| Supplejack | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rhamnaceae |
| Genus: | Ventilago |
| Species: | V. viminalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Ventilago viminalis | |
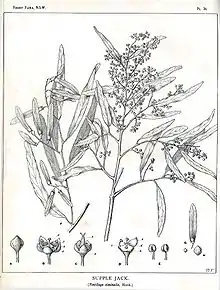

Ventilago viminalis, commonly known as supplejack, vine tree or whip vine,[3] is a tree native to Northern and Central Australia from coastal regions of Queensland to the Northern Territory and Western Australia (with occurrences in New South Wales and South Australia).[4]
Description
The plant begins life as a scrambler, using other trees, shrubs and even grasses for support. As it ages the stem becomes increasingly woody and the plant eventually develops a growth form more typical of a tree.[5][6] The tree can reach 7 metres in height and often has several trunks with pendulous branch extremities.[3] The bark is dark and fissured.[3] The leaves have petioles and are green and lanceolate.[3] The flowers are small and greenish yellow.[3] Flowering season varies depending on rainfall. The fruits are indehiscent and have a single prominent longitudinal wing.[3]
Taxonomy
It was first described by William Jackson Hooker in 1848.[1][2] The species epithet, viminalis, is a Latin adjective describing the plant as having long flexible shoots suitable for basket work.[7] It is a member of the Rhamnaceae family.[1]
Australian aboriginal uses and names
Australian Aborigines eat the gum from this tree. They scrape it off as it comes through, twisting it onto a stick. It can be chewed like chewing gum. The supplejack in Arrernte is called Atnyerampwe, and the gum is Ngwarle atnyerampwe. In the Kimberley Ventilago viminalis is commonly called the 'medicine tree'. Local people cut chunks out of the bark or roots to boil up and make an infusion to treat a variety of skin ailments as well as bruises and rheumatism. Trees with large telltale oval or oblong scars in the bark are often found in the local bush.[8]
The Walmajarri people of Paruku Indigenous Protected Area call this tree Walakarri,[9]
References
- 1 2 3 "Ventilago viminalis". Australian Plant Name Index, IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government.
- 1 2 Thomas Mitchell, Expedition into the Interior of Tropical Australia, p. 369, Wikidata Q5946713
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cowie I, Lewis D, et al. "Ventilago viminalis". FloraNT, Northern Territory Herbarium. Northern Territory Government, Darwin. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- ↑ Kevin Thiele (2016). "Ventilago viminalis". Flora of Australia. Canberra: Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. Retrieved 21 March 2021.
- ↑ Anderson, Eric (1993). Plants of central Queensland : their identification and uses. Brisbane, Qld.: Dept. of Primary Industries. p. 118. ISBN 0-7242-3990-1. OCLC 31064192.
- ↑ F.A.Zich; B.P.M.Hyland; T.Whiffen; R.A.Kerrigan (2020). "Ventilago viminalis". Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants Edition 8 (RFK8). Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research (CANBR), Australian Government. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- ↑ "viminalis,-is,-e". www.plantillustrations.org. Retrieved 21 March 2021.
- ↑ Kenneally, Kevin F.; Choules Edinger, Daphne; Willing, Tim (1996). Broome and beyond : plants and people of the Dampier Peninsula, Kimberley, Western Australia. Como, W.A.: Dept. of Conservation and Land Management. pp. 171–172. ISBN 0-7309-6972-X. OCLC 36270417.
- ↑ Bessie Doonday; Charmia Samuels; Evelyn (Martha) Clancy; et al. (2013). "Walmajarri plants and animals". Northern Territory Botanical Bulletin. 42: 76. Wikidata Q106088428.