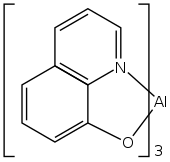
 | |
aluminium.jpg.webp) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium | |
| Other names
8-Hydroxyquinoline aluminium salt, Alq3, aluminium 8-hydroxyquinolinate, aluminium oxinate, | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.570 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H18AlN3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 459.43 |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Melting point | > 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| insoluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium is the chemical compound with the formula Al(C9H6NO)3. Widely abbreviated Alq3, it is a coordination complex wherein aluminium is bonded in a bidentate manner to the conjugate base of three 8-hydroxyquinoline ligands.
Structure
Both the meridional and facial isomers are known as well as several polymorphs (different crystalline forms).[1]
aluminium(III)-from-xtal-2000-CM-3D-ellipsoids.png.webp) | aluminium(III)-from-xtal-2003-CM-3D-ellipsoids.png.webp) |
| Thermal ellipsoid model of mer-Alq3[2] | Thermal ellipsoid model of fac-Alq3[3] |
Synthesis
The compound is prepared by the reaction of 8-hydroxyquinoline with aluminium(III) sources[4]
- Al3+ + 3 C9H7NO → Al(C9H6NO)3 + 3 H+
Applications
Alq3 is a common component of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Variations in the substituents on the quinoline rings affect its luminescence properties.[5]
References
- ↑ Cölle, M.; Dinnebier, R. E.; Brütting, W. (2002). "The structure of the blue luminescent δ-phase of tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminium(III) (Alq3)". Chemical Communications. 2002 (23): 2908–9. doi:10.1039/b209164j. PMID 12478807. S2CID 96135270.
- ↑ Brinkmann, M.; Gadret, G.; Muccini, M.; Taliani, C.; Masciocchi, N.; Sironi, A. (2000). "Correlation between Molecular Packing and Optical Properties in Different Crystalline Polymorphs and Amorphous Thin Films of mer-Tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminum(III)". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122 (21): 5147–57. doi:10.1021/ja993608k.
- ↑ Rajeswaran, M.; Blanton, T. N.; Klubek, K. P. (2003). "Refinement of the crystal structure of the δ-modification of tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminum(III), δ-Al(C9H6NO)3, the blue luminescent Alq3". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures. 218 (4): 439–40. doi:10.1524/ncrs.2003.218.jg.471.
- ↑ Katakura, R.; Koide, Y. (2006). "Configuration-Specific Synthesis of the Facial and Meridional Isomers of Tris(8-hydroxyquinolinate)aluminum (Alq3)". Inorg. Chem. 45 (15): 5730–2. doi:10.1021/ic060594s. PMID 16841973.
- ↑ Montes, V. A.; Pohl, R.; Shinar, J.; Anzenbacher, P. Jr. (2006). "Effective Manipulation of the Electronic Effects and Its Influence on the Emission of 5-Substituted Tris(8-quinolinolate) Aluminum(III) Complexes". Chemistry: A European Journal. 12 (17): 4523–35. doi:10.1002/chem.200501403. PMID 16619313.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.