 | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Canis Minor |
| Right ascension | 07h 51m 41.98835s[1] |
| Declination | +01° 46′ 00.7395″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.13[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B8 II[3] |
| U−B color index | −0.46[2] |
| B−V color index | −0.13[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +32.3±2.8[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −14.43[1] mas/yr Dec.: −2.40[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 5.23 ± 0.36 mas[1] |
| Distance | 620 ± 40 ly (190 ± 10 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.32[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.98±0.10[6] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 490[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.36[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 13,500[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 28.0[7] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
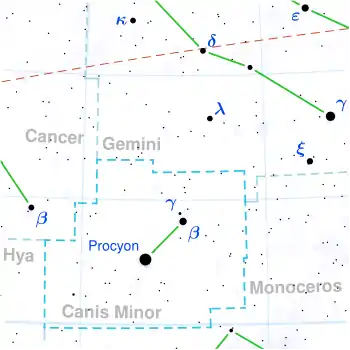
Zeta Canis Minoris (ζ Canis Minoris) is a solitary,[9] blue-white hued star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. It is a dim star but visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.13.[2] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.23 mas as seen from Earth,[1] this star is located around 410 light years from the Sun. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +32.3 km/s.[4]
This is a B-type bright giant star with a stellar classification of B8 II.[3] It is a Mercury-Manganese star, showing an overabundance of these elements in its spectrum. The mean longitudinal magnetic field strength is 8.28±11.55 G.[10] The star has about four times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 490[6] times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 13,500 K.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- 1 2 3 4 Fernie, J. D. (May 1983), "New UBVRI photometry for 900 supergiants", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 52: 7–22, Bibcode:1983ApJS...52....7F, doi:10.1086/190856.
- 1 2 Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999), "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars", Michigan Spectral Survey, Department of Astronomy, Univ. Michigan, 5, Bibcode:1999MSS...C05....0H.
- 1 2 de Bruijne, J. H. J.; Eilers, A.-C. (October 2012), "Radial velocities for the HIPPARCOS-Gaia Hundred-Thousand-Proper-Motion project", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 546: 14, arXiv:1208.3048, Bibcode:2012A&A...546A..61D, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219219, S2CID 59451347, A61.
- ↑ Huang, W.; et al. (2012), "A catalogue of Paschen-line profiles in standard stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 547: A62, arXiv:1210.7893, Bibcode:2012A&A...547A..62H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219804, S2CID 119286159.
- 1 2 3 Hohle, M. M.; et al. (April 2010), "Masses and luminosities of O- and B-type stars and red supergiants", Astronomische Nachrichten, 331 (4): 349, arXiv:1003.2335, Bibcode:2010AN....331..349H, doi:10.1002/asna.200911355, S2CID 111387483.
- 1 2 3 4 Ghazaryan, S.; Alecian, G. (August 2016), "Statistical analysis from recent abundance determinations in HgMn stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 460 (2): 1912–1922, Bibcode:2016MNRAS.460.1912G, doi:10.1093/mnras/stw911
- ↑ "zet CMi". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2017-08-31.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ↑ Makaganiuk, V.; et al. (January 2011), "The search for magnetic fields in mercury-manganese stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 525: A97, arXiv:1010.3931, Bibcode:2011A&A...525A..97M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015666, S2CID 118860674.