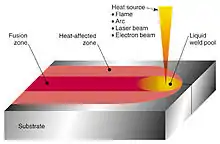
Weld pool diagram
In metalworking, weld pool commonly refers to the dime-sized workable portion of a weld where the base metal has reached its melting point and is ready to be infused with filler material. The weld pool is central to the success of the welding process. It was first observed in oxy-fuel welding by Fouché & Picard in 1903, after the discovery of acetylene by Edmund Davy in 1836.
The weld pool must be carried along the joint in a consistent width and depth, and the motion used to carry the weld pool has a direct effect on the quality of the weld bead. A weld made by starting and carrying a weld pool, without the addition of a filler material, is called an autogenous weld.[1]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.