| This | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Coelopidae |
| Subfamily: | Coelopinae |
| Tribe: | Coelopellini |
| Genus: | This McAlpine, 1991[1] |
| Type species | |
| This canus McAlpine, 1991[2] | |
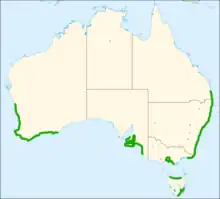 | |
| Distribution of T. canus in green[3] | |
This is a genus of kelp fly in the family Coelopidae. As of 2017, it is monotypic, consisting of its type species This canus. This and T. canus were respectively circumscribed and described in 1991 by the Australian entomologist David K. McAlpine. It is endemic to southern Australia.
Taxonomic history
| Tribe Coelopellini | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogenetic placement of This within the expanded tribe Coelopellini based on Meier and Wiegmann's 2002 analysis.[4][5][6][lower-alpha 1] |
David K. McAlpine of the Australian Museum circumscribed and named the genus This in a 1991 overview of Australian Coelopidae, which was published in the journal Systematic Entomology.[9] In the same paper McAlpine named and described its type species T. canus, the only species included in the genus.[10] McAlpine and Geoff Holloway collected the male T. canus holotype in 1971; it was deposited in the collections of the Australian Museum. Approximately 450 specimens of T. canus were designated as paratypes; collections holding paratypes include: the Australian Museum, the South Australian Museum, the Natural History Museum, London, the Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle, Paris, and the National Museum of Natural History, Washington.[11]
McAlpine placed This in a new tribe, Coelopellini; he initially included three genera in this tribe: his new genera This and Rhis, as well as Coelopella, which John Russell Malloch circumscribed in 1933.[12] McAlpine concurrently created the tribe Ammini, consisting of the genera Amma, Icaridion, and Beaopterus.[13]
Rudolf Meier and Brian Wiegmann conducted a phylogenetic study of twenty two species of Coelopidae based on genetic sequencing of EF-1α and 16S rDNA as well as morphological characteristics.[14] Meier and Wiegmann argued that neither Coelopellini nor Ammini as McAlpine had circumscribed them were monophyletic, but that together they formed a clade.[15] As of 2007, the Tree of Life Web Project follows Meier and Wiegmann's phylogeny.[5] In 2011, Smithsonian Institution entomologist Wayne N. Mathis and McAlpine combined Ammini with Coelopellini, resulting in an expanded, monophyletic tribe Coelopellini.[16]
The generic name This comes from the Ancient Greek word θίς (thís), which means "sea shore",[17] particularly in Homeric Greek.[18] Some have found it humorous that This is a homograph of the English proximal demonstrative this.[19] American entomologist Arnold S. Menke included This in a 1993 list of taxon names which he deemed to be either "funny" or "curious"; the list was printed in a biological humor magazine published by the American entomologist Neal L. Evenhuis. Menke also reported that McAlpine had a poster on his office door which illustrated a This specimen and was captioned "Look at This!".[20] The specific name for its type species is a Latin adjective, canus, with meanings including "white", "grey-haired", and "foam-capped".[21][22]
Description
| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Total length |
2.1–3.3 mm (0.083–0.130 in) |
2.2–3.2 mm (0.087–0.126 in) |
| Thorax length |
0.9–1.3 mm (0.035–0.051 in) |
0.9–1.3 mm (0.035–0.051 in) |
| Wing length |
2.2–3.1 mm (0.087–0.122 in) |
2.2–3.0 mm (0.087–0.118 in) |
| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean length |
2.313 mm (0.0911 in) |
3.227 mm (0.1270 in) |
| Standard error |
0.037 mm (0.0015 in) |
0.065 mm (0.0026 in) |
Genus
In McAlpine's 1991 as well as Mathis and McAlpine's 2011 keys to Coelopidae genera, This and Rhis formed a couplet. Some of the characteristics distinguishing This from Rhis include: moderately long vibrissal setae at a prominent angle, the presence of two humeral, postpronotum bristles, and a deeply bilobed surstylus on males.[24][25]
Other generic features include a face whose profile is concave and which lacks a medial carina, short setulae on its cheeks. Its arista is shorter than the diameter of its eye, and the segment 6 is covered in short hairs.[26]
Species
Both sexes of T. canus have a similar morphology. It has a pale grey head, a pale orange-brown cheek, orange-brown antennae, and a brown arista. Its thorax is light gray and is covered in black hairs. The legs are yellow or yellowish-brown. Both the tegulae and veins on its pale wings are yellow. The head is slightly narrower than the thorax, and the legs are stout.[27]
McAlpine provided similar measurements for both males and females,[11] although Jennifer Blyth argued T. canus exhibited sexual dimorphism due to the males' wing size being on average 71.6% than that of the females in her study.[28]
Distribution
The genus This is endemic to Australia,[29] and T. canus is one of the most common species of Coelopidae in Australia.[11][30] T. canus is found along the southern coast of Australia,[11] and had been found in the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria, and Western Australia.[31] Its range also includes Clarke Island, off the coast of Tasmania.[32] Its type locality is Dee Why, a suburb of Sydney.[11] It has been documented as far north as Noosa, Queensland on the east coast and Geraldton, Western Australian on the west coast.[11] It can also be found as far inland as Canberra.[11]
Biology

T. canus, like other coelopids, is found on wrack seaweed found in the wrack zone of Australian beaches.[30] K. R. Blanche of the University of New England conducted a field study and laboratory experiments on T. canus for a paper published in 1992.[33] Her field observations were from May 1987 to May 1988 along the coastline of the City of Gosford, near Sydney. Collection sites included beaches in Pearl Beach, Killcare, Putty, MacMasters Beach, and Copacabana.[34] She was able to collect T. canus specimens throughout the year, although their abundance varied, with peaks in June–August, December–January, and April. The average density of T. canus in each zone of wrack was approximately 2 flies per cubic meter (1.5/yd3) of low wrack, 3.4 flies per cubic meter (2.6/yd3) of mid wrack, and 2.8 flies per cubic meter (2.14/yd3) of high wrack.[35] The mid wrack is ideal for adults to gather and lay eggs due to its moisture and amount of decomposing seaweed; the decomposition emits various vapors which attract the kelp flies.[36]
Blanche's laboratory experiment found that T. canus was able to complete its life cycle on the kelp species Ecklonia radiata but not on the seagrass Zostera capricorni. There was a similar T. canus life cycle on both fresh, wet and old, wet E. radiata; they failed to successfully reproduce on dried E. radiata. Overall the life cycle took between six and nine weeks to complete.[37][lower-alpha 2] She concluded that Z. capricorni and dried E. radiata do not provide sufficient bacteria, which serves as a food source, or moisture for the larvae to develop.[36]
Jennifer Blyth, for her 2005 University of Leicester dissertation, studied the mating behavior of coelopids; one experiment examined the mating behavior of Chaetocoelopa littoralis, Chaetocoelopa sydneyensis, Gluma keyseri, Amma blanchae, and This canus in a laboratory setting.[39] T. canus were collected at Forresters Beach, New South Wales and Asling's Beach, Twofold Bay; instead of inhabiting beds of wrack seaweed, which were not present at these sites, the T. canus were in "wrack strings", i.e., small pieces of dried seaweed.[40]
Blyth found that T. canus and A. blanchae had similar mating behavior, which was "markedly different" from the other three species examined.[41] The mounting position of the male is far back on the female; he rests his prothoracic legs on her thorax unlike the other three species where he rests his legs on her antennae.[42] There is no courtship display prior to mounting. Chaetocoelopa females might attempt to reject a male by kicking him for the first thirty seconds after he mounts her, although these kicks were ineffective for all but the smallest males. If the male managed to endure these thirty seconds, copulation would occur. Otherwise, the female exhibited minimal struggling behavior while being mounted.[41] Females did not struggle when the males dismounted.[43] Blyth concludes that sexual conflict is not as present for T. canus and A. blanchae as it is for the other species.[44] On average, mount duration for T. canus was 91.9 seconds and copulation duration was 128.4 seconds.[45] Most mounts (61.02%) resulted in copulation: 6.78% ended due to the male rejecting and 32.2% ended due to the female's rejection.[46]
Blyth also provided a quantitative analysis looking for any effects of size, which was quantified by measuring wingspan. The mounting duration correlated positively with female size, but had no significant correlation with male size.[47] Blythe found no correlation between a male T. canus's desire to mate and the size of either the male or the female.[48] Males did not show a significant preference for large females.[48] Larger female were more successful at rejecting males.[48]
Notes
- ↑ Meier and Wiegmann did not include B. robustus, I. nasutum, and I. nigifrons in their analysis. A superscript T denotes the type species for each genus. Labels reflect nomenclatural changes made by Mathis and McAlpine in 2011, namely transferring Coelopella popeae to Rhis and combining Ammini with Coelopellini. The undescribed species was discovered on New Zealand's South Island by Peter Johns and is thought to be in its own genus.[7][8]
- ↑ The kelp conditions were: freshly collected from the sea; collected from the sea, exposed to sunlight, and soaked in sea water for an hour two times a day for a fourteen days; and collected from the sea and dried in the sun for fourteen days.[38]
References
- ↑ Pape, Thomas; Thompson, F. Christian (13 June 2013). "Nomenclator Detail Record: This McAlpine 1991: 67". Systema Dipterorum. 1.5. Natural History Museum of Denmark. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ↑ Pape, Thomas; Thompson, F. Christian (13 June 2013). "Nomenclator Detail Record: This canus McAlpine, 1991: 68". Systema Dipterorum. 1.5. Natural History Museum of Denmark. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ↑ Blanche (1992), p. 29.
- ↑ Meier & Wiegmann (2002), pp. 399–400.
- 1 2 Bayless, Keith (20 December 2007). "Coelopidae: Kelp Flies". The Tree of Life Web Project. Archived from the original on 26 November 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), pp. 188–191.
- ↑ Meier & Wiegmann (2002), p. 401.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), p. 171.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), pp. 67–68.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), pp. 68–70.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 McAlpine (1991), p. 69.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), p. 48, 65.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), pp. 48–49.
- ↑ Meier & Wiegmann (2002).
- ↑ Meier & Wiegmann (2002), pp. 401–403.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), pp. 176, 188.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), p. 68.
- ↑ Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert, eds. (1996). "θίς". "A" Greek-English lexicon: With a revised supplement 1996. A Greek–English Lexicon With a Revised Supplement. Revised and augmented by Henry Stuart Jones, with Roderick McKenzie et al. (9th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 801–802, S132. ISBN 978-0-19-864226-8.
- ↑ Milius, Susan (2001). "A Fly Called Iyaiyai: And other true stories of scientific name-calling". Science News. 159 (21): 330. doi:10.2307/3981700. JSTOR 3981700.
- ↑ Menke, Arnold S. (1993). "Funny or Curious Zoological Names". BOGUS. -2: 25. ISSN 1072-2556.
- ↑ Lewis, Charlton T.; Short, Charles (1879). "cānus". Harper's Latin Dictionary: A New Latin Dictionary Founded on the Translation of Freund's Latin-German Lexicon. A Latin Dictionary. New York: Harper & Brothers. p. 282.
- ↑ Glare, P. G. W. (1968). "cānus". Oxford Latin Dictionary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 268.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 143.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), pp. 49–50.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), p. 179.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), p. 67.
- ↑ McAlpine (1991), p. 68–69.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 138, 143, 152.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), p. 176.
- 1 2 Blanche (1992), p. 27.
- ↑ Mathis & McAlpine (2011), p. 191.
- ↑ Natural and Cultural Heritage Division (2014). lungtalanana (Clarke Island), Natural Values Survey 2014 (PDF). Nature Conservation Report Series. Vol. 15/2. Hobart: Hamish Saunders Memorial Trust, New Zealand and Natural and Cultural Heritage Division, DPIPWE. pp. 72, 83. ISBN 978-1-74380-007-2. ISSN 1441-0680.
- ↑ Blanche (1992).
- ↑ Blanche (1992), pp. 28–30.
- ↑ Blanche (1992), pp. 30–31.
- 1 2 Blanche (1992), p. 32.
- ↑ Blanche (1992), pp. 31–32.
- ↑ Blanche (1992), p. 30.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), pp. 128.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), pp. 129–130.
- 1 2 Blyth (2005), p. 137.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 137, 152.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 139.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 152.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 144.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 142.
- ↑ Blyth (2005), p. 138.
- 1 2 3 Blyth (2005), p. 141.
Works cited
- Blanche, K. R. (1992). "Preliminary observations on the distribution and abundance of seaweed flies (Diptera: Coelopidae) on beaches in the Gosford district of New South Wales, Australia". Australian Journal of Ecology. 17 (1): 27–34. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.1992.tb00777.x.
- Blyth, Jennifer Elizabeth (2005). Sexual conflict and cryptic female mate choice in the Coelopidae (PhD thesis). University of Leicester. hdl:2381/29730. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 November 2017.
- Mathis, Wayne N.; McAlpine, David K. (2011). "A Catalog and Conspectus on the Family Coelopidae (Diptera: Schizophora)". In Brake, Irina; Thompson, F. Christian (eds.). Contributions to the Systema Dipterorum (Insecta: Diptera). Myia. Vol. 12. pp. 171–205. hdl:10088/18924. ISBN 978-954-642-599-7.
- McAlpine, David K. (1991). "Review of the Australian kelp flies Diptera: Coelopidae". Systematic Entomology. 16 (1): 67–70. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3113.1991.tb00573.x. S2CID 83627067.
- Meier, Rudolf; Wiegmann, Brian M. (2002). "A phylogenetic analysis of Coelopidae (Diptera) based on morphological and DNA sequence data". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 25 (3): 393–407. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00276-2. PMID 12450746.
External links
- "K.81244 - This canus McAlpine, 1991 - Australia, New South Wales, D.Y. (Dee Why), (33° 45' S, 151° 17' E), 4 Nov 1971, Holotype". Australian Museum Collections. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- "Genus This McAlpine, 1991". Australian Faunal Directory. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
_(cropped).jpg.webp)