In Sweden, vehicle registration plates (Swedish: registreringsskylt) are used for most types of vehicles. They have three letters first, a space and two digits and one digit or letter after (e.g. ABC 123 or ABC 12A). The combination is mostly a random number and has no connection with a geographic location. The last digit is used to show what month the vehicle tax has to be paid, and before 2018 it was also used to show what month the car had to undergo vehicle inspection. Vehicles like police cars, fire trucks, public buses and trolley buses use the same type of plate as normal private cars and cannot be directly distinguished by the plate alone. Military vehicles have special plates. Part of the vehicle data is public and can be retrieved online.[1]
Ordinary plates
Ordinary plates have black text on a white background. They consist of three letters first, a space, two digits and one more digit or letter. The space was formerly used for a taxation sticker, and on newer plates the space is narrower. Above it a manufacturer code and the vehicle identification number (VIN) are printed and above the last digit the date of plate manufacture is printed. All vehicles must legally carry both a front and a rear plate except for motorcycles, trailers (rear only), tractors and other off-road machinery (front only).
The registration number is tied to the vehicle's VIN and remains unchanged, even after change of ownership, until the vehicle is scrapped or exported. It is possible to decommission a registered vehicle for any length of time. A decommissioned registered vehicle does not require road tax or a valid insurance. The registration plate remains on the vehicle while decommissioned. Registration numbers of scrapped, exported and de-registered vehicles are put in quarantine before they are re-used with new registered vehicles.
Disallowed letters and combinations
All letters in the Swedish alphabet are used, except the letters I, Q, V, Å, Ä and Ö. As of 2019 a letter may be used instead of the last number; this character also excludes the letter O so as not to risk confusion with 0 (zero).[2] 91 additional letter combinations are not used since they may be offensive, political or otherwise unsuitable.[3] Examples include: APA (monkey), ARG (angry), DUM (stupid, bad), FAN (devil, damn), FEG (cowardly), FEL (error, wrong), FUL (ugly), GAY (homosexual), HOT (threat), LAT (lazy), NRP (Nordiska Rikspartiet), OND (evil, cruel), SEX, SUP (snaps), TOA (toilet), UFO, USA, XXL (extra extra large) and many others. MLB (no meaning in Swedish) is reserved for examples, movies, ads and similar, where a real plate connected to a car which might be sold is not desired. English language was not considered when making the list, so for example WTF exists on plates. Until the rules were relaxed somewhat in October 2010, the list included 69 additional exclusions.[3] The Swedish Transport Agency has made this list, which is larger than those in most other countries, to avoid requests to replace issued plate numbers once they are deemed unacceptable, which would cause administrative problems.
Sizes and EU stripe
| Plate | Size (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Old ordinary plate (last production date 31 dec 2013) | 480×111 | |
| EU stripe plate | 520×111 | EU stripe |
| "American" plate | 300×111 | EU stripe |
| Square MC plate | 119x155 | EU stripe |
Starting in 1994, smaller plates of 30×11 cm were offered for special applications where standard plates would not typically fit, e.g. American domestic market vehicles. These plates are made in a narrower typeface. Up until then large, square plates were used for these applications; however, these were too large height-wise for some American cars, in which case motorcycle plates were issued instead. There is also a self-adhesive plastic 'plate' for use on snowmobiles, ATV's and similar, where the design of the vehicle can make it awkward to fit a real plate. The blue EU stripe was introduced in 2002 as option. As of 1 January 2014 all new manufactured plates have the EU-stripe, and there are no exceptions for older vehicles. Motorcycle owners have often changed plates since it is often hard to find a place for the oval "S"-sticker otherwise needed abroad.
Taxation sticker

In the middle of the rear plate, a sticker had to be attached to allow driving. This sticker was sent to the owner when the road tax and the liability insurance had been paid and the vehicle had been approved in the inspection. Valid for one year, its colour varied with the year, and the clearly visible month number of expiry could easily be discerned by police. It was introduced in 1973. Since 1 January 2010, the tax sticker was abolished in Sweden, and newer plates have no room for it.
Special plates
Personal plates
In addition to the ordinary registration plate of three letters and three digits, personal registration plates are allowed. The personal registration plate works as an alias to the ordinary plate and can have (almost) any text or number combination up to seven characters, if it isn't used already. It costs 6200 kr (about 590 €) to get personal number for a vehicle. They are valid for ten years and may be moved to another vehicle. The approval sticker was placed to the left, not in the middle. Text too offensive or illegal is not allowed. For instance, the 64SALE number was not allowed, as the number 6 and the word "sex" are homonyms in the Swedish.
In 2019 the application for the plate TRUMP was denied because the authority considered it provocative.[4] A sticker declaring the alias relationship between the ordinary plate and the personal plate must be attached in one of the vehicle's windows. The above-mentioned limitation on allowed letters (I, Q, V, Å, Ä, Ö) does not apply to personal plates.
Sometimes Swedish personalised plates may run into troubles in foreign countries. In 2018, authorities in Romania confiscated a Swedish plate that's reads "MUIEPSD", which means "fuck the PSD (Social Democratic Party)", Romania's then-ruling party, in Romanian, despite Swedish embassy in Bucharest issued a Facebook post that clarifies all-letter Swedish personalised plates are valid throughout the European Union, including Romania.
Dealer plates

Dealer plates have black text on a green background. These plates are used on vehicles without registration, insurance and vehicles which have failed inspection. The dealers have reported their car not to be driven, meaning they don't have to pay road tax. Cars can be parked for months awaiting sale. The cars can be used for short test drives with one of these licence plates. Unlike normal Swedish license plates, the dealer plate is not tied to any vehicle but to the plate owner. These plates can also be used by car manufacturers to test vehicles. The plate has a sticker indicating if the plate is for cars, trucks or trailers. The plate shows that the owner has a special insurance that covers test drives.
Diplomatic

Diplomatic plates have black text on a blue background. They consist of two letters, three serial digits and a last letter. The first two letters shows which diplomatic mission the vehicle belongs to (Letters I and Q not used). The letters don't correspond to any country acronym e.g. American diplomats don't have US as their first two letters. The first assigned codes were ordered by the sovereign states' name in the French language. Thus AA denotes South Africa (i.e. Afrique du Sud). AB denotes Albania (i.e. Albanie) and so forth up until DT. The three digits are just a serial number. The last letter shows what kind of task the diplomat has. The approval sticker was placed last on the right. Just like the personal plates these vehicles have a standard format registration as well, which means a re-registration is not needed if the vehicle changes owner.
|
|
Taxi

Taxi plates have black text on a yellow background. Taxis get yellow plates after they are approved. The plates have the same registration as the car had before it was a taxi. Thus if it isn't used as a taxi anymore, or if the car or the Taximeter fails inspection, the normal plates are put back on and the yellow ones are confiscated. Just like normal plates, taxi plates do not have an approval sticker. Until 1 April 2017, a smaller T indicating "taxi" was printed in the right hand corner (unless it had personal plates, in which case the T was omitted). The T was removed to streamline the manufacturing process, as taxi plates issued after this date solely differ from standard plates by background colour.[5]
Temporary

Temporary plates have white text on a red background. Used as a temporary registration for import and export. Like the standard plates, it has three letters and three digits, but with an expiry day and month to the left and year to the right. When an imported vehicle has been approved it will get ordinary white plates with the same registration as previously given on red plates.
Military


Military registration plates have yellow digits on a black background. The licences usually consist of four to six digits and may be used for all kinds of vehicles, from ordinary automobiles to tanks. Cars and lorries have plates with the number mounted to the vehicles, while on tanks and terrain vehicles the number is usually painted on the vehicle. The 1906 series format is still used. The register and issuing of plates is done by the Swedish Defence Materiel Administration thus completely separate from the civilian counterpart.
History
1906–1973 series

Until 1973 the plates contained one or two letters and up to five digits. The letters are standardised codes for the counties of Sweden. A second letter (A or B) was used for some counties for which the 5 digits were not enough to cover all vehicles.
The typeface used was not consistent as the vehicle owner bought either a plate or a kit from various dealers, such as petrol stations.
Opposite to many other countries, there were no special codes for police, post or other national services apart from the military. One tradition was that the official vehicle of the county governor had the number 1 after the county code, however "A 1" belonged to the king.
These plates were not used after 1974. All vehicles had to replace the plates. There are no historic plates in Sweden and historic cars have to use modern (post-1973) plates. All vehicles over 30 years old and not being used as a commercial vehicle are regarded as "veteran" by the road authority, becoming tax-exempt and only needing to pass vehicle inspection every second year. These vehicles use ordinary plates and approval stickers.
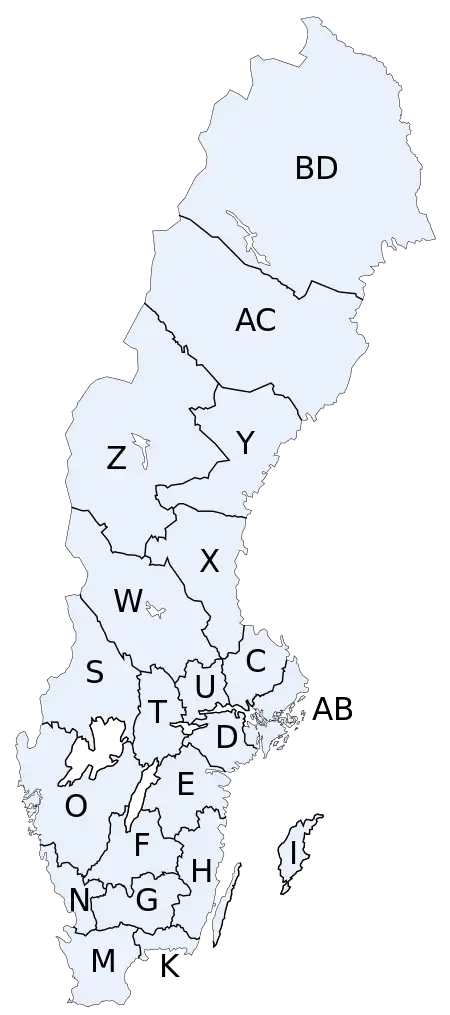
Codes
- A, AA, AB – City of Stockholm (today part of Stockholms län)
- B, BA, BB – Stockholms län
- C – Uppsala län
- D – Södermanlands län
- E, EA – Östergötlands län
- F, FA – Jönköpings län
- G – Kronobergs län
- H – Kalmar län
- I – Gotlands län
- K – Blekinge län
- L, LA – Kristianstads län (today part of Skåne län)
- M, MA, MB – Malmöhus län (today part of Skåne län)
- N – Hallands län
- O, OA, OB – Göteborgs och Bohus län (today part of Västra Götalands län)
- P, PA – Älvsborgs län (today part of Västra Götalands län)
- R – Skaraborgs län (today part of Västra Götalands län)
- S, SA – Värmlands län
- T, TA – Örebro län
- U, UA – Västmanlands län
- W, WA – Kopparbergs län (today Dalarnas län)
- X, XA – Gävleborgs län
- Y – Västernorrlands län
- Z – Jämtlands län
- AC – Västerbottens län
- BD – Norrbottens län
- no letter – military vehicles; still in use
After 1973
After 1973 the format changed to three letters followed by three digits. The typeface was custom made to increase readability, and the plates were made in embossed sheet steel. In January 1984 the plates were changed to plastic with reflective tape on them, still embossed. This caused problems since the tape would wear off and decrease the readability of the plate. In January 1994 a new plate was introduced that was made from a solid piece of plastic, with a customised Helvetica typeface. The issue of these plates was halted quickly when Photoblocker spray paint became popular and on 1 January 2002 they were replaced with embossed aluminium plates clad in 3M reflective film.
Post 2018
In 2015 Transportstyrelsen, the organisation responsible for the Swedish car registry submitted a proposal to the Swedish government on how to adapt the registration number system to avoid running out of registration numbers sometime during 2019. The necessary legal adjustments were made on 16 February 2017 to allow the last character to be either a letter or a digit.[6] The first registration plates using the new format were issued on 16 January 2019.[7] As before, the letters I, Q, V, Å, Ä, Ö are not in use, and the letter O is also not used for the last character.[2]
References
- ↑ biluppgifter.se
- 1 2 "Nu kommer de nya registreringsnumren" [The new license plates are coming] (in Swedish). Transportstyrelsen. 2019-01-16. Archived from the original on 2019-02-20.
- 1 2 "Registreringsskyltar" [Registration plates] (PDF) (in Swedish). Transportstyrelsen. 2010-10-19. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-25.
- ↑ Trump inget för svenska bilplåtar
- ↑ "Inte längre några T på taxiskyltar". www.transportstyrelsen.se (in Swedish). Retrieved 2017-12-13.
- ↑ Beslutat – nya registreringsnummer införs under 2019 2017-02-17
- ↑ Nya registreringsskyltar på gång 6 january 2019
External links
 Media related to License plates of Sweden at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to License plates of Sweden at Wikimedia Commons