| By transport mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By size (list) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change of gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By location | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
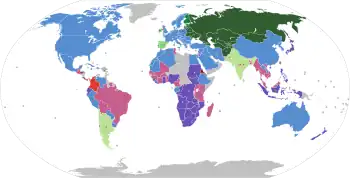 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Most railways in Europe use the standard gauge of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in). Some countries use broad gauge, of which there are three types. Narrow gauges are also in use.
Broad gauge
- Russian gauge
- 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in): former Soviet Union states
- 1,524 mm (5 ft): Finland and Estonia
- (The difference is within tolerance limits, so it is possible to exchange trains between 1520 mm and 1524 mm networks without changes to the wheelsets.)
- Irish gauge
- 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in): Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland
- Iberian gauge
Narrow gauge
High-speed rail
Apart from Russia and Finland, all high-speed rail in Europe uses standard-gauge (1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)) tracks.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
