
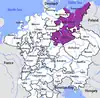
The Upper Saxon Circle at the end of the 16th century
The Upper Saxon Circle (German: Obersächsischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire, created in 1512.
The circle was dominated by the electorate of Saxony (the circle's director) and the electorate of Brandenburg. It further comprised the Saxon Ernestine duchies and Pomerania. The Lusatias that fell to Saxony by the 1635 Peace of Prague were never encircled.
Composition
The circle was made up of the following states:
| Name | Type of entity | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Principality | Emerged from Duchy of Saxony in 1212, re-united under the House of Ascania in 1570, divided into Anhalt-Dessau, Anhalt-Bernburg, Anhalt-Köthen and Anhalt-Zerbst from 1603 | |
| County | Imperial immediacy in 1497, fell to the Saxe-Weissenfels branch of the electoral House of Wettin in 1659 | |
| Electorate | Margraviate established in 1157, Prince-elector from 1356 | |
| Principality | Territory of the diocese established in 1140, under Pomeranian overlordship, Bishopric secularized from 1545, to Brandeburg | |
| Abbacy | Imperial abbey established in 961 by King Otto I, held by the House of Ascania from 1616 | |
| Hatzfeld-Gleichen | County | Established in 1631, principality from 1741, fell to Mainz in 1794 |
| County | Territory around Scharzfeld and Lauterberg, line extinct in 1593, fell to Brunswick-Grubenhagen | |
| Lohra and Klettenberg | Lordship | held by the Counts of Hohnstein, fell to Halberstadt in 1593, administrated by Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel |
| County | Established in 1069 by King Henry IV, seized by Saxony in 1579 | |
| Duchy | Ruled by the House of Griffins, internally divided from 1532 to 1625, Swedish Pomerania from 1637 on, Farther Pomerania to Brandenburg-Prussia in 1653 | |
| Abbacy | Established in 936 by King Otto I, occupied by Brandenburg-Prussia in 1698; 12th Prelatess of the Rhine | |
| Principality | Former lordship, to Saxon House of Wettin in 1635, held by Saxe-Weissenfels from 1656 to 1746 | |
| County | Established about 1080 by King Henry IV, partitioned in 1564 into Elder Line at Greiz (principality from 1778) and Junior Line at Gera | |
| Electorate | Successor of Saxe-Wittenberg from 1356, held by the House of Wettin from 1423 | |
| Duchy | Wettin Ernestine duchy established in 1572 | |
| Duchy | Wettin Ernestine duchy split off Saxe-Weimar in 1602, inherited by Saxe-Gotha in 1672 | |
| Duchy | Wettin Ernestine duchy split off Saxe-Weimar in 1640, Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg from 1672 | |
| Saxe-Coburg | Duchy | Wettin Ernestine duchy established in 1572 as Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach. Split between the Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld and the Duke of Saxe-Meiningen from 1725 |
| Duchy | Wettin Ernestine duchy split off Saxe-Coburg in 1596, personal union with Saxe-Weimar from 1741 | |
| County | Various territories, Imperial immediacy in 1182, acquired by Saxony in 1740 | |
| County | United under the House of Schwarzburg 1538-1583 | |
| County | subdivision established in 1599, raised to principality in 1697 | |
| County | subdivision established in 1599 as Schwarzburg-Arnstadt, raised to principality in 1697/1710 | |
| County | Stolberg-Stolberg from 1548, under Saxon supremacy from 1738 | |
| County | Split off Stolberg-Stolberg in 1706, under Saxon supremacy from 1738 | |
| Abbacy | Established in 1127, fell to Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel in 1648 | |
| County | Held by Stolberg from 1429, Stolberg-Wernigerode from 1645, under Prussian supremacy from 1714 |
Sources
- The List of states making up the Upper Saxon Circle is based on that in the German Wikipedia article Obersächsischer Reichskreis.
External links
 Media related to Upper Saxon Circle at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Upper Saxon Circle at Wikimedia Commons- Imperial Circles in the 16th Century – Historical Maps of Germany
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
-en.png.webp)