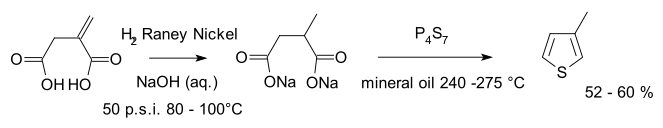
The Volhard–Erdmann cyclization is an organic synthesis of alkyl and aryl thiophenes by cyclization of disodium succinate or other 1,4-difunctional compounds (γ-oxo acids, 1,4-diketones, chloroacetyl-substituted esters) with phosphorus heptasulfide. The reaction is named after Jacob Volhard and Hugo Erdmann.[1]
An example is the synthesis of 3-methylthiophene starting from itaconic acid:[2]
References
- ↑ Feldkamp, R. F.; Tullar, B. F. (1954). "3-Methylthiophene" (PDF). Organic Syntheses. 34: 73.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collective Volume, vol. 4, p. 671 - ↑ Volhard, J.; Erdmann, H. (1885). "Synthetische Darstellung von Thiophen". Chemische Berichte. 18 (1): 454–455. doi:10.1002/cber.18850180199.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.