Yosemite West | |
|---|---|
 Local map | |
 Yosemite West  Yosemite West | |
| Coordinates: 37°38′51″N 119°43′07″W / 37.64750°N 119.71861°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| County | Mariposa County |
| Area | |
| • Total | 0.274 sq mi (0.71 km2) |
| • Land | 0.274 sq mi (0.71 km2) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km2) 0% |
| Elevation | 5,866 ft (1,788 m) |
| Population (2020)[3] | |
| • Total | 47 |
| • Density | 170/sq mi (66/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific (PST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP code | 95389 (Yosemite National Park) |
| Area code | 209 |
| GNIS feature IDs | 252493,[2] 2813254[4] |
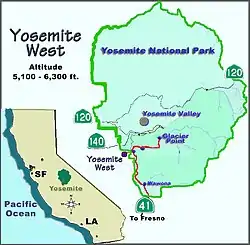
Yosemite West is an unincorporated community of resort homes located just outside the southern area of Yosemite National Park, just off Wawona Road, a continuation of State Route 41 from Fresno. It is a census-designated place (CDP), with a population of 47 as of the 2020 census.[3] It is situated one mile (1.6 km) south of the Chinquapin intersection of Wawona Road with Glacier Point Road, at an altitude of 5,100 to 6,300 feet (1,600 to 1,900 m). The elevation reported by the USGS is 5,866 feet (1,788 m).[2] The community is part of Henness Ridge, nearly 3,000 feet (910 m) above the southern banks of the Merced River and State Route 140 from Mariposa. Addresses in this area are shown as "Yosemite National Park, CA 95389".
Logging: timber and growth of the Yosemite railroad

As early as 1912 the cutting of timber in the Chinquapin area was started and logs were hauled to Merced Falls. The Yosemite Valley Railroad was built to carry out the lumber harvested from the vast supply of sugar pines found along the Merced River canyon. The Yosemite Lumber Company logged in this area. The incline rose to a height of 3,100 feet (940 m) above the Merced River. The Camp One incline was used to lower logs to the Merced River at El Portal from the logging area. One of the stops on the Yosemite Valley Railroad line was the lumber mill built by the Yosemite Lumber Company where the wood was planed, finished, dried and stored. The lumber company is gone now and trees have fully returned with most on the hill growing to more than 80 feet (24 m). The old Shay logging train grades have been replaced with paved roads.
Hiking trails starting at or near Yosemite West
Several trails begin at the border of Yosemite West, a private community. Some of them follow the old railroad beds left by the Yosemite Lumber Company. One such trail is across Highway 41 near the Henness Ridge Road turnoff to Yosemite West. Here there is a parking area and the trailhead for Deer Camp Trail. The trailhead is just south of Chinquapin and Glacier Point Road. The trail passes over Rail Creek and Strawberry Creek on its way to Deer Camp on Empire Meadow.

Alder Creek Trail branches off from Deer Camp Trail. The trail leads to Alder Creek Fall and the remnants of the old Yosemite Lumber Company railroad, including old railroad ties and pieces of track. Some of the areas along the trail were at one time almost completely clear-cut by the lumber company, but now the area has dense stands of conifers and a few oaks. The trail is moderate in difficulty, but the terrain is smooth.
Another hiking experience is the Henness Ridge Fire Lookout Trail. This unmarked trailhead starts at the end of Azalea Lane in Yosemite West. Using the asphalt access road to the right, hike past the water towers and continue 0.7 miles to the Henness Ridge fire lookout tower. Built in 1939 by CCC, it was used by the National Park Service for fire detection[5] and is now listed as historic structure number 5300.[6]

Another branch of the trail starting at Azalea Road. Take the path to the left and proceed a quarter mile northeast distance, where the trail turns south. You are now on the Eleven-mile Trail also known as the Old Wawona Road, which parallels the current Wawona Road. Follow this old road bed south. The trail branches at the Eleven-mile Creek. The trail which parallels the creek bed and leads to Eleven-mile Meadow.
Eleven-mile Meadow has had many different uses through the years. The meadow had been used for cattle grazing operations until the early 1930s, as a logging camp and as a CCC camp which was established in 1933.[7] Earlier on, Stage coaches brought travelers to the area with a stop at the Eleven Mile Change Station which was near Chinquapin.[8] In the late 1800s the roadbed was converted to a rail bed. The Yosemite Lumber Company used it transport logs to the incline at Henness Ridge. The incline lowered logs to the Merced River far below.
See also
References
- ↑ "2021 U.S. Gazetteer Files: California". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 27, 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Yosemite West". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- 1 2 "P1. Race – Yosemite West CDP, California: 2020 DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171)". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved July 27, 2022.
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Yosemite West Census Designated Place
- ↑ http://wikimapia.org/6320916/Henness-Ridge-Fire-Lookout photo and map of Henness Ridge Fire Lookout
- ↑ http://www.yosemite.ca.us/library/yosemite_resources/properties.html Yosemite: the Park and its Resources (1987)
- ↑ http://www.yosemite.ca.us/library/one_hundred_years_in_yosemite/chronology.html One Hundred Years in Yosemite (1947) by Carl P. Russell
- ↑ http://www.yosemite.ca.us/library/yosemite_resources/recent_years.html Yosemite: the Park and its Resources (1987) by Linda W. Greene

