré | 37,658 | 1,527,030 |
| Kankan Region | Kankan | 72,145 | 1,972,537 |
| Kindia Region | Kindia | 28,873 | 1,561,374 |
| Boké Region | Boké | 31,186 | 1,083,147 |
| Labé Region | Labé | 22,869 | 994,458 |
| Faranah Region | Faranah | 35,581 | 941,554 |
| Mamou Region | Mamou | 17,074 | 731,188 |
- The capital Conakry with a population of 1,660,973 ranks as a special zone.
Prefectures
Guinea's regions are subdivided into thirty-three prefectures and one special zone, Conakry.
Sub-prefectures
The Communes of Guinea or sub prefectures, known in French as sous-prefectures, are the third-level administrative divisions in Guinea. As of 2009 there were 303 rural communes of Guinea and 38 urban communes, 5 of which compose the Conakry greater urban area.

See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.