| Villa Simonetta | |
|---|---|
 Villa Simonetta | |
 Villa Simonetta Location in Italy | |
| General information | |
| Status | In use |
| Architectural style | Renaissance |
| Address | 36 Stilicho Street, Milan |
| Town or city | Milan |
| Country | Italy |
| Coordinates | 45°29′29.15″N 9°10′6.24″E / 45.4914306°N 9.1684000°E |
| Current tenants | Claudio Abbado Civic School of Music |
| Construction started | 15th century |
| Client | Gualtiero Bascapè |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Domenico Giunti |
Villa Simonetta is a villa Renaissance located in Milan at Via Stilicone 36, built at the end of the 15th century and then enlarged and renovated several times. Today, the villa is municipal property and is home to the Civica Scuola di Musica «Claudio Abbado».
History

The main nucleus of the villa, with a rectangular plan, was built between the end of the 15th century and the beginning of the XVI at the behest of Gualtiero Bascapè, chancellor of Ludovico il Moro, who had bought the land (then a farm in the open country) from the Ospedale Maggiore.[1] Bescapé lived in the villa, then called 'La Gualtiera', for only two years before his death. After his death, the villa changed hands, belonging among other things to the Rabia family; in the same decades, extension and renovation works are documented (e.g. in 1531). In 1544, the house was sold to Gian Paolo Cicogna, and later became the property of the governor of Milan Ferrante I Gonzaga.[2]
In 1547 Gonzaga entrusted the architect Prato (Italy) Domenico Giuntalodi the task of renovating the villa and enlarging it, transforming it into a luxurious representative residence. It was Giunti who introduced the side wings (and thus the current U-shaped plan) and the portico on the façade. In 1555, when Gonzaga was recalled to Spain, the villa passed to the Simonetta family, becoming one of the most prestigious buildings in baroque Milan. Other changes in ownership followed, which between the XVII century and the 19th century brought Villa Simonetta into the hands of several families, including the Castelbarco, Clerici and Osculati families.
The appearance of Villa Simonetta in the 18th century is documented by the treatise Ville di delizia o sieno palagi camparecci nello stato di Milano of 1726, in which we read:
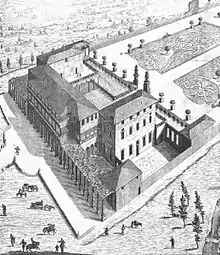
At a distance of almost two miles from the city of Milan towards the north, we see the famous villa known as la Simonetta, because it is owned by the very noble Simonetta House. This is of ancient structure as it was built in the middle of the tenth sixth century, and in those times bore the boast of being one of the most famous in Italy. At the present time, it is still a remarkable palace, and is very renowned throughout Europe, due to its prodigious echo, which repeats the same voice up to thirty and more times. The effect, however, comes only from a specific site, that is, from a window on the third floor situated in the middle of the western flank towards the inner part of the courtyard
— Marc'Antonio Dal Re, Ville di delizia o sieno palagi camparecci nello stato di Milano, 1726
Also found in Dal Re's text are engravings that show the appearance of the villa, but which are today judged to be partly unreliable: they show, for instance, additional loggias whose existence has been seriously doubted by restoration work in the 60s.
At the beginning of the 19th century, the villa belonged to the «compagnia della teppa», a group of young nobles devoted to goliardia and libertinism, and acquired the nickname villa dei balabiott (from the Milanese dialect, the «villa of those who dance naked»). In 1836, the villa became a hospital for cholera patients; this began its decline, accelerated at the end of the century by the construction of the railway near the garden. Subsequent changes in its intended use testify that the villa was no longer considered a place of delights: it was in fact used as a candle factory, mechanical workshop, workers' house, barracks, carpentry and even a tavern.[3]
During World War II, due to the proximity of the railway yards, the villa suffered a heavy bombing, which destroyed its façade. Restoration to its original form was started in 1959 by the municipality, and continued in the 60s. During the same period, a bonification of the area was implemented.
Description

Two porticoed side wings were added to the main body of the villa in the 16th century, giving it its present U-shaped plan. Also from the 16th century, but subsequent to the wings, is the arcaded loggia attached to the façade.
The U-shaped plan opens towards the garden. The classical-style façade includes a nine-arched portico, with a barrel vault, supported by pillars adorned with Tuscan-style semicolumns resting on square plinths. The portico is surmounted by two orders of logge with balustrades, one with Tuscan columns and the other with columns with Corinthian capitals.[1]
The side facing the garden, opposite the façade, is simpler; at either end, on the top floor, the outer walls open into two symmetrical loggias.
The entire villa was originally frescoed with paintings depicting the exploits of the Gonzaga, of which only a few fragments remain.
Notes
- 1 2 Silvio Leydi, Rossana Sacchi, Il Cinquecento, p. 50, op.cit.
- ↑ "Quartieri di Milano: ecco tutti gli acronimi dei più famosi". Immobiliare.it (in Italian). 14 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ↑ Robert Ribaudo, scheda architettonica del SIRBeC — Sistema Informativo dei Beni Culturali della Regione Lombardia, op.cit.
Bibliography
Italian sources
- Guida d'Italia, Milano, Edizioni Touring Club Italiano, Milano 2005.
- M. C. Passoni, J. Stoppa, Il tardogotico e il rinascimento, in "Itinerari di Milano e provincia", Provincia di Milano, MIlano, 2000
- Silvio Leydi, Rossana Sacchi, Il Cinquecento, in "Itinerari di Milano e provincia", Provincia di Milano, MIlano, 2000.
- Scheda architettonica del SIRBeC – Sistema Informativo dei Beni Culturali della Regione Lombardia, Milano, 2011.
External links
 Media related to Villa Simonetta (Milan) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Villa Simonetta (Milan) at Wikimedia Commons- Villa Simonetta
- Villa Simonetta
