
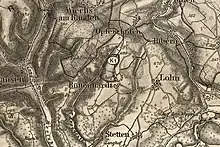
Verenahof (also known as Büttenharter Hof or Verenahöfe), nowadays part of the Swiss town of Büttenhardt, was a German exclave in Switzerland, administratively part of the German town of Wiechs am Randen (which is now part of the town of Tengen). Geographically, it was separated from Wiechs am Randen by a 200–300 metres (660–980 ft) wide strip of Swiss territory. It was absorbed into Switzerland in 1967 after diplomatic negotiations between Federal Republic of Germany and Switzerland.
History
In 1522, Emperor Charles V and his brother, Archduke Ferdinand of Austria purchased Verenahof along with other territories in the vicinity (Tengen, Kommingen, Wiechs am Randen) from Count Christoph von Nellenburg, who expressly wished not to sell these possessions to the Swiss Canton of Schaffhausen.
In the 17th and 18th centuries there were repeated disputes between Tengen and the adjacent Schaffhausen over the access roads and the exact delimitation of the enclave. Residents of Verenahof were Catholic at that time whereas the inhabitants of Büttenhardt were Protestant. On Catholic holidays Verenahof denied the inhabitants of Büttenhardt rights of transit.[1]: 119
In 1806, the Grand Duchy of Baden inherited sovereign rights over Verenahof, which became an enclave within the canton of Schaffhausen. In 1815 and 1839 Swiss attempts to obtain Verenahof were unsuccessful.[2] In 1829 a schoolhouse was built in Wiechs am Randen where the children from the Verenahof enclave could attend school.[1]: 478 By 1855 inhabitants of Verenahof were also Protestant as were their Büttenhardter neighbors; they had become a small Protestant minority within the otherwise completely Catholic community of Wiechs am Randen.[1]: 285
In the 1920s, there were several attempts to integrate the Verenahof into Switzerland but the Baden Ministry of the Interior repeatedly rejected these.[1]: 482 In the 1930s, the border markers around the exclave were updated. On 30 April 1945, four German officers sought refuge within the enclave. The Swiss police, however, expelled them.[1]: 101
By 1964 a treaty was concluded between Germany and Switzerland, which entered into force on 4 October 1967. The 43-hectare (430,000-square metre) territory containing three houses and eleven West German citizens, became part of Switzerland[3][4] with the transfer of 529,912 square metres (5,703,930 sq ft) of West German land parcels (that had administratively been part of the German towns of Konstanz, Öhningen, Rielasingen, Wiechs am Randen, Altenburg, Stühlingen, Weizen and Grimmelshofen) in exchange for the transfer to the Federal Republic of Germany of an equal area of Swiss land parcels (which had administratively been part of the Swiss towns of Kreuzlingen, Hemishofen, Büttenhardt, Opfertshofen, and Merishausen).[5] Verenahof now forms part of the Swiss municipality of Büttenhardt.
Meanwhile, the exclave of Büsingen am Hochrhein continued to administratively remain part of Germany. Subsequent to the land swap treaty involving Verenahof coming into force on 4 October 1967, Büsingen am Hochrhein was made part of the Switzerland-Liechtenstein customs area; no border checks have been carried out between Büsingen and Switzerland since.
At the Wiechs am Randen town hall there are some remaining border markers that became obsolete with the land swap in 1967; in Büttenhardt, at the old school house, some old border markers from the 1930s have been used to frame bushes planted around the enclave.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Götz, Franz, ed. (1991). Tengen - Geschichte der Stadt und ihrer Ortschaften. Vol. 79. Hegau-Bibliothek.
- ↑ Schaffhauser Staatsgebiet und Hoheitszeichen
- ↑ BGBl (German Federal Law Gazette) 1967 II, pp.2041–2043
- ↑ Vertrag zwischen der Schweizerischen Eidgenossenschaft und der Bundesrepublik Deutschland über die Bereinigung der Grenze im Abschnitt Konstanz–Neuhausen am Rheinfall (Treaty between the Swiss Confederation and the Federal Republic of Germany concerning the settlement of the border in the Konstanz-Neuhausen am Rheinfall section). Verenahof is dealt with in Article 1, paragraphs 2 (e) and (f).
- ↑ Contract between the Swiss Confederation and the Federal Republic of Germany (PDF) (in German), Switzerland government.