UV-B lamps are lamps that emit a spectrum of ultraviolet light with wavelengths ranging from 290–320 nanometers. This spectrum is also commonly called the biological spectrum due to the human body's sensitivity to light of such a wavelength.[1] UV-B light does not tan the skin very much, compared to the UV-A lamps that are used in tanning beds.
Treating skin diseases
The main use of UVB lamps is as phototherapy lamp, meaning treating skin diseases with light. The diseases UV-B lamps treat are psoriasis,[2] vitiligo, lichen planus, atopic dermatitis (eczema), and other skin diseases.
Thousands of dermatology clinics around the world treat skin ailments using UV-B lamps. Many people who suffer from psoriasis or other skin diseases have their own UV-B lamp at home. A small lamp is used to treat small areas of the skin, while full body cabins treat the whole body, mainly at clinics and hospitals.
Overexposure to UV-B light can burn the skin, so the exposure time must be regulated by a timer that turns off the lamp.
Increasing vitamin D3
When the skin is exposed to UVB light of 290-300 nanometer, it creates vitamin D3.[3]
Types of UVB lamps
The optimal lamp for the generation of vitamin D3 are LED lamps, that emit UVB light at a peak wavelength of 297 nanometer.

Thanks to the exact wavelength, the dose that the skin needs, to cure from skin diseases (mainly psoriasis) is 0.1 joules per square centimeter. LED lights safer, more effective in producing Vitamin D3 than sunlight
There are also fluorescent UVB lamps, called broadband UVB, or wideband UVB that have a peak wavelength of 306 nanometer. The dose that the skin needs with these lamps, to cure from skin diseases is 0.5 joules per square centimeter.

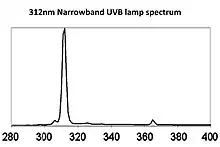
There are also narrowband UVB lamps, that emit 311-312 nanometer. Output spectrum of Philips PS-S 9W/12 narrow-band UV-B fluorescent lamp. The dose that the skin needs with these lamps, to cure from skin diseases is 2 joules per square centimeter.
UVB light in the sun rays
The sun rays include low amount of light at 290-300 nanometer, that is why 15 –30 minutes of sunshine every day are usually needed. In Northern European countries especially in the winter when sunlight is scarce, pregnant women may receive UVB light in clinics to assure that their babies have an adequate amount of vitamin D3 when born.
Animals need UV-B light to produce vitamin D3 and strong bones. There are UVB lamps for reptiles, snakes, turtles and other animals in zoos and at the owner's houses.
Cancer risks
UV-B treatments for treating skin diseases (psoriasis, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, etc.) are given in a very low dosage. The treatments take only few minutes, or less than a minute when the lamp is 290-300 nanometer.
This low dosage does not increase the risk of skin cancer and UV-B phototherapy remains a very safe treatment.[4] Research citing ten years of experience with phototherapy in Yonsei Medical Center has not revealed any cases of malignancy in the skin.[5]
Too much UV ultraviolet radiation of an undesirable wavelength may lead to direct DNA damage, sunburn, and skin cancer.[6] In contrast to exposure to UV-B light given at low dosage, it was found that UV-A light increases the risk of skin cancer because it penetrates the epidermis and it is given in a much higher dosage.
References
- ↑ http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/wrk/wrk1/ArtificialUVRad&Skin4.pdf%5B%5D
- ↑ "Treat Psoriasis at Home: Ultraviolet Lamps".
- ↑ Kalajian, T. A.; Aldoukhi, A.; Veronikis, A. J.; Persons, K.; Holick, M. F. (2017). "Ultraviolet B Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) Are More Efficient and Effective in Producing Vitamin D3 in Human Skin Compared to Natural Sunlight". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 11489. Bibcode:2017NatSR...711489K. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11362-2. PMC 5597604. PMID 28904394.
- ↑ Lee, Ernest; Koo, John; Berger, Tim (2005). "UVB phototherapy and skin cancer risk: A review of the literature". International Journal of Dermatology. 44 (5): 355–60. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02186.x. PMID 15869531. S2CID 11332443.
- ↑ Park, Sang Hoon; Hann, Seung Kyung; Park, Yoon Kee (1996). "Ten-year experience of phototherapy in Yonsei Medical Center". Yonsei Medical Journal. 37 (6): 392–96. doi:10.3349/ymj.1996.37.6.392. PMID 9048491.
- ↑ Matsumura, Yasuhiro; Ananthaswamy, Honnavara N (2004). "Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 195 (3): 298–308. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2003.08.019. PMID 15020192.
The action spectrum for Vitamin D3: Initial skin reaction and prolonged exposure